How Old is China?
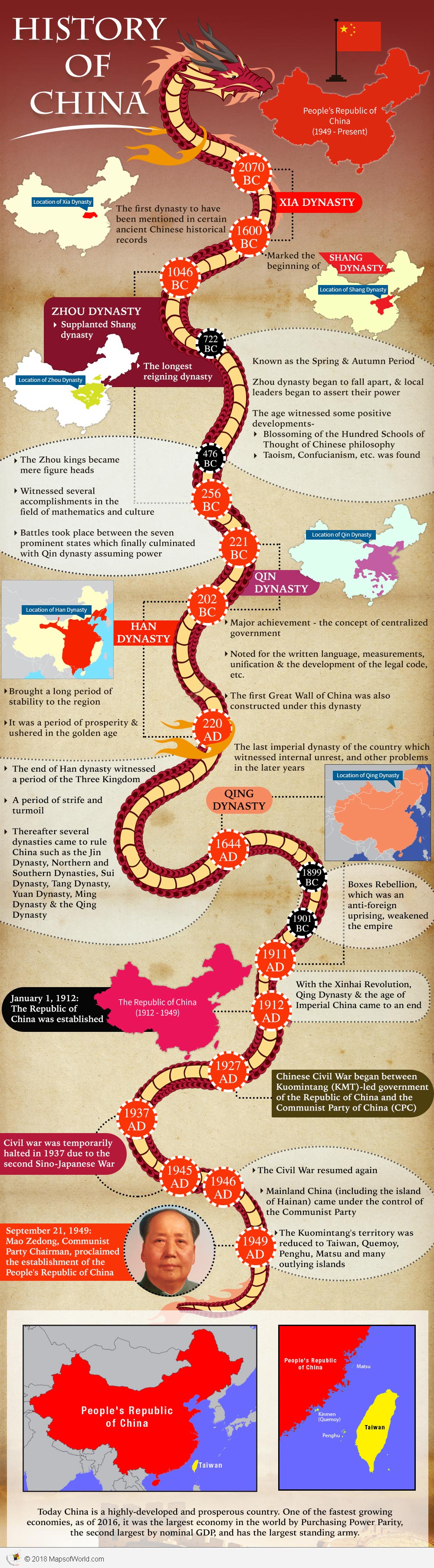
The country has existed for many centuries, thus it is hard to determine the exact age of China. Being one of the world’s oldest civilizations, the history of China can be traced back to antiquity. It has also been referred to as the Cradle of Civilization. Archeological evidence states that many cultures flourished in the region during the Neolithic and the bronze age; however, the Xia dynasty, which existed from 2070 to 1600 BC is the first dynasty to have been mentioned in certain ancient Chinese historical records.
The end of the Xia dynasty in 1600 BC, marked the beginning of the Shang dynasty. In 1046 BC, the Zhou dynasty supplanted Shang dynasty. The Zhou was the longest reigning dynasty and its rule lasted from 1046 to 256 BC.
The period from 722 to 476 BC has been referred as the Spring and Autumn Period. During this period the Zhou dynasty began to fall apart, and local leaders began to assert their power. Though the power of the Zhou dynasty declined, and a period of wars and political consolidation followed, the age witnessed some positive developments such as the blossoming of the Hundred Schools of Thought of Chinese philosophy, and the founding of Taoism and Confucianism.
The Zhou kings became mere figureheads during the period of warring states (476 to 221 BC). This period saw battles between the seven prominent states which finally culminated with Qin dynasty assuming power These years witnessed several accomplishments in the field of mathematics and culture.
The period of Imperial China began from 221 BC with the Qin Dynasty. One of the major achievement of this dynasty was the concept of centralized government. Also, the dynasty is noted for the written language, measurements, unification, and the development of the legal code. The first Great Wall of China was also constructed under this dynasty. But, the Qin Dynasty lasted only 15 years and was replaced by the Han Dynasty in 202 BC. The Han dynasty lasted until 220 AD and brought a long period of stability to the region. It was a period of prosperity and ushered in the golden age.
The end of Han dynasty witnessed a period of the Three Kingdoms. This was a period of strife and turmoil. Thereafter several dynasties came to rule China such as the Jin Dynasty, Northern and Southern Dynasties, Sui Dynasty, Tang Dynasty, Yuan Dynasty, Ming Dynasty and the Qing Dynasty. The Qing Dynasty, which ruled China from 1644 to 1911, was the last imperial dynasty of the country. The later years of the Qing Dynasty witnessed internal unrest and other problems. The empire was also weakened by the Boxes Rebellion, which was an anti-foreign uprising and took place between 1899 and 1901.
With the Xinhai Revolution of 1911–12, the Qing Dynasty and the age of Imperial China came to an end. The Republic of China was established on January 1, 1912. In 1927, the Chinese Civil War began between Kuomintang (KMT)-led government of the Republic of China and the Communist Party of China (CPC). The civil war was temporarily halted in 1937 due to the second Sino-Japanese War (1937 to 1945). The Civil War resumed again in 1946 and by 1949, the major combat had ended. While mainland China (including the island of Hainan) came under the control of the Communist Party, the Kuomintang’s territory was reduced to Taiwan, Quemoy, Penghu, Matsu and many outlying islands. Mao Zedong, Communist Party Chairman, proclaimed the establishment of the People’s Republic of China on September 21, 1949. Mainland China, aka the People’s Republic of China, does not recognize the government of Taiwan, and considers it a rogue province…and still part of Mainland China’s territory.
Today China is a highly-developed and prosperous country. One of the fastest growing economies, as of 2016, it was the largest economy in the world by Purchasing Power Parity, the second largest by nominal GDP, and has the largest standing army.
Related Maps: