What are the Key Facts of Tuvalu?
|
Official Name |
Tuvalu |
|
Continent |
Oceania |
|
Capital |
Funafuti |
|
Largest City |
Funafuti |
|
Coordinates |
-8.520521, 179.196708 |
|
Area |
10 sq. mi ( 26 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Coastline |
15 mi ( 24 km) |
|
Currency |
Tuvaluan dollar, Australian dollar (AUD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Kiribati, Nauru, Samoa, Fiji |
|
Population |
11,192 (2017 Census ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, Tuvaluan |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
1 October (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Tuvalu mo te Atua” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary non-partisan parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Elizabeth II |
|
Prime Minister |
Kausea Natano |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 4,042.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 3,700.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
NA |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+688 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+12 |
|
Internet TLD |
.tv |
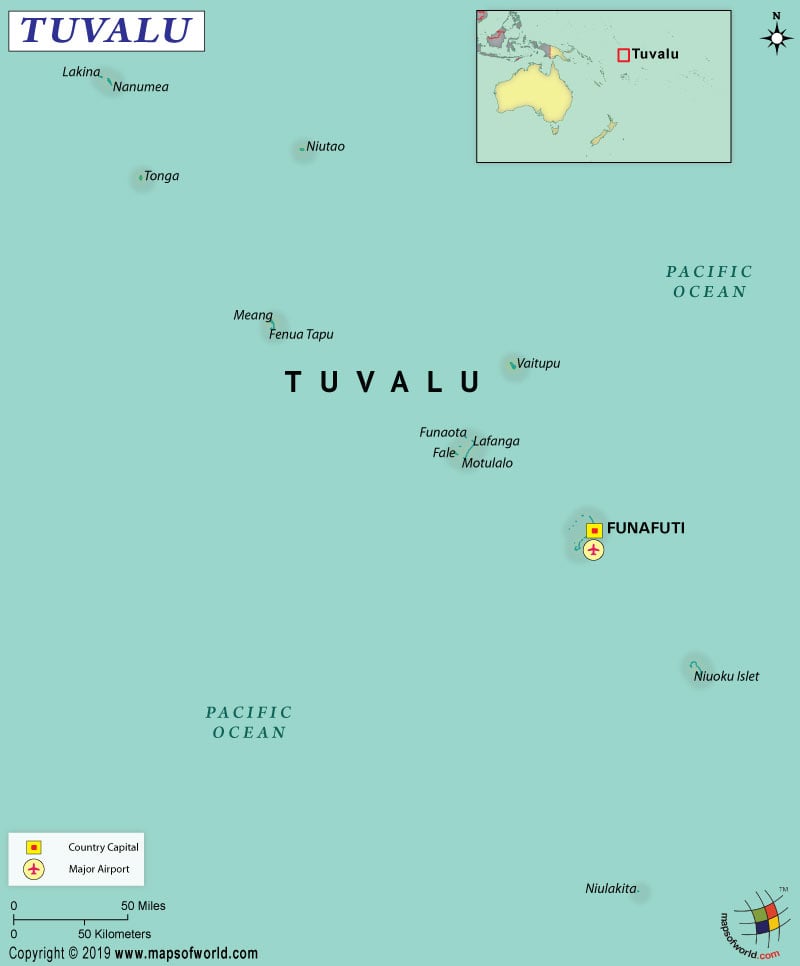
Where is Tuvalu?
Tuvalu is a group of islands in Oceania that consists of 9 coral atolls (3 reef islands and 6 true atolls) in the South Pacific Ocean. It is located around halfway from Australia to Hawaii. Tuvalu is located in the east-northeast direction of Solomon Islands’ Santa Cruz Island. To be very specific, it is located to the south of Kiribati, southeast of Nauru, west of Tokelau, north of Fiji, and northwest of Samoa as well as Wallis and Futuna.
What is the Geography of Tuvalu?
The total area of Tuvalu is just 26 sq. km (10 sq. mi), out of which the entire area is land area and no water area. In Oceania, Tuvalu is the second smallest nation. It doesn’t have any land boundaries. Tuvalu (formerly called Ellice Islands) has a 24 km (15 mi) long coastline.
The highest elevation point of this island nation is just 5 m (16 ft) and the lowest point is the Pacific Ocean at 0 m (0 ft). The terrain is low-lying and mainly consists of narrow coral atolls. No rivers, lakes, or streams are present on the islands.
Tuvalu has 3 reef islands as well as 6 coral atolls. All the reef islands have a separate structure than the atolls. They can be termed as reef platforms having smaller tabular reef platforms not having a salt-water lagoon. However, these platforms do have a completely closed dry land rim having lagoon remnants with no connection to the open sea. There are two lakes in Niutao and they are brackish to saline. As the lagoon got filled with coral debris, they are now degraded lagoon.
The soil in the islands of Tuvalu is poor. The country has low-lying land having narrow coral atolls. The sea level is rising. The extent of the rise in sea level at the Funafuti tide gauge is around 3.9 mm (0.15 in) per year, which is around twice that of the global average. The increased transfer of wave energy (caused by the rapidly rising sea levels) across the reef surfaces has resulted in accretion to island shorelines. However, this hasn’t resulted in an additional habitable land.
Tuvalu has a typical tropical warm climate having two different seasons. The dry season starts from December and continues till the beginning of February. It again persists from June-to-mid-September. Rainy season prevails two times in the year. The first rainy season starts in February and lasts till the end of May. The second rainy season starts from September and continues till the end of November. The tropical temperature is moderated during April-November by the easterly winds.
The average temperature revolves within 26-32 °C (78.8-89.6 °F) throughout the year. The average water temperature revolves within 28-29 °C (82.4-84.2 °F).
What is the Economy of Tuvalu?
The economy of Tuvalu is dependent upon fishing licenses, overseas workers’ remittances (especially the seamen as well as the ones living in New Zealand), the export of copra in small scale, sale of passports, sale of postage stamps/coins, resale of rights to international telephone codes, and many more. In 2018, Tuvalu’s nominal GDP grew at a rate of 2.5% to reach US$ 43 million, which is an increase of around US$2 million with respect to 2017.
The country has a negative balance of trade of around US$31.6 million. While it exported $4.02 million value of items, it imported $35.6 million value of items. The main exports are Non-fillet Frozen Fish, Aqueous Paints, Non-Knit Active Wear, Polyacetals, Laboratory Reagents, etc. The major import items of Tuvalu are Refined Petroleum, Gravel and Crushed Stone, Refined Copper, Fishing Ships, Iron Structures, and many more.
Tuvalu is considered as one of the poorest economies in the world. Reports say that just 1,500 people out of the total population of 11,200 people (2011 Census) are employed with each worker having an average income of just US$1,000 per year. Rough estimates say that 26.3% of the population lives below the national poverty line.
What is the Transportation System of Tuvalu?
The transportation system in Tuvalu is highly limited. There is just 8 km (5 mi) of roadway present in the country. Air travel is also highly limited. There is just one airstrip in Funafuti. The usual forms of transport inside the country include small pickup trucks, bicycles, and motorcycles. Travelers can hire these transport services from the hotels. Limited services of privately operated minibuses and taxis are also available. The only major seaport is located in Funafuti, from where passenger and cargo vessels are available. There are 254 merchant marine ships available in Tuvalu.
What International Organizations is Tuvalu part of?
UN, IMF, ILO, UNESCO, ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, IBRD, IDA, IFAD, IMO, IOC, ITU, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, IFRCS (observer)
Related Link:

