What are the Key Facts of Indiana?
|
State |
Indiana |
|
State Capital |
Indianapolis |
|
Largest City |
Indianapolis |
|
Coordinates |
40°N 86°W |
|
Nickname(s) |
“The Hoosier State” |
|
Postal Abbreviation |
IN |
|
Area |
36,418 sq. mi (94,321 sq. km) |
|
Highest Point |
Hoosier Hill, 1,257 ft (383 m) |
|
Number of Counties |
92 |
|
Neighboring States |
Michigan, Illinois, Kentucky, Ohio |
|
Population |
6,691,878 (2,018) |
|
Date of Entering the Union |
December 11, 1816 |
|
State Anthem |
On the Banks of the Wabash, Far Away |
|
Governor |
Eric Holcomb (Republican) |
|
Lieutenant Governor |
Suzanne Crouch (Republican) |
|
U.S. Senators |
Todd Young (Republican), Mike Braun (Republican) |
|
U.S. House Delegation |
7 Republicans, 2 Democrats |
|
GDP (Millions of Dollars) |
366801 |
|
Demonym |
Hoosier |
|
Time Zones |
80 counties UTC-05:00 (Eastern), Summer (DST) UTC-04:00 (EDT); 12 counties UTC-06:00 (Central), Summer (DST) UTC-05:00 (CDT) |
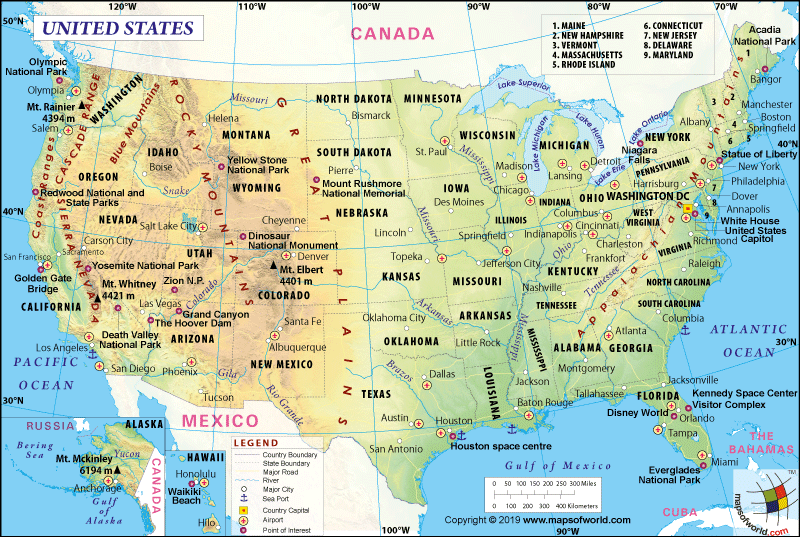
Where is Indiana?
Indiana (the 19th state admitted to the union on December 11, 1816) is located in the Midwestern and Great Lakes Regions of the US. It is one of the eight states with which the Great Lakes Region is created. Indiana is a landlocked state in the United States that is bordered by Illinois to the west, Ohio to the east, and Michigan to the north. On the northwest, this state is bordered by Lake Michigan, and on the south, the Ohio River separates it from Kentucky.
What is the Geography of Indiana?
Indiana is spread across a total area of 36,418 sq. mi (94,321 sq. km), making it the 38th largest state in terms of total area. The state has 35,868 sq. mi (92,897 sq. km) of land area and 550 sq. mi (1,424 sq. km) of the water area. Water occupies over 1.6% of the total area.
Three regions are found in Indiana, and they are the Great Lakes Plains (located in the northern parts), Till Plains (located in the central region), and the Southern Plains and Lowlands (situated in the south).
The Great Lakes Plains is spread along the Great Lakes region, and it starts in Wisconsin, passes through Illinois and Indiana, and ends in Ohio. Large dunes are present along Lake Michigan. As you move south of the dunes, the land changes to fertile black soil. It is perfect for farmers to grow crops. Many low hills, as well as small lakes, are also present to the south of the dunes. This region is also called Northern Lake and Moraine Region. The Moraines are low hills of rock and earth.
