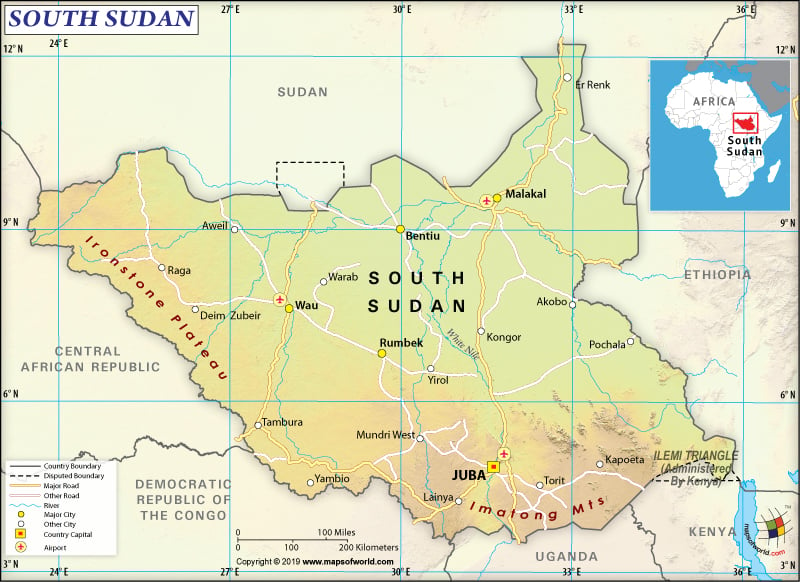
What are the Key Facts of South Sudan?
|
Official Name |
Republic of South Sudan |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Juba |
|
Largest City |
Juba |
|
Coordinates |
8.000000, 30.000000 |
|
Area |
239,285 sq. mi ( 619,745 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
7,575 mi ( 4,797 km) |
|
Coastline |
2,981 mi ( 19,920 km) |
|
Currency |
South Sudanese pound (SSP) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Sudan, Central African Republic, Ethiopia, Kenya, Uganda, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
|
Population |
12,230,730 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
English and Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Christian, Muslim, animist |
|
National Day |
9 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“South Sudan Oyee!” |
|
Form of Government |
Presidential republic |
|
President |
Salva Kiir Mayardit |
|
Vice President |
James Wani Igga |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 1,811.7 (World Bank, 2016) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 283.5 (World Bank, 2016) |
|
HDI |
0.388 (2017), Rank: 187 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
137 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+211 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (East Africa Time) |
|
Internet TLD |
.ss |
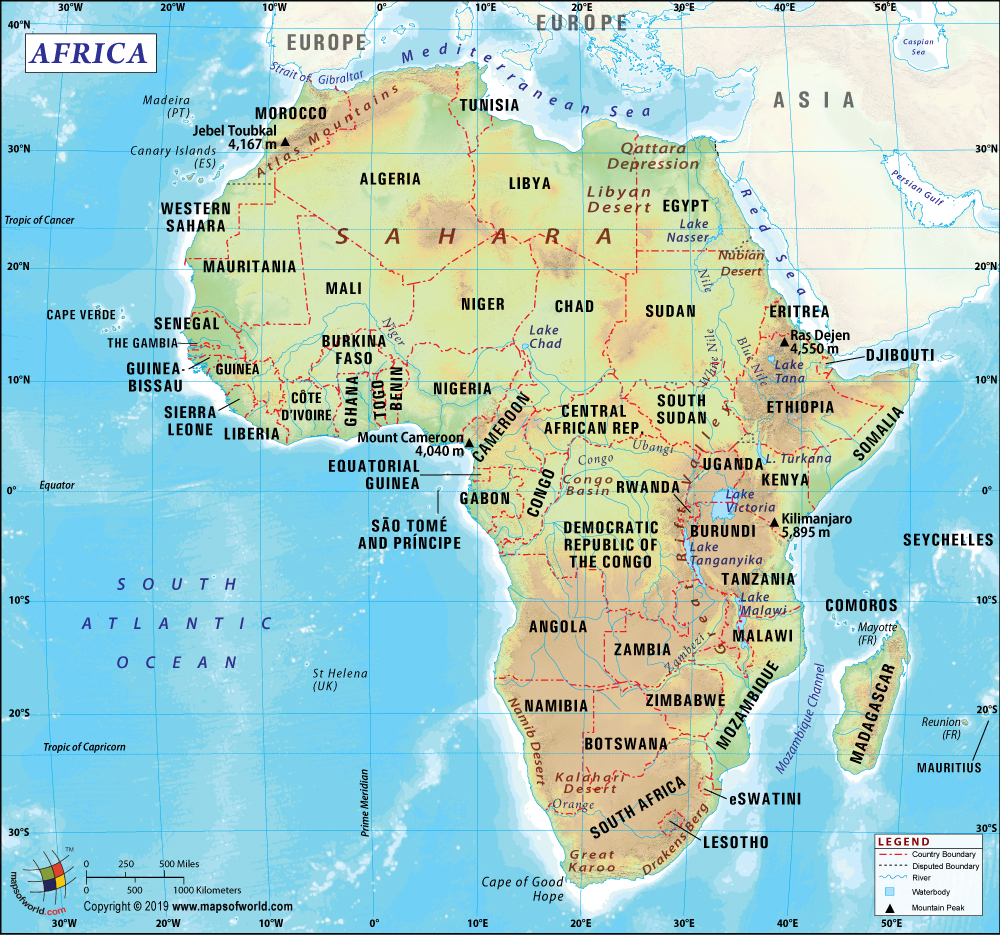
Where is South Sudan?
South Sudan is located in East-Central Africa. It is a landlocked country that shares its borders with Sudan (in the north), Central African Republic (in the west), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (in the southwest), Uganda (in the south), Kenya (in the southeast), and Ethiopia (in the east).
What is the Geography of South Sudan?
South Sudan is spread over an area of 644,329 sq. km (248,777 sq. miles) and its total boundary is 6,018 km (3,739 miles) long. The landscape of the country has grasslands, swamps, and tropical forests. Along the Ugandan and Kenyan borders, the plains located in the northern and central parts of South Sudan rise to sovereign highlands. One of the major geographical features of this country is the White Nile River, which flows north out of the uplands of Central Africa.
A large swampy area called The Sudd is spread over 130,000 sq. km (50,193 sq. miles). While it is the largest wetlands of the world, Nile basin is the world’s largest freshwater wetland. White Nile, dominating the central parts of South Sudan, feeds the vast swampy areas. Other major water sources of the country are Sobat River, Bahr el Ghazal, and Sudd.
The highest point of the country is Kinyeti with an elevation of 3,187 m. The White Nile is the lowest elevation point, which has an elevation of 381 m. The highest mountains of the country are Kinyeti, Konoro, Lotuke, Dongotona Mountains, Itibol, Jabal Kedong, Aripewi, Isubhak, Kamia, and Garia.
South Sudan has an Equatorial or tropical climate. The rainy season is characterized by large amounts of rainfall and high humidity. May-October is the rainy season. However, sometimes it can start in April and continue till November. The maximum amount of rainfall takes place in May. This season is followed by a drier season.
The average temperature of the country is always high. While March is the warmest month with temperature varying from 23 to 37 °C (73 to 98 °F), July is the coolest month with the average temperature varying from 23 to 37 °C (73 to 98 °F). Inter-Tropical Zone’s annual shift influences the rainy season. Higher humidity, slightly lower temperature, and enhanced cloud coverage takes place due to southerly and southwesterly winds.
At the end of the dry season, the temperature remains highest. The skies remain cloudless. The dry northeasterly winds influence the January to March season. No rainfall takes place throughout South Sudan during these months. The moist southwesterly winds reach the country by early-April, which cause heavy rainfall as well as thunderstorms. The far south region of the country has a short dry season.
What is the Economy of South Sudan?
South Sudan is known as one of the poorest countries of the world having the highest maternal mortality/female illiteracy rates. Most of the villages in South Sudan neither have any electricity nor running water. The country lacks overall infrastructure and there are only a handful of paved roads.
The economy is extremely fragile and is characterized by low literacy levels, ethnic violence, high poverty level, significant gender inequality, weak institutions, and limited access to the basic infrastructure. In fact, that’s why the recorded nominal GDP of South Sudan (2016) was just US$3 billion. The nominal GDP contracted by 4.28% in 2017.
While 83% of the population still lives in rural areas, more than 80% of the population is extremely poor (living at less than US$1 per day). Over one-third of the population lacks food security. South Sudan is overdependent on oil exports, and had a negative trade balance of US$5.2 billion (US$9.9 billion import and only US$4.67 billion export) in 2017.
What is the Transportation System of South Sudan?
After attaining its independence in July 2011, the transport sector of the country is growing fast. The government has prioritized to develop the transport infrastructure (with donor support) for accelerating South Sudan’s economic development.
Most of the people in the country avail road public transport for traveling. For rural accessibility, around 7,000 km (4350 miles) of roadways are required. The government is also improving the national and regional networks of roads. The paved road network is also being extended.
With help from the United Nations, the South Sudan government is rehabilitating the single-track railway connecting Babanusa and Wau Town 248 km (154 miles). The country is seriously going through the proposals of connecting with Kenya and Uganda with the help of railway lines.
Airways of South Sudan have strategic importance. Juba International Airport helps connect the country with important international destinations of Africa including Khartoum, Addis Ababa, Cairo, Nairobi, and Entebbe. Other important international airports are Malakal and Wau.
What International Organizations is South Sudan Part Of?
UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, AU, FAO, G-77, WHO, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IMF, Interpol, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, UPU, WCO, WMO