West Virginia Physical Map
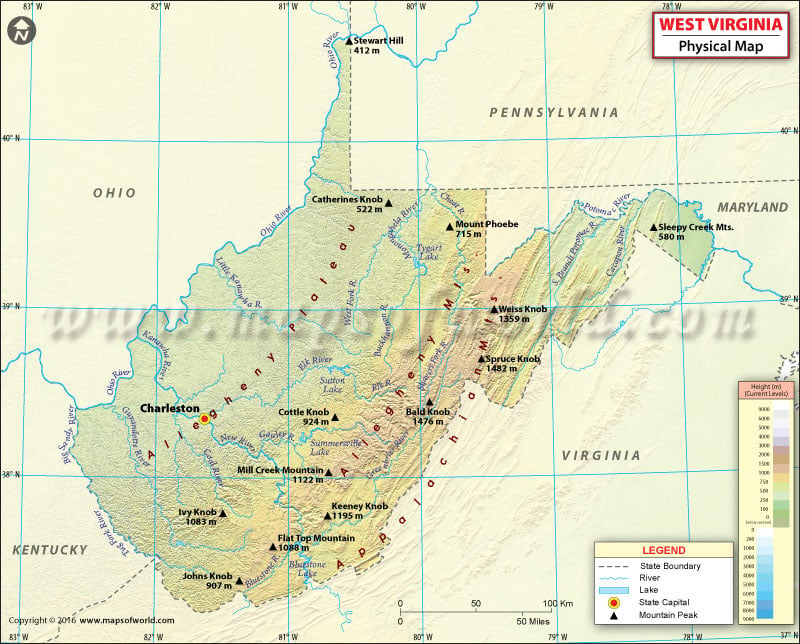
Physical regions and landforms of West Virginia shape its appeal as a destination. The state of West Virginia is included in three geographical regions: the Mid-Atlantic, the Upland South, and the Southeastern United States. It is the only state in the United States that lies completely within the Appalachian region. The Ohio River forms the western and southern boundary of the state.
Nicknamed ‘The Mountain State’, its average elevation is roughly 1,500 feet (460 meters) above the sea level. About 75% of West Virginia’s land is included in the Cumberland Plateau and Allegheny Plateau regions. The unglaciated Allegheny Plateau in the western portion of the state ranges from 270-to-460 m in elevation.
West Virginia features two panhandle regions. The narrow northern panhandle extends between the Ohio River and the western border of Pennsylvania. This panhandle is the northernmost extension of West Virginia. The second one, eastern panhandle is bounded by the Shenandoah and Potomac Rivers. Standing at 1,482 m (4,862 ft), Spruce Knob is the tallest peak in the state. The Blue Ridge Mountains stretch along the state’s eastern boundary with Maryland and Virginia. On the other hand, the Allegheny Mountains lie west of the Blue Ridge range.
The Allegheny Front separates the panhandle region from the rest of West Virginia. The southeastern region of West Virginia comprises ridges and valleys along its border with Virginia. The state’s mountain terrain levels off along the Ohio River Valley to the west.

 Wall Maps
Wall Maps