What is The Trans-African Highway Network?
Africa, which is the poorest and most underdeveloped continent in the world, is finally making economic progress. Recently, developments have been made with Chinese companies investing in the continent. The infrastructure is also improving and will be boosted further with the Trans-African Highway network.
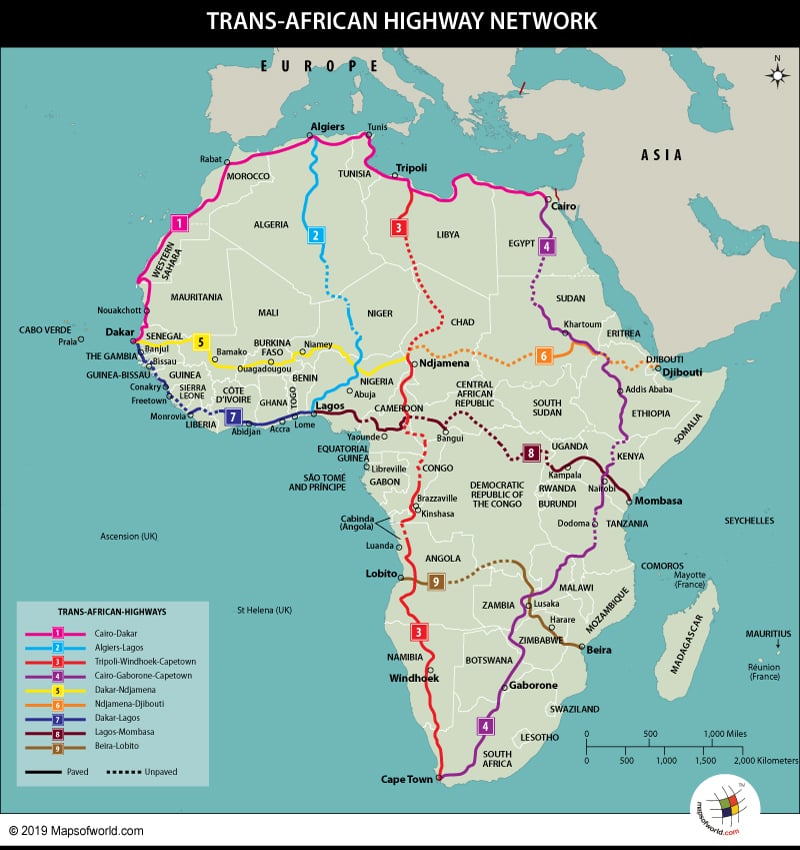
The Trans-African Highway Network, a 35,221 mile long highway under development, will connect various countries and major cities in the African continent. The highway is being constructed by the African Development Bank, United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, and the African Union. The highway, once complete, would play a pivotal role in the development of Africa, which is mostly ravaged by poverty, underdevelopment, corruption, illiteracy, human rights violations, etc, by promoting trade. Since the highway would connected almost the entire continent, it would help to improve healthcare and the educational infrastructure by bringing them to areas that were earlier out of bounds or inaccessible. The Trans-African Highway is also known by other names which include Trans-African Corridors or Road Corridors.
The network will be connecting all the countries of continental Africa, barring a few which include Somalia, Rwanda, Burundi, South Sudan, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Swaziland, Lesotho, and Malawi.
The Trans-African Highway network comprises nine highways which include three north-south routes and six east-west routes. The East-west routes are the Cairo-Dakar Highway (5,366 miles), Dakar-Ndjamena Highway (2,794 miles), Ndjamena-Djibouti Highway (2,622 miles), Dakar-Lagos Highway (2,490 miles), Lagos-Mombasa Highway (3,889 miles), and Beira-Lobito Highway (2,189 miles). The north-south routes are Algiers–Lagos Highway (27,99 miles), Tripoli–Windhoek–(Cape Town) Highway (6,716 miles), and Cairo–Gaborone–(Pretoria/Cape Town) Highway (6,355 miles).
But there are many missing links and maintenance problems that the highway is facing. Adverse weather conditions, devastating wars and human activity etc have severely impacted roads in some parts of the Trans-African Highway network. Lack of paved highways in central Africa is inhibiting the flow of trade within the region and is also prohibiting road trade between eastern and western Africa and western and southern Africa.
Other Information of Africa:
– Top Ten Smallest Countries In Africa
– Most Populated Countries In Africa