What are the Key Facts of Sweden?
| Official Name | Kingdom of Sweden |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Stockholm |
| Largest City | Stockholm |
| Coordinates | 62.000099, 14.999959 |
| Area | 173,860 sq. mi (450,295 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,550 mi (2,333 km) |
| Coastline | 2,000 mi (3,218 km) |
| Currency | Swedish krona (SEK) |
| Neighboring Countries | Norway and Finland Maritime Neighbors: Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia |
| Population | 10,223,505 (2018) |
| Official Languages | Swedish, official minority languages- Finnish, Romani, Yiddish, Sami, and Meankieli |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | June 06 |
| National Anthem | Du gamla, du fria |
| Form of Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Monarch | Carl XVI Gustaf |
| Prime Minister | Stefan Löfven |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $51,404.8 (World Bank, 2017) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $53,253.5 (World Bank, 2017) |
| Literacy Rate | NA |
| Space Agency | Swedish National Space Agency |
| Military Expenditure Ranking (SIPRI) | 33 |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 652 |
| Calling Code | +46 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Internet TLD | .se |
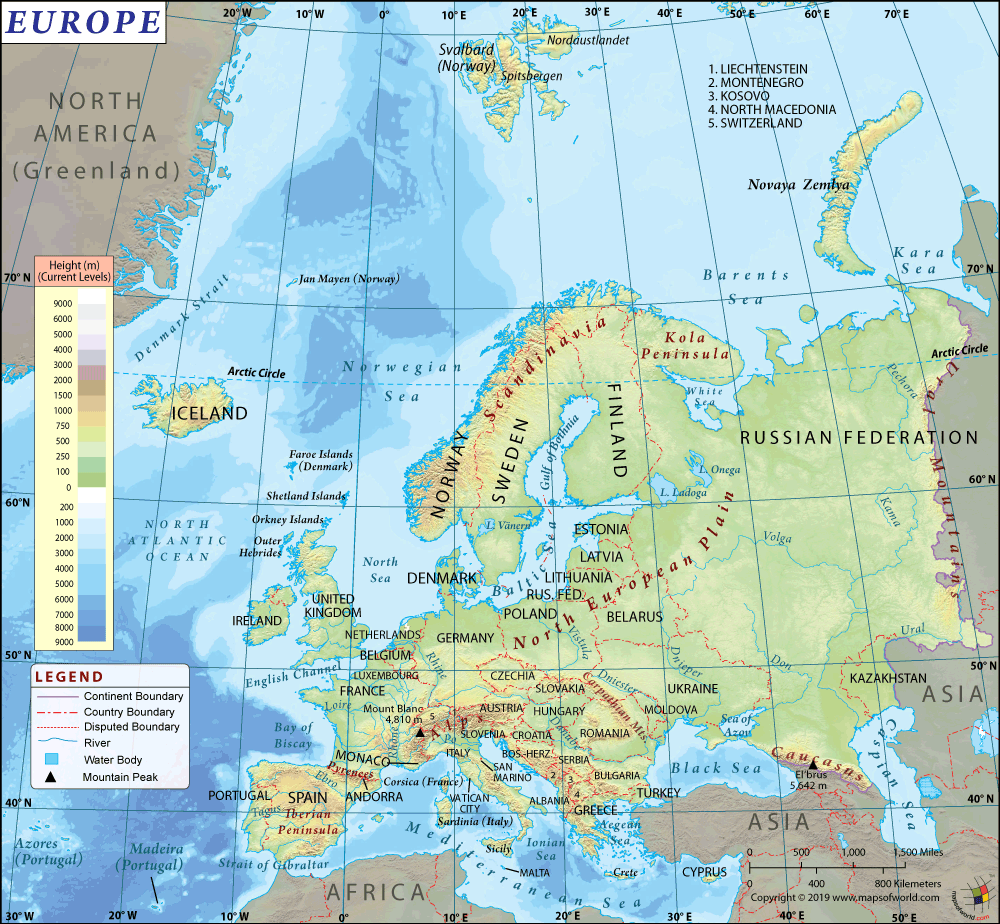
Where is Sweden?
A Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula, the Kingdom of Sweden is located in Northern Europe. Lying west of Baltic Sea, it shares its maritime borders with Denmark, Germany, Poland, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. It shares its land borders with Norway and Finland.
What is the Geography of Sweden?
Sweden has a deeply-indented coastline in the south. In addition, the country abounds in several islands, lakes, rivers and streams scattered across the entire landscape. The northern part of Sweden above the Arctic Circle has rugged terrain with snow-covered mountains and thick forests. Central Sweden has somewhat lower mountains in the west. Next come the heavily forested hills and ridges, several rivers and around 100,000 lakes. Towards the south, some of the large lakes are linked by canals that irrigate vast plains stretching across the land. Sweden’s border with Norway is straddled by the Scandinavian Mountains, which are called the Kolen (or Kjolen) Mountains in Swedish. Sweden’s highest point, Kebnekaise, is located at 2,111 meters (about 7,000 ft.)
There are innumerable small islands and reefs, especially in the east and southwest dotting Sweden’s coastline. Sweden’s largest islands are Gotland and Oland, that are situated to the south of Stockholm. White sandy beaches can be seen along the southern coastline. Sweden’s largest rivers are the Angerman, Eman, Indal, Lagan, Ljusnan, Lule, Osterdal, Skellefte, Storuman, Torne and Ume. The largest lakes in Sweden are Siljan, Storsjom, Varern and Vattern.
Gulf stream, a warm ocean stream off Sweden’s west coast reduces the impact of the severity of temperature given its location in the far north. In July, the temperatures average 13 to 17 degree celsius. February is usually the coldest month, with temperatures ranging from -22 to -3 degree celsius. In northern parts, temperatures normally drop to -30 degree celsius. From December to April, most of the country usually witnesses snowfall. In summers, northern part of Sweden has continuous daylight for a few months, while in winters it has complete darkness for about two months.
What is the Economy of Sweden?
Sweden combines free market capitalism with social welfare benefits. The economy of Sweden is developed, diverse and export oriented economy. Services sector accounts for 73.7% of the GDP, followed by industry including construction: 25.1%, and primary sector: 1.2%. Unemployment rate stands at 6.3%. Telecommunications equipment, motor vehicles, pharmaceuticals, home goods and appliances, chemicals, wood pulp and paper products, and iron and steel are the major industries. Its major trade flows are with Germany, Norway, Finland, US, Denmark, UK, Netherlands, and China.
What is the Transportation System in Sweden?
Sweden has 8 registered air carriers, with around 231 airports. It has around 14,127 km of railway tracks, and 573,124 km of roadways. Moreover, Brofjorden, Goteborg, Helsingborg, Karlshamn, Lulea, Malmo, Stockholm, Trelleborg, and Visby are its major seaports.
What International Organizations is Sweden part of?
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, Schengen Convention, UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNMOGIP, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Related Link: