Royal Families Around the World
Despite the fact that the flame of royal families is dwindling, its embers still remain in some or the other way. Monarchs of the nations across the world have varying degrees of power, with some holding absolute power, while others merely symbolic or ceremonial figureheads. From kings and queens, to sultans, emperors and emirs, there are many types of monarchs around the world.
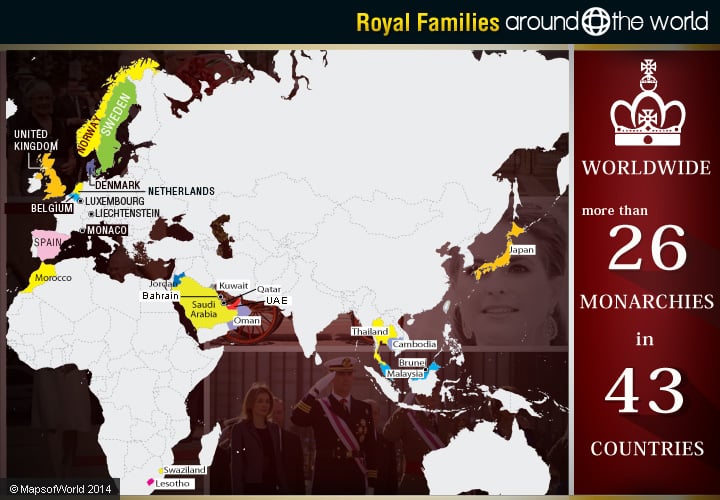
There are more than 26 monarchies worldwide, ruling in over 43 countries. Some of these are: Queen Elizabeth II in the UK, Felipe VI in Spain, Prince Albert II in Monaco, King Abdullah II in Jordan, King Philippe in Belgium, King Norodom Sihamoni in Cambodia, Prince Hans Adam II in Liechtenstein, Grand Duke Henri in Luxembourg, etc.
While some countries have elected monarchies, as is partially the case in Malaysia, and the unusual case of the Vatican (which is indeed a monarchy, although it does not follow a hereditary succession), most countries have a ruling house made up of a family dynasty. These take different forms, from the historic House of Saud, to the complicated interrelationships of many European leaders, and the Japanese emperor. Here is a look at a few of the royal families around the world.
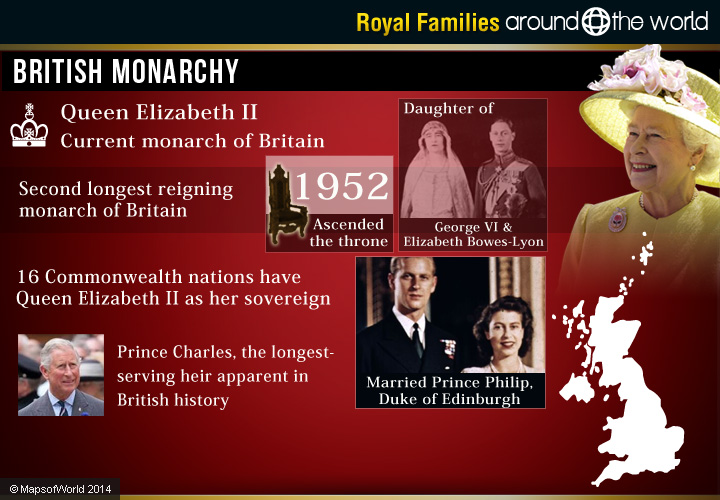
British Monarchy
The British Royal family is likely the most popular of royal families around the world. It is largely due to the British imperial history with the Commonwealth countries around the world that are technically subjects of the British monarchy. The British Royal family belongs to the House of Windsor and Queen Elizabeth II is at the head of the family today.
Queen Elizabeth II ascended the throne in 1952, ruling over the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Pakistan and Ceylon, at the time. However, some of these Commonwealths have gained independence or otherwise changed in status since then, and others have been added, including many island nations. The 16 Commonwealth realms that presently have Queen Elizabeth II as their sovereign are Antigua and Barbuda, Australia, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Canada, Grenada, Jamaica, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, St. Lucia, St. Kitts & Nevis, St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Soloman Islands,Tuvalu, and the UK.
Queen Elizabeth II is the longest reigning monarch of Britain. Queen Elizabeth is the child of George VI and Elizabeth Bowes-Lyon. She married Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, who had to renounce his foreign titles, in 1947 and became the Duke of Edinburgh. Their first child was Prince Charles, followed by Princess Anne, Prince Andrew and Edward.
Prince Charles, the longest-serving heir apparent in British history is also the oldest heir since 1714. He married Lady Diana Spencer in 1981 and had two children, Prince William, the Duke of Cambridge and Prince Harry. In a controversial move, the couple divorced in 1996, and soon after, Diana Princess of Wales died in a tragic car accident. Prince Charles remarried Camilla Parker Bowles in 2005, and she became the Duchess of Cornwall.
Prince William, Duke of Cambridge, is next in line for the throne. He married Catherine Middleton in a ceremony watched around the world in April 2011. The couple had their first child in July 2013, Prince George of Cambridge.
Spanish Monarchy
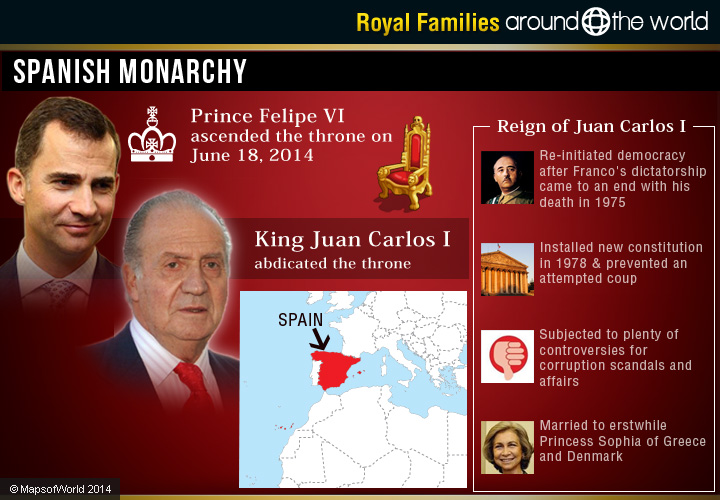
The Spanish Royal family belongs to the House of Bourbon, which has French origins. The current King of Spain is Felipe VI, who acquired the throne on June 19, 2014. He is the son of King Juan Carlos I, who brought democracy back to Spain after Franco’s dictatorship came to an end with his death in 1975. Juan Carlos dismantled Franco’s regime, installing a new constitution in 1978. He thwarted an attempted coup in 1981.
However, Juan Carlos has been the subject of plenty of controversy during his reign as the King of Spain. He faced backlash after an elephant hunting trip to Botswana, in which he broke his hip and his grandson shot himself in the foot, as well as corruption scandals and rumors of an affair. Juan Carlos, who is an enthusiastic skier and sailor, competed in the 1972 Olympic Games. King Juan Carlos married erstwhile Princess Sophia of Greece and Denmark, who gave birth to their daughters Elena, Duchess of Lugo, Cristina, Duchess of Palma de Mallorca, and their son, Felipe, Prince of Asturias.
Felipe married Princess Letizia in 2004 and have two daughters: Infanta Leonor, who is the princess of Asturias, and Infanta Sofia. Other than holding official roles, Felipe VI is also contributing towards other social activities. He serves as Honorary President of Imperial Munitions Board. It takes care of social and economic progress in several countries. Also, he was chosen in 2001 by UN Secretary General Kofi Annan as “UN-Eminent Person” because of his contributions towards developing the significance of voluntary work.
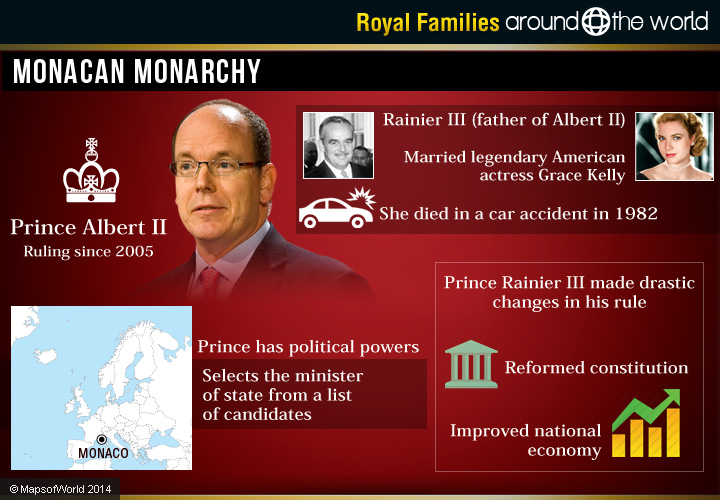
Monacan Monarchy
Monaco is ruled by Prince Albert II, who has been on the throne since 2005. Monaco’s system of government does include an elected legislature as a constitutional monarchy, but the prince also has political powers, including selecting the minister of state from a list of candidates.
Prince Albert II is the head of the ruling Princely House of Grimaldi, having an approximate worth of more than US$1 billion. Prince Albert II is reported to be one of the richest royals on earth, owning extensive lands not only in Monaco, but in France as well. Besides this, he established the Monaco Foundation in 2006 that chiefly works upon three main issues: Climate change, combating the loss of biodiversity, and expanding renewable energies.
Albert II is the son of Rainier III, who was Prince of Monaco, ascending in 1949, and known for his romance and marriage to the legendary American actress Grace Kelly. Their romantic story, however, came to a tragic end with her 1982 death in a car accident, caused by her having a stroke while driving.
The couple had three children: Princesses Caroline Louise Marguerite, Stephanie Marie Elizabeth, and Prince Albert II. Prince Rainier III made drastic changes during his rule, including reforming the constitution and improving the national economy. After his death in 2005, he was succeeded by his son Albert. Albert married South African Olympic swimmer, Charlene Wittstock in 2011; though prior to his marriage he had at least two children from other women.
Swedish Monarchy
The Royal Family of Sweden is the Royal House of Bernadotte, which includes the extended family of the king. This Swedish dynasty was founded by Frenchman, Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte, who became a marshal in Napoleon’s republican army, where he met a Swedish officer who later brought him to Stockholm to become the heir.
The current monarch of the Kingdom of Sweden is King Carl XVI Gustaf who has reigned since 1973, after his grandfather Gustav VI Adolf died. King Carl Gustaf is a ceremonial figurehead, and among other duties, he presents each year’s Nobel Prizes. King Carl married Silvia Sommerlath, a German-Brazilian in 1976. The two met at the Summer Olympics of 1972. The king made headlines for his partying and rumors of affairs.
Sweden’s new system allows for female succession, so the king and queen’s eldest child became heir to the throne, regardless of gender. Princess Victoria Ingrid Alice Desiree is the oldest of the couple’s children, who will become Queen of Sweden after her father. The heiress married her fitness coach, Daniel Westling in June 2010, and gave birth to their first child in February 2012, Princess Estelle. Princess Victoria has a brother, Prince Carl Philip and a sister, Princess Madeleine.
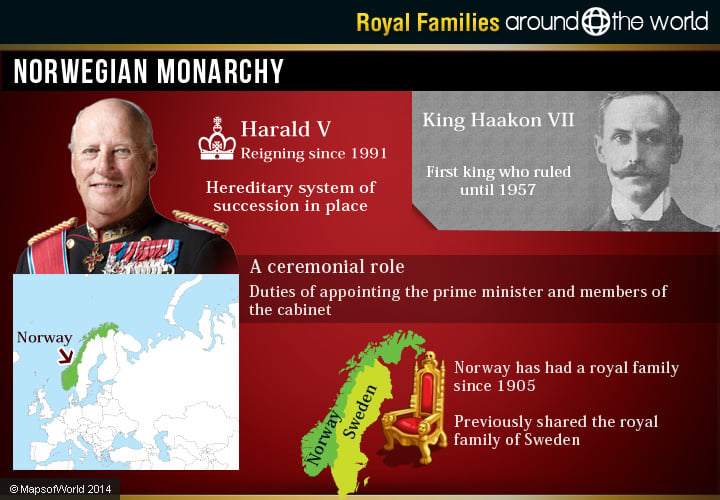
Norwegian Monarchy
Norway has had a royal family since 1905, as it previously shared the royal family of Sweden. The monarch of Norway has largely a ceremonial role, with duties including appointing the prime minister and members of the cabinet. There is a hereditary system of succession in place. The first king was born Prince Carl of Denmark, who ruled as King Haakon VII until 1957. He was married to his cousin, Maud, the daughter of Edward VII. The current monarch is Harald V, who has ruled since 1991 and is married to Queen Sonja. Their son is the Crown Prince Haakon, the heir to the throne, who married Mette-Marit Tjessem Hoiby in 2001.
The Crown Princess Mette Marit had a storied past, as a single mother with plenty of familial drama, particularly with the father of her child and her own father who has since passed away. Though she was a controversial choice, she has grown into a proper princess and has since given birth to two more children, Princess Ingrid Alexandra and Prince Sverre Magnus.
Qatari Monarchy
The newly-ascended Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad al Thani is the current ruler of Qatar and of the House of Thani. The royal family is made up of three branches, the Al-Jassim, Al-Ahmed, and Al-Jaber families, and a total of about 3,000 members. The royal family is extremely wealthy and connected to the oil industry. They have been the ruling family of Qatar since 1825.
Sheik Tamim ascended the throne after his father, Jasim bin Hamad bin Khalifa al Thani, abdicated the throne in June 2013. The 20th century saw a series of forced abdications, with sons and nephews pushing for their turn as “sheikh”. However, the current “sheikh” was the first in three successions to become the ruler without forcing abdication. Prior to becoming “Emir”, Tamim served several other roles in the government. He was the youngest reigning monarch in the world at the time at 33 years old. He married his second cousin, Sheikha Jawahir bint Hamad bin Suhaim al-Thani in 2005 and they have two sons and two daughters.
Saudi Arabian Monarchy
The Royal Family of Saudi Arabia is the House of Saud, made up of between 15,000 and 30,000 descendants of Muhammad bin Saud and brothers. The main ruling branch of the family is the descendant of Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud, of which there are about 2,000 powerful members.
Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy, ruled by Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud.
The House of Saud has been in power since 1744, and they are a very wealthy family, thanks to oil revenue, with a net worth estimated at US$1.4 trillion. The House of Saud has been the subject of criticism, since they rule as nearly absolute monarchs and are sometimes seen as dictators. Uprisings of the people have occurred as well as attempted coups.
Monarchy of UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is made up of seven emirates, each ruled by a hereditary monarch, or an “Emir”. The “emirs” make up the Federal Supreme Council that rules the UAE, and the “emir” of the capital, Abu Dhabi, is also the president of the entire federation. The current Abu Dhabi ruler is Emir Sheikh Khalifa bin Zayed al-Nahyan. He has been “emir” since 2004 when his father, the late Emir Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, died. The Al Nahyan royal family members serve as the other government officials in Abu Dhabi. The Crown Prince of the family is Sheikh Mohammad bin Zayed Al Nahyan. They are also a very wealthy family, thanks to the oil industry, and the “emir” of Abu Dhabi is noted to be worth around US$5 billion.
The other royal families across the UAE include the Al Maktoum family of Dubai, the Al Qasimi family of Sharjah, the Al Qasimi family of Ras al-Khaimah, the Al Nuaimi family of Ajman, the Al Mualla family of Umm al-Quwain, and the Al Sharqi family of Fujairah.
Swazi Monarchy
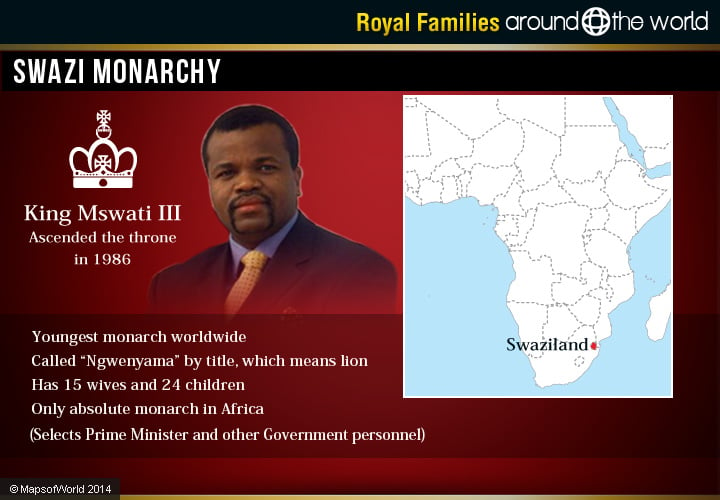
King Mswati III is the monarch of Swaziland. Mswati III is the son of King Sobhuza II and Queen Mother Ntombi Tfwala. Her only child, he was then called Makhosetive. His father, however, had 125 wives and many other children. King Sobhuza died in 1982, and while the-then 14-year-old Makhosetive finished his schooling, the late king’s wives became interim rulers. Mswati III ascended the throne in 1986, becoming the youngest monarch at the time worldwide.
