- Neighboring Countries - Mongolia, Nepal, India, South Korea, Pakistan
- Continent And Regions - Asia Map
- Other China Maps - China Map, Where is China, China Blank Map, China Road Map, China Rail Map, China River Map, China Cities Map, China Political Map, China Flag
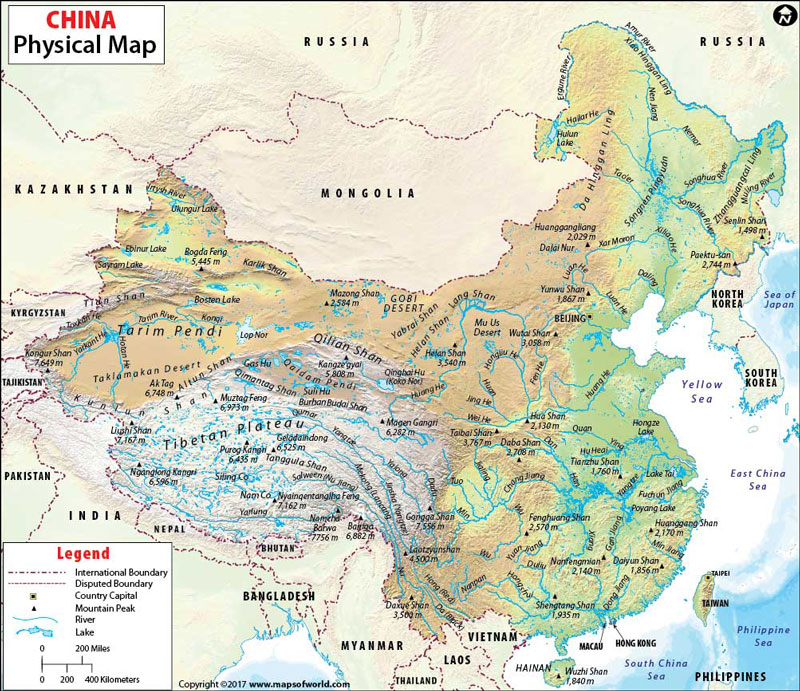
China is known as the People’s Republic of China in East Asia. The country spans five geographical time zones and borders 14 different countries and is the most populous country globally. The National capital of China, Beijing, is marked on the map. You can use this China Physical Map for schoolwork, presentation and other purposes.
Physical Features of China
The country covers an area of over 9,596,960 square kilometres (3,705,410 sq mi). The country of China lies between latitudes 18. N and 54. N and longitudes 73. E and 135. E. The landscape of China is diverse and varies significantly across its territory, from deserts in the arid north to the Subtropical forests in the south. The mountain ranges, including Himalaya, Karakoram, and Tian Shan mountain ranges, divide China from Central and South Asia. The topography of China is divided into the following Physical macro-regions:
Eastern China
The region of Eastern China can be further divided into:
Northeast Plain:
The northeast of Shanhaiguan is a vast Northeast China Plain. The area extends north to the crown of the ”Chinese rooster” near the convergence of the Greater and Lesser Hinggan range, and Changbai Mountains lie to the east. Commonly known as Manchurian Plain, the region is densely populated due to its adequate climate and topography.
North Plain:
The region is a large-scale downfaulted rift basin modified by the deposits of the Yellow River. The plains share its boundary to the north by the Yanshan Mountains, the south by Dabie Mountains, the west by Taihang Mountains, and the east by the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea.
South Hills:
The area lies east of the Tibetan Plateau. The region deeply folded mountains fanning out towards the Sichuan Basin. The basin floor has an average height of 500 metres (1,600 ft) and is one of China’s most densely populated and agriculture-oriented regions.
Xinjiang-Mongolia
The region lies between the northern slope of Kunlun and the southern slope of the Tian Shan, northwest of the Tibetan Plateau. The area is the vast Tarim Basin of Xinjiang, consisting of the Taklamakan Desert. The Tarim basin descends into the Hami-Turpan Depression of eastern Xinjiang, where lies the lake bed of Lake Ayding at 154m below sea level. Another Basin north of Tian Shan is the Junggar basin containing the Gurbantunggut Desert.
Highlands
The Western border of China has the world’s tallest mountains, the Karakorum, Pamirs, Himalayas and the Tian Shan. The tallest peak of the world, Mount Everest (8848 m), is located on the Nepal and China border in the Himalayas, and the second tallest mountain, k2 (8611 m), is on the border with Pakistan. East of Karakorum and North of Himalaya lies the vast Tibetan plateau, the highest plateau in the world, also known as the “Roof of the world”.
Rivers in China
The rivers in the country have a total length of 420,000 kilometres. The majority of rivers in China flow west to east in the Pacific Ocean. Some of the Significant rivers in China are Yangtze (Chang Jiang)-the third-longest river in the world, Huang He (Yellow River), Heilongjiang (Black Dragon River), Zhujiang (Pearl River) and more.