The Till Plains are the second most important landform that stretches along the central part of the state and are situated to the south of the Great Lakes Plains. This fertile broad plain is part of the great Midwestern Corn Belt. Low hills, as well as valleys, are characteristic features of this landscape. The highest elevation point (Hoosier Hill) of the state is located in this region.
The Southern Plains and Lowlands are located in the southern part of the Till Plains. This is the hilliest portion of Indiana. The most common landforms here are the “Knobs”, which are steep hills that are divided by lowlands. Some of the famous caves such as Marengo and Wyandotte caves are located here. The underwater streams have made these caves by carving in the limestone.
The major rivers in Indiana are Ohio River, Wabash River, White River, St. Joseph River, East Fork White River, Tippecanoe River, Patoka River, Great Miami River, Maumee River, Kankakee River, etc. The major lakes in this US state are Monroe Lake, Lake Michigan, Lake Michigan-Huron, Patoka Lake, Brookville Lake, Gibson Lake, Lake Wawasee, Mississinewa Lake, Salamonie Lake, etc.
The state of Indiana is 270 mi (435 km) long and 140 mi (225 km) wide. The mean elevation is 700 ft (213 m) above sea level. While Hoosier Hill in Franklin Township at 1,257 ft (383 m) above sea level is the highest elevation point, the Wabash River flowing into the Ohio River in Posey County at 320 ft (98 m) above sea level is the lowest elevation point.
The other significant mountains in Indiana are Hells Point, Sand Hill, Weed Patch Hill, Diamond Hill, Paradise Point, The Knob, Bearwallow Hill, Limekiln Ridge, Baby Mountain, etc.
What is the Climate of Indiana?
A humid continental type of climate is found in the northern and central regions of Indiana. However, in the southern part, a humid subtropical climate is found. The climate in Indiana is characterized by hot summers as well as cold winters. As you move to the south, the climate becomes warmer gradually.
Indiana has an invigorating climate with strongly marked seasons. The summer season is characterized by hot, humid, and wet weather. The peak of summer is reached in July when the temperature gets more than 100 °F (37.8 °C). The humidity becomes oppressive during this point in time.
Cold and bitter climate prevails during winter. During January in the north, the night temperature remains below 15 °F (-9.4 °C). In winter, frequent weather changes take place. This is because of the northward movement of the hot weather from the tropics and southward movement of the cold air masses from the polar region.
With a change in the weather from cold to hot during springtime, the season gets lots of tornadoes and thunderstorms. During autumn the climate remains pleasant with sunny skies, comfortable temperature, and low humidity. Lake Michigan influences northern Indiana’s climate in all seasons.
The annual rainfall in this state revolves around 42 inches (1066.8 mm). The rain increases as you move from north to south. The north-central snow belt in Indiana, near Lake Michigan, gets around 76 inches (1930.4 mm) snowfall. It is higher than the 14 inches (355.6 mm) snowfall in the southwest.
The months from mid-November to mid-April is the snow season in Indiana. The Great Lakes region in the state remains cloudiest. While the winter season is the cloudiest, the autumn season continues to be sunniest. Around 2,400 hours is the average yearly sunshine time. The cloud-cover during daylight hours remain less than 40% for 190-200 days in a year.
What is the Economy of Indiana?
The economy of the state is dominated by manufacturing. The job market has expanded at a rate of 1.9% over last year. Estimates reveal that the economy is expected to grow at a rate of 34.8% in the coming decade.
The unemployment rate has remained low than the national average. It was 3.4% in Indiana, less than the national average of 3.9%. The rate of unemployment in Indiana reached as high as 11% in January 2010, but the economy recovered, and the unemployment rate came down to 3.2% in November 2019.
The total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for Indiana has increased from US$272,845.6 million in 2008 to US$366,800.5 million. The per capita personal income has increased from US$35,228 to US$47,149 during 2008-2018. The real median household income (2018 CPI-U-RS Adjusted Dollars, Not Seasonally Adjusted) was US$54,389 in 2008, but it fell to US$49,730 in 2011. It then recovered and reached US$59,892 in 2018.
The total value of exports and imports in Indiana in 2018 were $322,291,568,431 and $617,945,603,077 respectively, resulting in a trade balance of -$295,654,034,646. The major exports are Oil and Mineral Fuels, Precious Stones and Metals, Industrial Machinery, Motor Vehicles and Parts, Organic Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, Electrical Machinery, Iron and Steel, Cotton, Non-Knit Apparel, etc.
The principal imports of Indiana are Oil and Mineral Fuels, Precious Stones and Metals, Electrical Machinery, Industrial Machinery, Organic Chemicals, Plastics, Iron and Steel, Fats and Oils, Precision Instruments, Inorganic Chemicals, etc.
There are over 871,247 poor people in Indiana out of the total population of 6,463,636 in 2018. Around 13.5% of the total population in the state lives below the poverty line.
What is the Transportation System of Indiana?
Indiana has a developed transport system with roadways being the lifeline. The major Interstate highways in this state are I-69, I-65, I-74, I-70, I-90, I-64, I-80, I-94, I-164, I-165, I-265, I-275, I-294, I-465, I-469, and I-865. Some of the state roads that pass through Indiana are SR 1, SR 2, SR 3, SR 4, SR 5, SR 6, and many more.
The major airports in Indiana are Evansville Regional Airport (in Evansville), South Bend International Airport (in South Bend), Indianapolis International Airport (in Indianapolis), Fort Wayne International Airport (in Fort Wayne), and many more.
Why Indiana is called “The Hoosier State”?
Indiana is officially called “The Hoosier State” because it is deep-rooted in the history of the state. The general use of this name started in the 1830s, and the name is synonymous with the rustic individualism of the state. Various theories are there regarding the origin of this nickname.
The earliest mention of the word “Hoosier” is found in G.L. Murdock’s letter to General Tom Tipton in 1831. The Indianapolis Journal used the poem of John Finley “The Hoosier’s Nest” as their “Carriers’ Address” on January 1, 1833. “The Hoosier State” nickname is officially used since January 8, 1833.
Some of the popular theories regarding the reason behind giving the nickname “The Hoosier State” to Indiana revolve around: the “The Who’s Here Story”, “Who’s Ear Story”, “The Fighting Indianans”, “Mr Hoosier”, story of the Indiana Historian Jacob Piatt Dunn Jr. referring to woodsmen and rough hill people. Other stories behind the reason for the nickname revolve around the southern, black Methodist preacher named Harry Hoosier.
Other nicknames of Indiana are “Crossroads of America” and “Hospitality State”.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Indiana?
Indiana Dunes National Park, Hoosier National Forest, Eiteljorg Museum of American Indian and Western Art (in Indianapolis), Fort Wayne Children’s Zoo (in Fort Wayne), Snite Museum of Art (in Notre Dame), Indiana University (in Bloomington), The Children’s Museum of Indianapolis (in Indianapolis), Prophetstown State Park (in West Lafayette), Studebaker National Museum (in South Bend), WonderLab Museum of Science (in Bloomington), Lanier Mansion State Historic Site (in Madison)
Facts About Indiana
1) Indiana is nicknamed “The Hoosier State”.
2) The capital of the state is Indianapolis and it is also the biggest city.
3) The state of Indiana forms a portion of the “Corn Belt” of the United States.
4) Indiana achieved statehood on December 11, 1816.
5) Bloomington is the hometown of David Lee Roth, a past member of the famous rock band Van Halen.
6) The neighboring states of IN are Ohio, Michigan, Kentucky, and Illinois.
7) The official tree is the Tulip.
8) The official motto is “The Crossroads of America”.
9) With an elevation of 1,257 feet, the tallest point in the state is the Hoosier Hill.
10) The official bird is the Cardinal.
11) The official flower is the Peony.
12) The official song is “On the Banks of the Wabash”.
13) The official poem is “Indiana”.
14) The official colors are blue and gold.
15) The major industries of the state are vehicle manufacturing, chemicals, machinery, steel manufacturing, musical instruments, publishing, and refrigerators.
16) The eminent residents of the state include Michael Jackson, James Dean, and David Letterman.
17) The state of IN is famous for containing natural resources like natural gas, bituminous coal, gemstones, petroleum, and timber.
18) The official beverage is Water.
19) The official stone is the limestone.
20) The official flag of the state was assumed in 1917.
Related Links: