What are the Key Facts of Zambia?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Zambia |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Lusaka |
|
Largest City |
Lusaka |
|
Coordinates |
-15.398829, 28.318349 |
|
Area |
290,587 sq. mi ( 752,618 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
3,755 mi ( 6,043 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Zambian kwacha (ZMW) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Malawi, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, Namibia, Angola |
|
Population |
16,591,390 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
English |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
24 October (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Lumbanyeni Zambia” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Edgar Lungu |
|
Vice President |
Inonge Wina |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 4,216.5 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,539.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.588 (2017), Rank: 144 |
|
Literacy Rate |
86.75 % (2018, UNESCO) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
96 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+260 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (CAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.zm |
Where is Zambia?
Zambia is a Southern African country that is located to the south of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and east of Angola.
What is the Geography of Zambia?
Zambia is spread across a total area of 752,618 sq. km (290,587 sq. mi), out of which 743,398 sq. km (287,087 sq. mi) is land area and 9,220 sq. km (3,560 sq. mi) is water area. It is a landlocked country and that’s why there is no coastline.
The Republic of Zambia shares its 6,043.15 km (3,755 mi) long land boundary with 8 countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo (2,332 km or 1,449 mi), Angola (1,065 km or 662 mi), Malawi (847 km or 526 mi), Zimbabwe (763 km or 474 mi), Mozambique (439 km or 273 mi), Tanzania (353 km or 219 mi), Namibia (244 km or 152 mi), and Botswana (0.15 km or 0.09 mi).
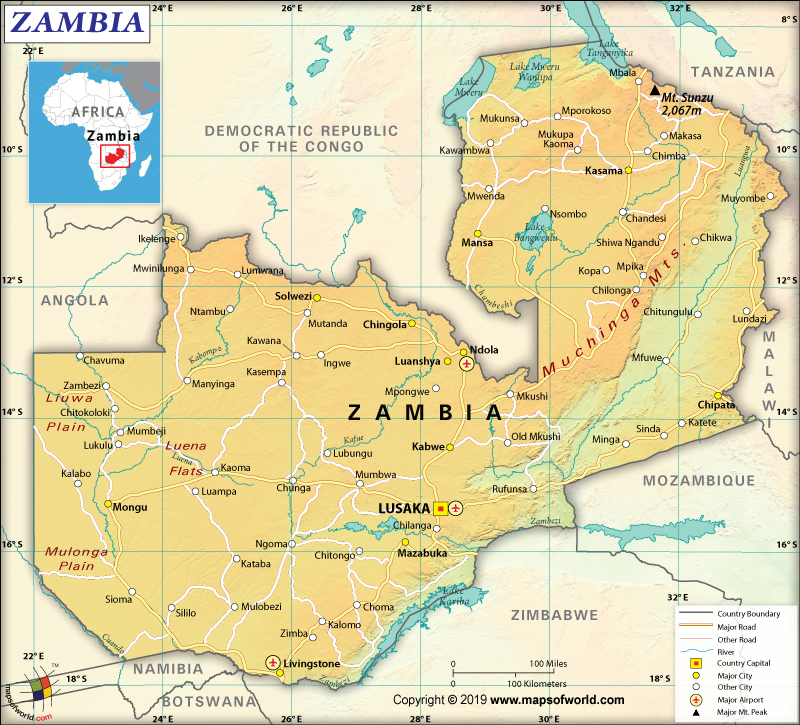
The Zambian terrain mainly consists of a high plateau. Some hills and mountains are also there in the north and central parts. Some of the major mountains of the country are Chimwami, Mundi, Chitendi, Ndembela, Mwenze, etc. The highest elevation point of the country is an unnamed point on the Mafinga Hills at 2,301 m (7,549 ft). Zambezi River at 329 m (1,079 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Zambia is 1,138 m (3,734 ft).
The Zambezi River along with its tributaries (the Luangwa and Kafue Rivers) forms the major river system in the country. Deep valleys and waterfalls (such as Victoria Falls along the southern Zambian border with Zimbabwe) are formed by the Zambezi River system by cutting into the Zambian plateau. Some of the major lakes of the country are Tanganyika, Mweru, and Bangweulu.
A swamp basin is located around Lake Bangweulu and the savanna grasslands. A large part of southwest Zambia is covered by woodlands and Rhodesian teak forests.
Zambia has a generally acceptable temperature across the year. The climate is tempered by plateau, which covers a major part of the landscape. Depending upon the altitude, the climate can be categorized as tropical or sub-tropical.
While the rainy season lasts from mid-November to March, the dry season lasts from April to mid-November. The rainy season generally remains hot and humid. During mid-May to mid-August, the temperature remains cool during the dry season. The climate starts to get progressively hotter from September to mid-November. Though the heat gets torrid, the humidity remains low during this time of the year. The hottest month of the year is October.
Mid-May to mid-August is the coolest period of the year. The temperature in the southern region can drop to around 0 °C (32 °F). The northern regions including the Northern Province, the Copperbelt Province, and the North-Western Province get maximum rainfall. The annual rainfall level here exceeds 1,000 mm (40 in) every year. In some areas, the extent of rainfall can also reach 1,400 mm (55 in) per year. However, the south-west region including the southern part of Barotseland gets the least rainfall (around 600 mm or 23.5 per year).
What is the Economy of Zambia?
Zambia is a middle-income economy. It attained an average economic growth of 7.4% per year during 2004-2014. However, the fall in copper prices has made the Zambian economy to slow down. Other factors for the economy’s slowdown include reduced power generation and depreciation of the Malawi currency Kwacha.
The economy of Zambia grew at a rate of 3.5% and 3.8% in 2017 and 2018 respectively. In 2018, the nominal GDP was US$26,720 million or US$26.72 billion. One of the main problems of the economy is its overdependence on copper production & export along with a lack of economic diversification. The economy received a severe blow in 2015 when there was a decline in the demand for copper from China. The economic growth again picked up in 2017 (when the mineral price increased again) after slowing down in 2015.
In 2017, the Zambian economy had a trade surplus of US$1.21 billion. The country exported US$9.7 billion of goods and imported US$8.5 billion of goods. Though the country has a high GDP growth rate, it has one of the highest levels of inequality in the world. The unemployment rate in 2018 was 7.21%. While 60% of the Zambian population lives in poverty, 42% of the population lives in extreme poverty.
What is the Transportation System of Zambia?
Zambia has 67,671 km (42,049 mi) long roadway, out of which 14,888 km (9,251 mi) is paved and 52,783 km (32,798 mi) is unpaved. It has a 3,126 km (1,942 mi) long narrow-gauge railway network system. The waterway is mainly concentrated on Zambezi and Luapula Rivers along with Lake Tanganyika. The total waterway is 2,250 km (1,398 mi) long. There are 88 airports in Zambia, out of which 8 have paved and 80 have unpaved runways.
What International Organizations is Zambia part of?
WTO, ACP, AfDB, AU, C, COMESA, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (compliant country), ISO (correspondent).