He is called “Ngwenyama” by title, which means “lion”. He is the head of the House of Dlamini. Mswati III has 15 wives, as polygamy is the typical practice in the culture, and from them he has 24 children. As per tradition, his first two wives were chosen by the councilors.
King Mswati III is the only absolute monarch in Africa, meaning he selects the prime minister and other government officials. The Queen Mother also takes on an advisory role. The successor to the throne is chosen through the mother.
Moroccan Monarchy
Morocco is ruled by King Mohammed VI, who has ruled the country since July 1999. Prior to Mohammed VI, his father, King Hassan II ruled Morocco until his death. Mohammed’s mother is Lalla Latifa Hammou. His brother is Prince Moulay Rachid, and his sisters are Princesses Lalla Meryem, Lalla Asma, and Lalla Hasna. Mohammed VI studied law, earning a PhD, and spent time in the Royal Moroccan Army and the Royal Armed Forces, becoming a Major General. He married Salma Bennani, and they have a son, the Crown Prince Moulay Hassan, and Princess Lalla Khadija.
Mohammed VI is unusual in that he voluntarily gave up some of his power after the 2011 Arab Spring uprising, in which citizens protested against political corruption and the economic crisis. In response, King Mohammed VI began to reform the government, making it a constitutional monarchy. The reforms, chiefly include making Berber (along with Arabic) as an official state language, preserving the linguistic aspects of the culture of Morocco, and changing the electoral system, which means limiting the powers of the monarch. He also ended the king’s ability to call for new elections and guaranteed women, civic and social equality.
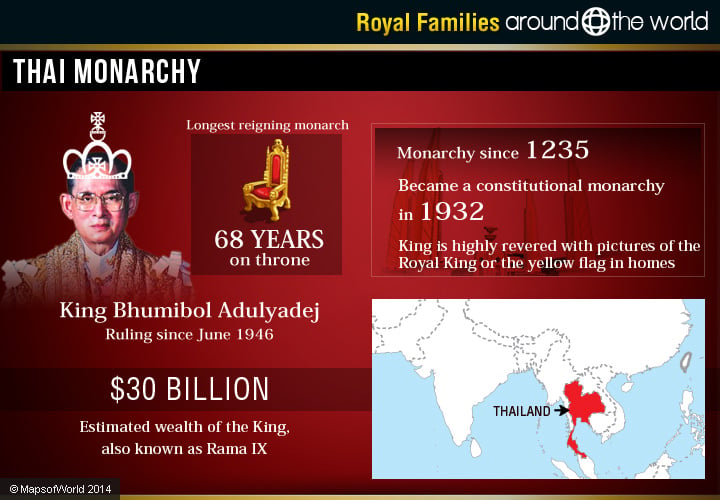
Thai Monarchy
Thailand is ruled by a monarch, currently King Maha Vajiralongkorn Bodindradebayavarangkun, who has been serving since 2016. He succeeded Bhumibol Adulyadej, who ruled from 1946 to 2016. Thailand’s monarch has constitutional powers such as legislative veto power, the ability to pardon criminals, and serves as the head of the national Armed Forces. He also must uphold religions. The Royal Family of Thai is looked up with great regard and veneration by its people as either the picture of the royal head or the yellow-colored flag of the monarch can be seen in nearly all homes. The king, who is also referred to as Rama X, is the oldest Tahi monarch to ascend to the throne. Thailand has been a monarchy since 1235, but became a constitutional monarchy in 1932, when the Siamese Revolution took place.
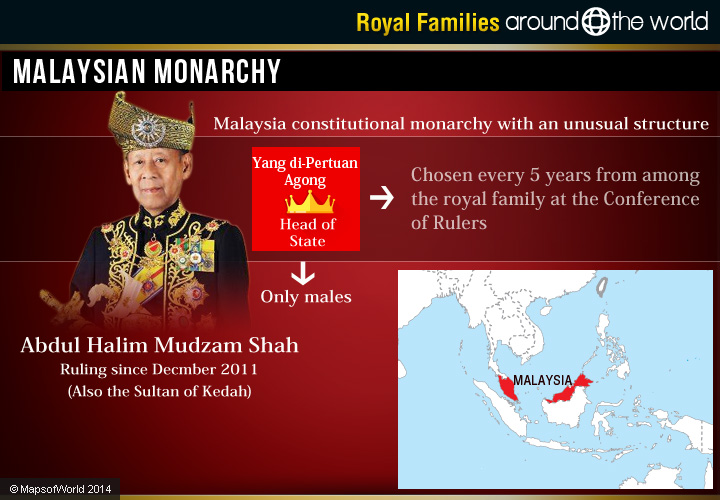
Malaysian Monarchy
Malaysia has a constitutional monarchy as part of the federation, with an unusual structure – Malaysia’s monarch is a sultan, who is chosen every five years from among the royal family of each state at the Conference of Rulers. There, they select the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, who heads all of Malaysia, choosing from the monarchs of the various states of Malaysia.
There are nine Malay States and seven are hereditary monarchies: Kedah, Kelantan, Johor, Perlis, Pahang, Selangor, and Terengganu. The remaining two states are Perak and Negeri Sembilan. In Perak, the monarch is chosen by agnatic seniority (where the younger brother of monarch is chosen over the monarch’s own sons) and Negeri Sembilan follows elective monarchy.
Only male members of royal descent are entitled to inherit the throne. Interestingly, all rulers except those of Negeri Sembilan and Perlis are styled Sultans, whereas the ruler from Negeri Sembilan is called Yamtuan Besar and the ruler from Perlis is known as Raja.
Since December 2011, the sultan has been Tuanku Abdul Halim Muadzam Shah, whose consort is Sultanah Haminah.
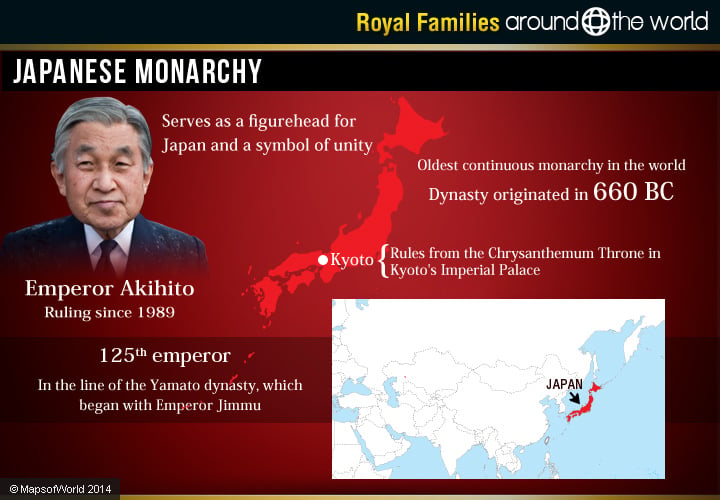
Japanese Monarchy
Japan is ruled by an emperor who serves as a figurehead for Japan and a symbol of unity. The position follows hereditary succession, and Japan holds the title of the oldest continuous hereditary monarchy in the world, as the dynasty originated in 660 BC. Currently, Japan’s emperor is Akihito, referred to as His Imperial Majesty, who ascended to the throne in 1989. The emperor of Japan rules from the Chrysanthemum Throne in Kyoto’s Imperial Palace. Akihito is (approximately) the 125th emperor in the line of the Yamato dynasty, which began with Emperor Jimmu (660 BC).
Akihito’s reign is known as the Heisei era and he will be known as Emperor Heisei in history. Before taking the throne, he was Prince Tsugu. He married Michiko Shoda, who then became the Crown Princess, in 1959. The couple has three children, Naruhito, the heir and Crown Prince of Japan, Fumihito (Prince Akishino), and Sakayo (Princess Nori).
The royal family of Japan is known as the Imperial House or Family, and includes the Emperor, Empress, Regent, Crown Prince, and Crown Princess. Other than the emperor, the other members serve only ceremonial (non-governmental) duties.
Read More
- Most Expensive Cheese around the World
- Wines and Vineyards Around the World
- Drinks To Try Around the World
- Dance Forms Around the World
- Christmas Myths and Legends
- How to Say Hello around the World?
- The Dying Art of Hand Writing
- China to do away with one-child policy
- All you need to know about Halloween
- Top 10 Favorite Wines
- Ten Most Relished Foods Around the World
- Tribes Around the World
- Gay Laws Around the World
- Matriarchy Around the World
- Royal Families Around the World