Among the ancient civilizations of the world, the Egyptian civilization has fascinated archeologists, historians, art historians, and common men alike. Evidence of a rich and prosperous civilization dating back to 3200 BC have been found in Egypt. The history of the ancient Egyptian civilization has been classified as the Old, the Middle, and the New Kingdoms. The last of the Ptolemaic kings to have been known as the ruler of Egypt reigned until about 30 BC.
Gift of the Nile :
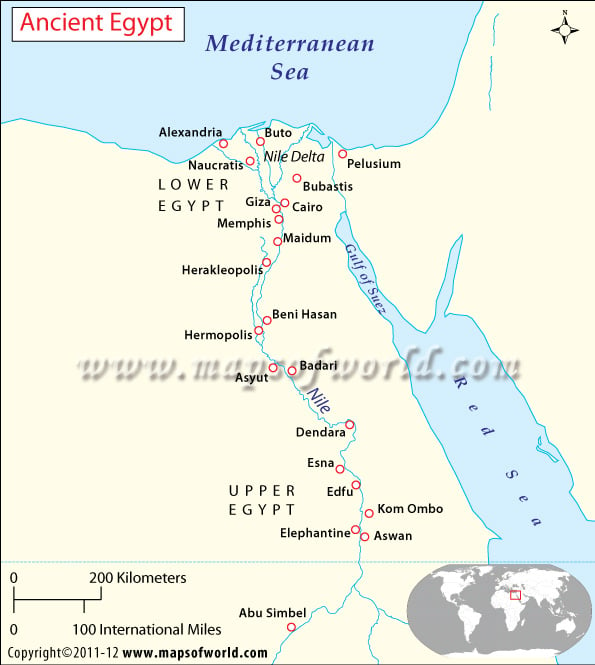
The Nile Valley stands in sharp contrast to the arid deserts of Africa. Egypt owes much of its prosperity to the fertile alluvial deposits left behind by the flooding Nile. As Greek historian Herodotus rightly remarked, Egypt is indeed the gift of the Nile.
Religion and Magic :
Religion and magic was at the center of life in ancient Egypt. A pantheon of deities was worshipped. The best known of these are Isis, Osiris, Thoth, Ra, Anubis, Bastet, Horus, Nut, Ptah, Ma’at, and Amun. Most gods and goddesses were symbolically represented by animals. This demonstrates that the worship of nature and natural phenomena was an important part of the Egyptian religion.
Priests were often healers and were well versed in herbal treatment. They were believed to employ magic, and intercede with the gods to favor the kings and common men alike. Priests worshipped Heka, the goddess of magic and healing. The ruler, or pharaoh, was believed to be a descendent of Ra, the sun god. A strong belief in the afterlife characterized the rituals of ancient Egypt.
Art and Culture :
Art and music were used as aids in ritual worship. Pictorial depiction of the gods and pharaohs was important. Durability was more important than aesthetics. Many religious texts were graphically carved and painted on the walls of tombs and temples. The use of natural dyes and colors often overshadowed the natural beauty of the pottery, paintings, and carvings of ancient Egypt. Egyptian society was highly advanced in science, astronomy, mathematics, and architecture.
Architecture :
The pyramids of Egypt are the most popular and enduring symbols of ancient Egypt. These enormous tombs of the Egyptian royalty were built about 5000 years ago. Each pyramid was elaborately planned and meticulously built with the help of thousands of laborers. Underground chambers and secret pathways made the pyramids intriguing architectural wonders. The Great Pyramid of Giza and the Sphinx are among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
In addition to the pyramids, Egyptian kings commissioned the building of marvels such as the Temple Complex of Karnak, the Luxor Temple Complex, and the Temple of Horus at Edfu. Religious texts were inscribed in these temples and provide an uncanny insight into the life and religion of the ancient Egyptians.
Hieroglyphics and the Hieratic Script :
Ancient Egyptians used hieroglyphics to record matters of significance as early as 3200 BC. The elaborate symbols used to record religious texts and rituals were difficult to decipher. Symbolic and phonetic usage was common, and this hindered the decipherment of the hieroglyphics. The discovery of the Rosetta Stone in 1799 provided a bilingual text – in Greek and in hieroglyphics. This made it possible for historians to understand the Egyptian script.
For recording mundane details such as the crop yield, endowments, and taxes Egyptians used the hieratic script. While the language was the same, the hieratic script was made of simpler symbols. Scribes in ancient Egypt were proficient in the use of both hieroglyphics and the hieratic script. The hieratic script first made its appearance in the Protodynastic Period.
 Ancient Armenia
Ancient Armenia