- Japan Cities - Hiroshima, Sagamihara, Tokyo
- Neighboring Countries - South Korea, North Korea, China, Russia
- Continent And Regions - Asia Map
- Other Japan Maps - Japan Map, Where is Japan, Japan Blank Map, Japan Road Map, Japan Rail Map, Japan River Map, Japan Physical Map, Japan Flag
Background:
Japan is a nation of rich cultural heritage and many natural wonders. Referred to as ‘The Land Of The Rising Sun”, Japan has become the epicenter of international trade and finance with the technological advances made by the Japanese and by Japanese companies.
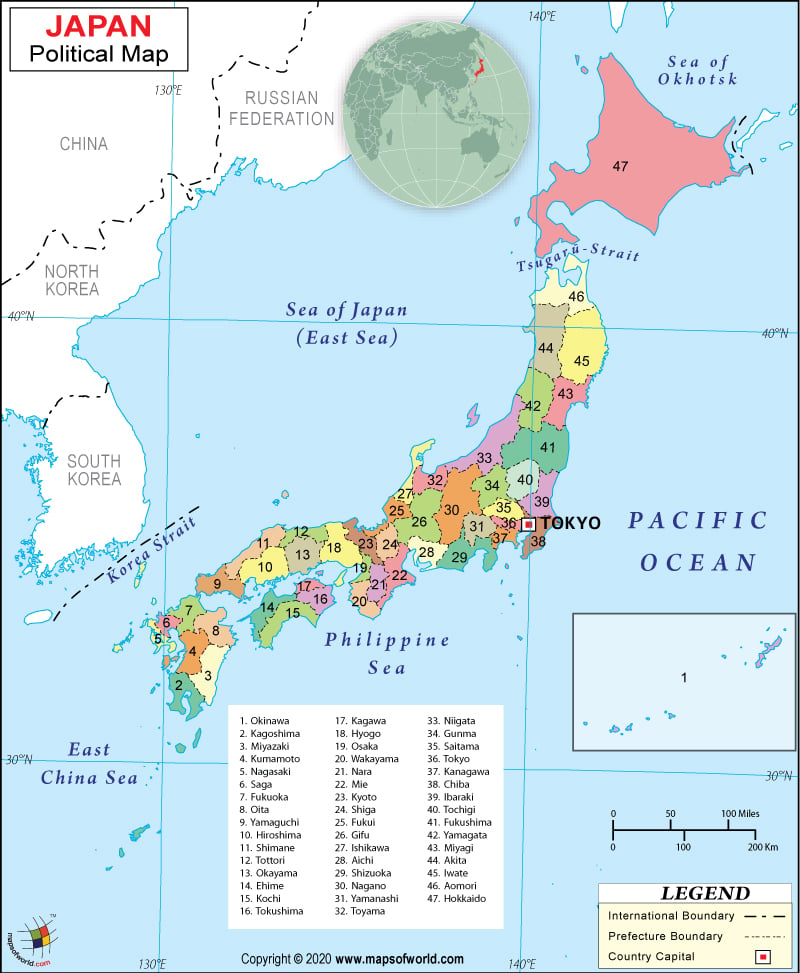
Situated in East Asia, Japan is an archipelago of 6,852 islands. It is surrounded by the North Pacific Ocean to the east, the Sea of Japan to the west, and the East China Sea, and the Philippine Sea to the south. China, North Korea, South Korea, and Russia share maritime boundaries with Japan. Japan’s Geographic Coordinates are 35.41⁰ N and 135.83⁰E.
Economy and Agriculture
Japan’s economic growth after World War II has been phenomenal. The shrewd government policies and dedicated work culture have propelled the country’s economy to great heights.
For three decades from the 1960s to the 1980s, Japan’s real economic growth had been remarkable. In the 1990s however, Japan faced an economic crisis. with government spending having been promptly cut and investments made, the economy recovered again in 2009-2010.
Japan’s TimeLine |
|---|
| 30,000BC | Earliest Known Inhabitation of Japan |
| 535 AD | Contact with Korea and China introduced Buddhism |
| 710AD | Japan’s First Permanent Capital Founded At Nara |
| The Golden Age of Japan starts at the beginning of the Nara period. | |
| 784 AD | Hein Period follows |
| 1192 | Yoritomo of the Minamoto clan sets up a military government known as Shogunate |
| 1543 | Portuguese enter Japan for trade |
| 1603-1867 | Tokugawa period starts |
| 1633 | Foreigners banned; trade with foreign countries suspended |
| 1853 | The US demands a reopening of trade |
| 1867 | Edo Shogunate fails |
| 1868 | Meiji Emperor ascends the throne |
| 1894 | Japan and China go to war |
| 1904 | Russia and Japan go to war |
| 1912 | Meiji Emperor dies |
| 1914 | In world war I, Japan joins the British Allies |
| 1940 | Japan become allies with Germany and Italy in Second World War |
| 1945 | Two Japanese cities were bombed by the USA (Hiroshima and Nagasaki)- the only known use of nuclear bombs in a war |
| 1947 | Japan signs peace treaties with the United States and other countries |
| 1952 | Japan regains full independence |
| 1956 | Liberal Democratic party formed |
| 1956 | Japan becomes a member of the United Nation |
| 1982 | Japanese automaker (Honda) opens its first plant in the US |
| 1993 | Seven Party coalition government formed |
| 1994 | Coalition government collapses, LDP and socialist support new administration take over. |
| 2011 | Earthquake hits Japan, followed by Tsunami causing a nuclear disaster |
| 2011 | China overtakes the Japanese economy, pushing Japan to the fourth position. |
Unfortunately, Japan suffered again in 2011 due to a major earthquake and Tsunami, forcing Japan’s position down to the 4th largest economy in the world. Japan has a GDP (PPP) of $4.389 trillion (2011 est.) Japan’s agriculture sector is small and highly subsidized. Its major agricultural products are rice, fish, vegetables, dairy products, etc. Japan imports about 60% of its food and its industrial sector also heavily import its fuel and raw materials. PM Noda has currently proposed to open the service sector and agricultural sector to foreign competition to boost its export.
Political History and Divisions
Japan has a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary government, with the Prime Minster as the head of the government. The role of the monarch is mainly ceremonial. After the death of the Meiji emperor in 1912 followed by the world wars, the reign of monarchs almost ended. By 1952, Japan had regained its full independence and in 1956 Liberal Democratic Party was formed. By this time constitutional monarchy was completely taken over by the parliamentary government. The Japanese government has two houses; the House of Representatives and the House of Councilors. Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which are further divided into cities. Each prefecture has a governor and an assembly elected by the people. There are about eight to nine informal geographic regions in Japan, which do not serve any political purpose.
Major Cities of Japan
Tokyo: Tokyo is actually a prefecture and a metropolis with 23 municipal wards. It is also the capital of Japan and is the seat of the Japanese government. Considered the third pillar of the world economy after New York and London, Tokyo is also one of the most expensive cities in the world.
Yokohama: It is the capital of Kanagawa prefecture and the second largest city in the country by population. It is also a major commercial hub of the country.
Osaka: This is the capital of Osaka Prefecture. This city is the third largest in the country and is also one of the command centers of Japan’s economy.
Kyoto: It is the capital of the Kyoto Prefecture. It is also one of the academic centers of the country. Kyoto has the second largest transportation station in the country.
Besides the above mention cities Nagoya, Sapporo, Kobe, Kawasaki, Saitama, Hiroshima, etc, are also prominent cities in Japan.
| Prefecture | Population | Area(km.²) | Area(mi.²) | Region | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aichi | 7,043,300 | 5,105 | 1,971 | Chubu | Nagoya |
| Akita | 1,189,279 | 11,609 | 4,482 | Tohoku | Akita |
| Aomori | 1,475,728 | 9,614 | 3,712 | Tohoku | Aomori |
| Chiba | 5,926,285 | 5,103 | 1,970 | Kanto | Chiba |
| Ehime | 1,493,092 | 5,664 | 2,187 | Shikoku | Matsuyama |
| Fukui | 828,944 | 4,188 | 1,617 | Chubu | Fukui |
| Fukuoka | 5,015,699 | 4,934 | 1,905 | Kyushu | Fukuoka |
| Fukushima | 2,126,935 | 13,781 | 5,321 | Tohoku | Fukushima |
| Gifu | 2,107,700 | 10,596 | 4,091 | Chubu | Gifu |
| Gumma | 2,024,852 | 6,356 | 2,454 | Kanto | Maebashi |
| Hiroshima | 2,878,915 | 8,453 | 3,264 | Chugoku | Hiroshima |
| Hokkaido | 5,683,062 | 78,515 | 30,315 | Hokkaido | Sapporo |
| Hyogo | 5,550,574 | 8,362 | 3,229 | Kinki | Kobe |
| Ibaraki | 2,985,676 | 6,087 | 2,350 | Kanto | Mito |
| Ishikawa | 1,180,977 | 4,196 | 1,620 | Chubu | Kanazawa |
| Iwate | 1,416,180 | 15,277 | 5,898 | Tohoku | Morioka |
| Kagawa | 1,022,890 | 1,877 | 725 | Shikoku | Takamatsu |
| Kagoshima | 1,786,194 | 9,149 | 3,532 | Kyushu | Kagoshima |
| Kanagawa | 8,489,974 | 2,384 | 920 | Kanto | Yokohama |
| Kochi | 813,949 | 7,106 | 2,744 | Shikoku | Kochi |
| Kumamoto | 1,859,344 | 7,383 | 2,851 | Kyushu | Kumamoto |
| Kyoto | 2,644,391 | 4,612 | 1,781 | Kinki | Kyoto |
| Mie | 1,857,339 | 5,774 | 2,229 | Kinki | Tsu |
| Miyagi | 2,365,320 | 7,288 | 2,814 | Tohoku | Sendai |
| Miyazaki | 1,170,007 | 7,734 | 2,986 | Kyushu | Miyazaki |
| Nagano | 2,215,168 | 13,585 | 5,245 | Chubu | Nagano |
| Nagasaki | 1,516,523 | 4,098 | 1,582 | Kyushu | Nagasaki |
| Nara | 1,442,795 | 3,692 | 1,425 | Kinki | Nara |
| Niigata | 2,475,733 | 12,577 | 4,856 | Chubu | Niigata |
| Oita | 1,221,140 | 6,331 | 2,444 | Kyushu | Oita |
| Okayama | 1,950,828 | 7,079 | 2,733 | Chugoku | Okayama |
| Okinawa | 1,318,220 | 2,244 | 866 | Ryukyu | Naha |
| Osaka | 8,805,081 | 1,845 | 712 | Kinki | Osaka |
| Saga | 876,654 | 2,416 | 933 | Kyushu | Saga |
| Saitama | 6,938,006 | 3,799 | 1,467 | Kanto | Saitama |
| Shiga | 1,342,832 | 4,016 | 1,551 | Kinki | Otsu |
| Shimane | 761,503 | 6,627 | 2,559 | Chugoku | Matsue |
| Shizuoka | 3,767,393 | 7,770 | 3,000 | Chubu | Shizuoka |
| Tochigi | 2,004,817 | 6,414 | 2,476 | Kanto | Utsunomiya |
| Tokushima | 824,108 | 4,144 | 1,600 | Shikoku | Tokushima |
| Tokyo | 12,064,101 | 2,145 | 828 | Kanto | Tokyo |
| Tottori | 613,289 | 3,492 | 1,348 | Chugoku | Tottori |
| Toyama | 1,120,851 | 4,252 | 1,642 | Chubu | Toyama |
| Wakayama | 1,069,912 | 4,722 | 1,823 | Kinki | Wakayama |
| Yamagata | 1,244,147 | 9,325 | 3,600 | Tohoku | Yamagata |
| Yamaguchi | 1,527,964 | 6,090 | 2,351 | Chugoku | Yamaguchi |
| Yamanashi | 888,172 | 4,463 | 1,723 | Chubu | Kofu |
| 47 divisions | 126,925,843 | 372,273 | 143,732 |
 Wall Maps
Wall Maps