How Many Countries were Created by Disintegration of USSR?
Ukraine Russia Standoff – Latest Update
- Russian Attack on Yavoriv Military Base
- Renowned US journalist Brent Renaud was killed when Russian troops opened fire on a car
- Ukraine Accuses Russia of using Banned Phosphorus Munitions
- Jake Sullivan Warns China to Avoid Helping Russia
Here are some important maps related to Ukraine-Russia War Crisis:
- Ukraine-Russia War Crisis – Updated Information
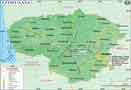
- Ukraine Map
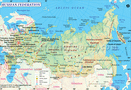
- Russia Map
- Russia Ukraine Map
- Kyiv (Kiev) Map
- Where is Kyiv (Kiev)
- NATO Members Map
- Where is Russia on Map
- Where is Ukraine on Map
- Where is Crimea on Map
- Where is Chernobyl
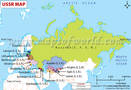
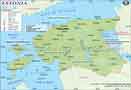
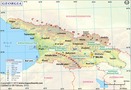
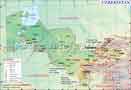
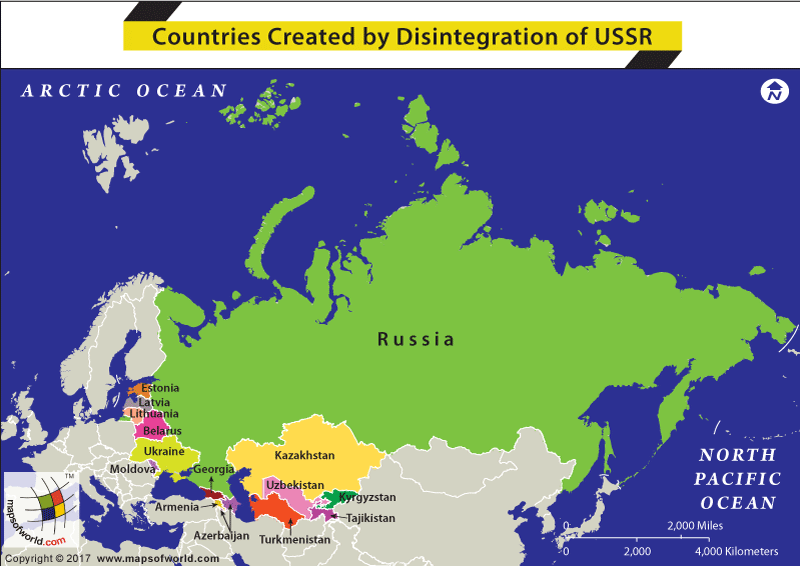
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) was a federation of fifteen distinct republics, the largest of which was Russia. The Union lasted from 1922 till its disintegration in 1991. The disintegration of the USSR led to the establishment of these 15 constituent republics as independent republics in Central Asia and the Baltic regions. These countries are –
| Country | Capital |
|---|---|
| Armenia | Yerevan |
| Azerbaijan | Baku |
| Belarus | Minsk |
| Estonia | Tallinn |
| Georgia | Tbilisi |
| Kazakhstan | Astana |
| Kyrgyzstan | Bishkek |
| Latvia | Riga |
| Lithuania | Vilnius |
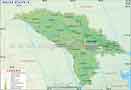
| Moldova | Chisinau |
| Russia | Moscow |
| Tajikistan | Dushanbe |
| Turkmenistan | Ashgabat |
| Ukraine | Kiev |
| Uzbekistan | Tashkent |
The final months of World War I witnessed the disintegration of two large empires. On the one hand, was Austria-Hungary and on the other was the breakdown of Czarist Russia with the outbreak of the Bolshevik Revolution. In the post-revolution era, Russia was joined by other Socialist Republics to form the USSR. Vladimir Lenin and the Marxist Party were at the helm of this Soviet Union. The ascent of Joseph Stalin in 1924, however, was a turning point in the history of the USSR. The government espoused totalitarian dictatorship in the guise of communism. Through the two decades that followed, the US and the international community remained occupied with the developments in Europe and the destruction wrought by World War II. It was only after the war ended, did USSR and its policies come into focus. The polarization of international policies and politics and the mounting tensions between the US and the USSR led to the Cold War.
Stalin’s death in 1953 did not, as had been hoped at the time, end the Cold War. The USSR, in fact, indulged in a rather expensive arms race and in the brutal suppression of anti-communist views. The effects of the USSR’s sharp policies were felt, rather acutely, across Eastern Europe. It is only with the political reforms that Mikhail Gorbachev (who assumed leadership of the USSR in 1985) that things began to change. With more freedom came criticism. Political reforms led to economic reforms but ultimately the staggering USSR had to collapse. Initially the three Baltic republics – Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia – declared their secession from the USSR. Soon after all the other republics (except Georgia) met in Alma-Ata and decided that they would no longer be part of the USSR. The Soviet Union was ultimately dissolved on December 26, 1991, and 15 new republics were formed. Russia was deemed the successor of the USSR and Russian President Boris Yeltsin replaced Soviet President Mikhail Gorbachev in international forums.
Related Links:
Related Maps: