Dominican Republic Map
- Neighboring Countries - Haiti, Jamaica, Cuba, Puerto Rico
- Continent And Regions - North America Map, Americas Map
- Other Dominican Republic Maps - Where is Dominican Republic, Dominican Republic Blank Map, Dominican Republic Road Map, Dominican Republic Rail Map, Dominican Republic River Map, Dominican Republic Cities Map, Dominican Republic Political Map, Dominican Republic Physical Map, Dominican Republic Flag
History of Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic covers part of the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean. Its early history involves the Tainos, who were indigenous to South America and migrated to Hispaniola around 650, where they established their societies. The Tainos divided the island into five primary chiefdoms, or caciquedoms, which were Marien, Magua, Maguana, Jaragua, and Higuey. Around the 15th century, the Caribs arrived and forced the Tainos to migrate northward.
European explorers, beginning with the first voyage of Christopher Columbus in 1492, began to arrive in Hispaniola. The Spanish colony at Santo Domingo became the first permanent New World settlement by Europeans, soon spreading to build plantations across the island and further drove out the Tainos. As Spain focused their colonization efforts on mainland Americas, the French seized control of Hispaniola.
The part of the island that is now Haiti became French in 1697, and the island came to be owned by the French in 1795 in the aftermath of the French Revolutionary War. In the early 1800s, Santo Domingo rose up against the French, and came under the control of Spain again. In 1821, it became the independent Spanish Haiti, but was soon invaded by Haiti. An opposition group formed, called La Trinitaria, declaring their independence from Haiti in 1844. The country became the Dominican Republic, and faced years of government changes and conflicts with frequent invasions by Haiti. In 1861, the country again became a Spanish colony in an effort to gain protection from Haiti, but the revolutionaries resisted the change and Spain gave the colony up in 1865. The Dominican Republic finally gained a sense of stability in the 1880s with the General Ulises Heureaux as president, though he lost popularity and was assassinated in 1899.
The US intervened in 1905, and the US occupation of the Dominican Republic in 1916 lasted until a new government was set up by 1924. That government was replaced by General Rafael Leonidas Trujillo Molina in the 1930 elections, who ruled as a dictator but was able to pull the country out of debt. Under his rule, the Dominican Republic suffered El Corte (the cutting) a massacre that sought out Haitians in the DR and killed up to 35,000 of them in 1937. Trujillo was assassinated in 1961, and to prevent a Communist takeover, the US intervened once again, supervising elections.
Neighboring Countries :
The Dominican Republic shares a border with Haiti on the island of Hispaniola. Other nearby islands include Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, Cuba, Turks and Caicos, and Jamaica.
Major Cities :
- Santo Domingo
- Higuey
- Santiago
- Punta Cana
Geography :
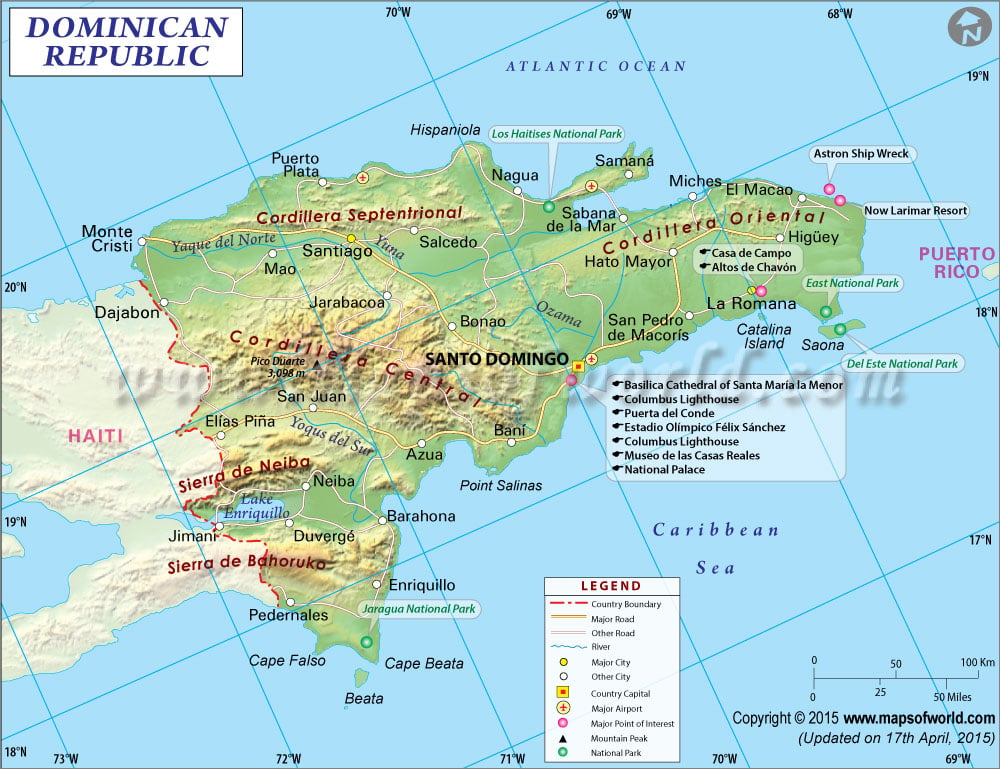
The Dominican Republic makes up the eastern two-thirds of the island Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean. Also included in the territory of the Dominican Republic are many small islands and cays, including Saona and Beata to the south.
The terrain of the Dominican Republic features coastal plains and several mountain ranges. Many of the coastal plains are home to savannahs and sugar plantations. These mountain groups include the Cordillera Septentrional (northern), Cordillera Central, Sierra de Neiba and Sierra de Bahoruco in the north and south respectively. The highest of the Dominican Republic’s mountains are the Central range, with the highest points in the entire Caribbean region, including highest point, Pico Duarte, at 3,098 meters (10,164 feet) above sea level.
The major rivers in the Dominican Republic are the Yaque del Norte and Yaque del Sud, Yuna River, and the Artibonito, which flows into Haiti. Lake Enriquillo is the country’s largest lake and is the lowest point in the whole Caribbean at 45 meters (148 feet) below sea level.
Points of Interest :
Santo Domingo, the capital, offers colonial historical sites of the oldest European colony in the New World, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Colonial Zone is home to Victorian architecture and the Palacio Nacional, which is the seat of government. Also in the capital are museums, the National Theater, and the waterfront. The city of Santiago also offers colonial and island architecture and culture, the historic monument, nightlife and an art and culture scene. Punta Cana in the east is surrounded by beach resorts and is a good place to take island trips or safari excursions.
Transportation :
The Dominican Republic has seven international airports. The largest airport in the country is Las Americas International Airport in Santo Domingo. Other important airports include Punta Cana International serving Higuey, Cibao International in Santiago, as well as airports in Puerto Plata, La Romana, Samana, Barahona. Frequent service is available from several destinations in Europe and the Americas. Cars and buses are available for transportation to Haiti and between the cities of the Dominican Republic. Ferries are another option for getting around, and also offer service to Puerto Rico.
 Wall Maps
Wall Maps