What are the Key Facts of Somalia?
|
Official Name |
Federal Republic of Somalia |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Mogadishu |
|
Largest City |
Mogadishu |
|
Coordinates |
10.000000, 49.000000 |
|
Area |
246,201 sq mi ( 637,657 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,470 mi ( 2,366 km) |
|
Coastline |
1,879 mi ( 3,333 km) |
|
Currency |
Somali shilling (SOS) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Djibouti, Ethiopia, and Kenya |
|
Population |
11,031,386 (2017 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Somali, Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
1 July |
|
National Anthem |
“Qolobaa Calankeed” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed |
|
Prime Minister |
Hassan Ali Khayre |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
NA |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 498.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
NA |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
252 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (EAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.so |
Where is Somalia?
Somalia has a strategically important location. It is located at the tip of the Horn of Africa (the mouth of the Bab el Mandeb), which is considered the gateway to the Suez Canal and the Red Sea. The country shares its border with the Gulf of Aden (to the north), Djibouti (to the northwest), Ethiopia (to the west), Kenya (to the southwest), the Guardafui Channel and the Indian Ocean to the east.
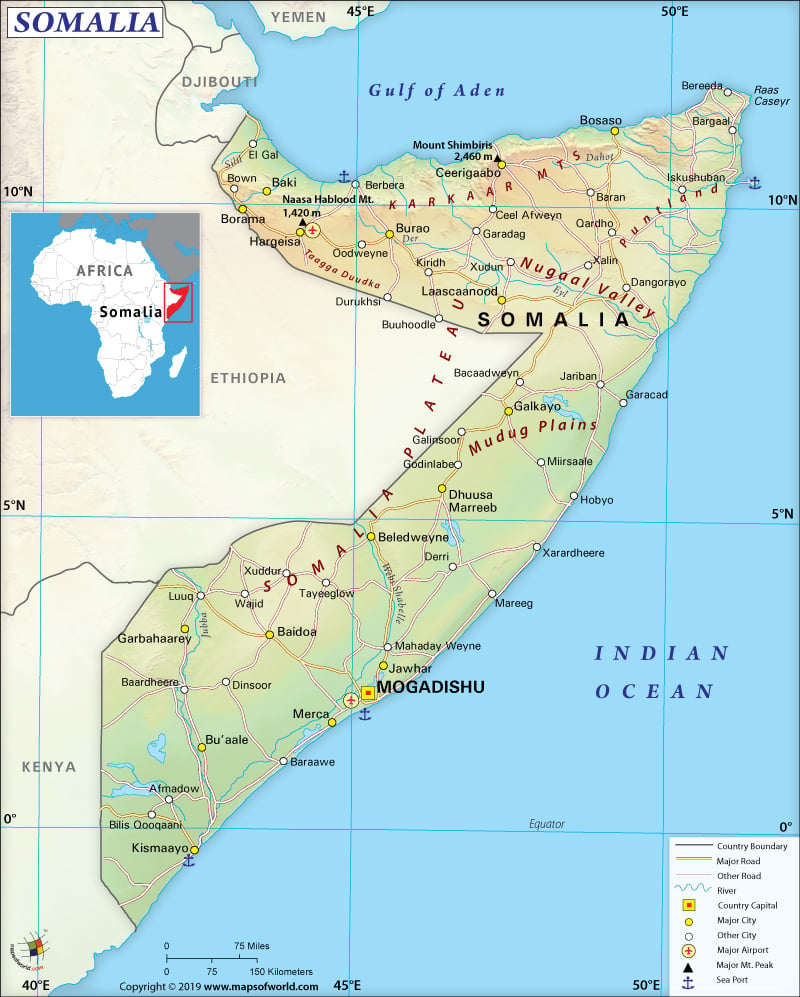
What is the Geography of Somalia?
Somalia is the easternmost country of Africa. It is spread over a total area of 637,657 sq. km (246,201 sq. miles), out of which only 10,320 sq. km (3,985 sq. miles) is water area.
The terrain of the country consists of plains, plateaus, and highlands. The Karkaar Mountains’ rugged east-west ranges are located in the far north at varying distances from the coast of Gulf of Aden. The topography of Somalia includes hilly regions ranging from 900 meters (2,953 feet) to 2,100 meters (6890 feet) above sea level in the north. The central and southern regions of the country are mainly flat.
The country has 3,025 kilometers (1880 miles) long coastline, which increases the importance of the location, as it helps in carrying out trade with the Middle Eastern countries as well as the rest of Africa.
While Shimbiris or Surud Cad (2,416 meters or 7,927 feet) is the highest point of the country, sea level of Indian Ocean denotes the lowest point. More than 500 peaks are located in the country. Most of the peaks are situated in the Bari and Sanaag regions. The major mountains of Somalia are Shimbiris, Karkoor, Warraq, Hurarka, Jifiyo, Gacan Libaax, Da’aro, and Tardaale.
Major rivers of the country are Shebelle, Dawa, Ewaso Ng’iro, and Jubba. Each of these rivers is shared with the neighboring countries – Kenya and Ethiopia.
Seasonal variation of climate is the least in Somalia because of its proximity to the equator. Sometimes unpredictable rainfalls take place here. Hot conditions, irregular rainfall, and monsoon winds are the characteristic features of the climate that prevail throughout the year.
Mean daily maximum temperature revolves within 30 °C to 40 °C (86 to 104 °F). However, along the eastern seaboard as well as higher elevations, a cold offshore current is felt. Mean daily minimum temperature revolves within 15 °C to 30 °C (59 to 86 °F).
Northern Somalia experiences the greatest temperature variation. While the littoral plains experience above 45 °C (113 °F) temperature in July, the highlands experience below freezing point temperature during December. Relative humidity in this region ranges from 40% in the mid-afternoon to 85% at night. This humidity change is mainly dependent upon the season. Northeast monsoon takes place from December to February. During this time, the temperature becomes moderate in the north. However, in the south, the temperature remains hot. During May-to-October, a southwest monsoon arrives, when the north remains extremely hot. Between the monsoons, hot and humid conditions prevail.
What is the Economy of Somalia?
United Nations classifies Somalia as the least developed nation. However, an informal economy (including livestock, telecommunications, and remittance/money transfers) is maintained despite experiencing two decades of a debilitating civil war by the country. In 2018, the nominal GDP of Somalia was US$7.48 billion, which expanded at the rate of 2.30% with respect to the previous year. A severe drought also led to crop failure and high livestock mortality in 2017.
Both traditional and modern production systems are available in the economy. However, a gradual shift is taking place towards modern production. Most of the population in Somalia is either nomadic or semi-nomadic pastoralists. Livestock management is the main source of livelihood. They rear animals, mainly goats, sheep, cattle, and camels. To supplement their income, they also gather resins and gums. 42% of the population live in urban areas, 23% in rural areas, 26% are nomadic, and 9% internally displaced persons.
United Nations Development Program (UNDP) says that the country has some of the lowest development indicators of the world. One of the main reasons for conflict among different social groups in the region is inequality. The worrying aspect is that significant inequality still exists in Somalia and it is widening. In fact, 24% of the estimated 15 million population of the country lives in extreme poverty (living a life within US$1 per day). This percentage is as high as 53% in rural areas. Unemployment is severe in Somalia. 50% of the labor force is unemployed.
What is the Transportation System of Somalia?
Highways, airports, and seaports are all there in Somalia. However, roadways are mainly unpaved. 61 airports are there in the country, out of which only 6 are paved and the other 55 are unpaved. Berbera and Kismaayo are the main seaports. Five merchant marines are there, out of which one is for general cargo.
What International Organizations is Somalia Part of?
UN, IMF, ACP, AfDB, UNCTAD, AFESD, AMF, AU, UNESCO, FAO, G-77, WHO, IBRD, ILO, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, Interpol, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, NAM, IGAD, IMO, IOC, IOM, UNHCR, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAS, UNIDO, OIC, OPCW, UPU, WIPO, WMO, WFTU (NGOs), OPCW (signatory), CAEU (candidate)