What are the Key Facts of Suriname?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Suriname |
|
Continent |
South America |
|
Capital |
Paramaribo |
|
Largest City |
Paramaribo |
|
Coordinates |
4.000000, -56.000000 |
|
Area |
63,252 sq. mi ( 163,821 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,185 mi ( 1,907 km) |
|
Coastline |
240 mi ( 386 km) |
|
Currency |
Surinamese dollar (SRD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Guyana, Brazil, French Guiana |
|
Population |
575,990 (2018 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Dutch |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity, Hinduism |
|
National Day |
25 November (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“God zij met ons Suriname!” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary republic |
|
President |
Dési Bouterse |
|
Vice President |
Ashwin Adhin |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 15,497.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 5,950.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.72 (2017), Rank: 100 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
94.38 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+597 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC-3 (SRT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.sr |
Where is Suriname?
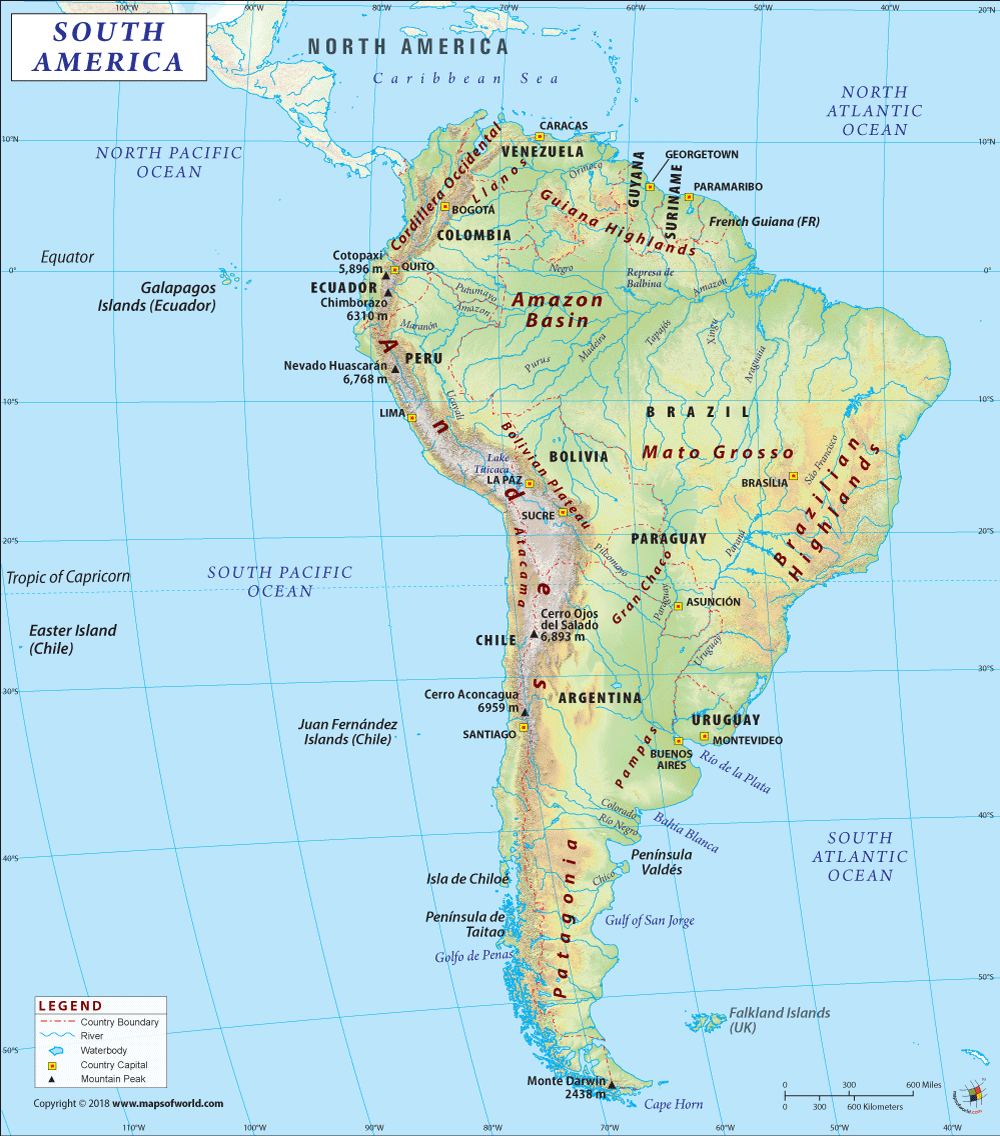
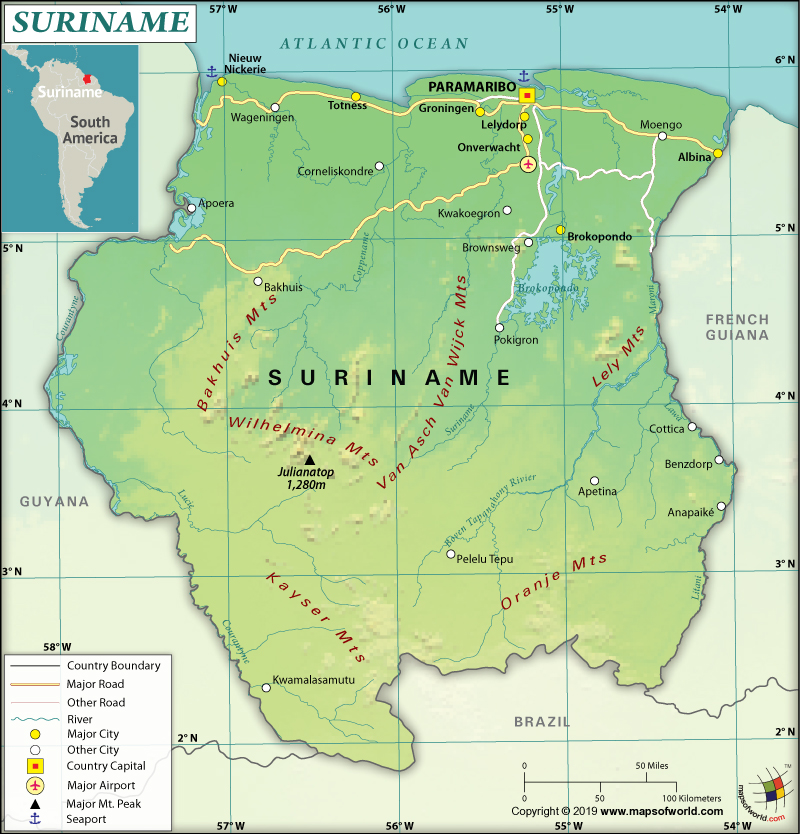
Suriname is a South American country that is in its northeastern Atlantic coast. This country shares its borders with Brazil to the south, Guyana to the west, French Guiana to the east, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north.
What is the Geography of Suriname?
Suriname is the smallest sovereign country in South America that is spread across a total area of 163,821 sq. km (63,252 sq. mi), out of which 156,000 sq. km (60,231 sq. mi) is land area and 7,820 sq. km (3,019 sq. mi) is the water area. It has a 1,907 km (1,185 mi) long land boundary and a 386 km (240 mi) long coastline. Suriname shares its land boundaries with three countries: Guyana (836 km or 519 mi), French Guiana (556 km or 345 mi), and Brazil (515 km or 320 mi).
The landscape of the country is dominated by rolling hills along with a narrow coastal plain having swamps. While Juliana Top (the major mountain of Suriname) at 1,230 m (4,035 ft) is the highest elevation point of the country, an unnamed location in the coastal plain at -2 m (-6.6 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Suriname is 246 m (807 ft).
The landforms of Suriname can be divided into two distinct geographical regions. While the western and southern parts are dominated by the tropical rainforests and savanna, the northern part is the coastal lowlands.
The fertile land is dissected by a handful of small mountains and the most significant ones are the Van Asch Van Wijck and De Hann mountain ranges. One of the world’s largest reservoir lakes, the WJ van Bloomenstein Lake, is in this country. Suriname is drained to the Atlantic Ocean by seven rivers. The major rivers are the Marowijne, Corantijn, Coppename, Suriname, Nickerie, Saramacca, and Commewijne rivers.
A tropical climate persists in Suriname. This climate is characterized by both dry and rainy seasons. The rainy season persists for a short period. It starts in December and continues until January. A longer rainy season is also there in Suriname. It starts in April and continues until July.
The annual average temperature remains within 21-32 °C (69.8-89.6 °F). It doesn’t come within the hurricane zone and therefore, the heavy rain shower is the most extreme weather condition that prevails in the country.
What is the Economy of Suriname?
The economy of Suriname is mostly dependent on mining (mostly oil and gold). Export of oil and gold contributes around 85% of the total exports as well as 27% of government revenues. The price volatility of the minerals affects the stability of Suriname’s economy.
In 2018, the economy increased at a rate of 1.997% to reach US$ 3.427 billion. The major items exported by the country are gold, precious metal scraps, refined petroleum, bananas, rough wood, etc. The major items imported by Suriname are refined petroleum, large construction vehicles, cars, delivery trucks, excavation machinery, etc. In 2017, the value of export and import was US$2.69 billion and US$1.38 billion, resulting in a positive balance of trade of US$1.31 billion.
The unemployment rate decreased from 9.7% in 2016 to 7.6% in 2017. The rate of poverty in the country was 47%. Over 6% of the population suffers from multidimensional poverty (including lack of living standards, education, and good health).
High poverty exists in Suriname despite having relatively high per capita income. This is because of high inequality among geographical locations as well as ethnic groups. Reports say that thousands can be lifted out of poverty in the country by growing the small and medium enterprises by a 10% rate in the coming five years.
What is the Transportation System of Suriname?
A wide range of transport forms is present in Suriname including airways, roadways, waterways, and railways. Around 4,304 km (2,674 mi) of roadway network is present in the smallest sovereign country in South America. While 1,119 km (695 ft) is paved, 3,185 km (1,979 ft) is unpaved.
Buses are the most convenient and reliable means of transports to commute within the country. Medium-sized jumbos are operated by both government and private services. Taxis are available in abundance, but they are not as cheap as buses. You can also rent vehicles for domestic travel. However, they tend to be quite expensive.
There are 55 airports across Suriname, out of which 6 have paved runways and 49 have unpaved runways. Johan Adolf Pengel International Airport is the largest and busiest airport in Suriname. Other important airports are Zorg en Hoop Airport and Vincent Fayks Airport.
A 1,200 km (746 mi) long waterway is present in Suriname and vessels can be navigated by ships with drafts up to 7 m (23 ft). Two major seaports of Suriname are Wageningen and Paramaribo. There are ten merchant marine ships available in the country.
A 166 km long single railway track is available in Suriname, out of which 80 km (50 mi) is standard-gauge, and 86 km (53 mi) is narrow-gauge.
What International Organizations is Suriname part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, ACP, AOSIS, CARICOM, CD, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IADB, IBRD, ICAO, ICCT, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, LAES, MIGA, NAM, OAS, OIC, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, Petrocaribe, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WIPO, WMO, ISO (correspondent), ITUC (NGOs)