What are the Key Facts of Singapore?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Singapore |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Singapore (It is a City State) |
|
Coordinates |
1.366667, 103.800000 |
|
Area |
279.0 sq. mi ( 722.5 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Coastline |
120 mi ( 193 km) |
|
Currency |
Singapore dollar (S$) (SGD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Malaysia, Indonesia |
|
Population |
5,638,700 (2018 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, Malay, Chinese, Tamil |
|
Major Religion |
Buddhism |
|
National Day |
9 August (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Majulah Singapura” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Halimah Yacob |
|
Prime Minister |
Lee Hsien Loong |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 101,352.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 64,581.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.932 (2017), Rank: 9 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
97.05 (UNESCO, 2016) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
23 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
5 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+65 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+8 (Singapore Standard Time) |
|
Internet TLD |
.sg |
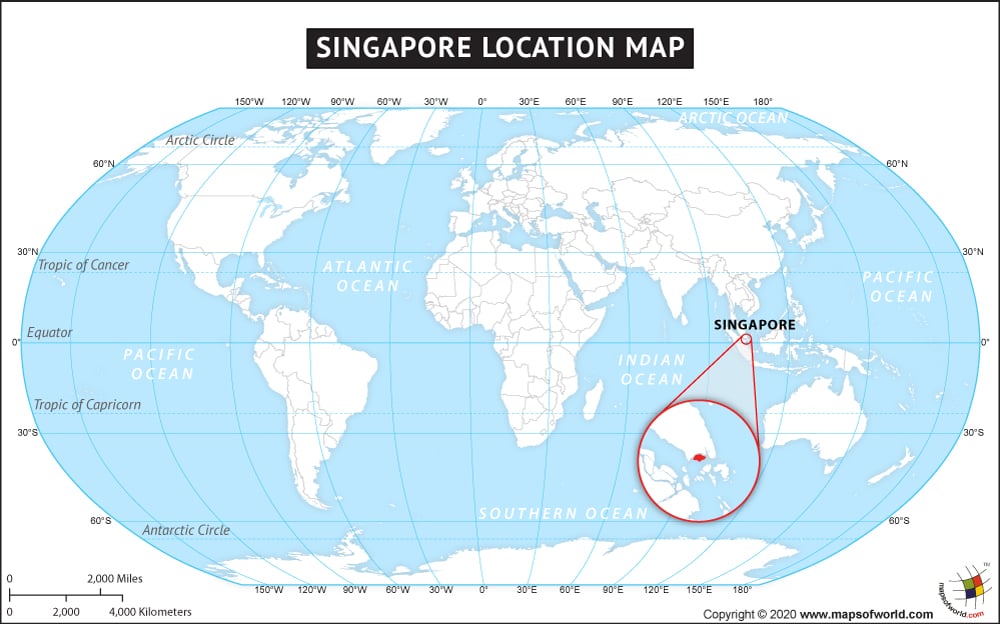
Where is Singapore?
Singapore is a tiny city-state located at the Malay Peninsula’s southern tip, 137 km (85 mi) to the north of the equator. Peninsular Malaysia is located in the north and Riau Islands of Indonesia to the south of Singapore.
What is the Geography of Singapore?
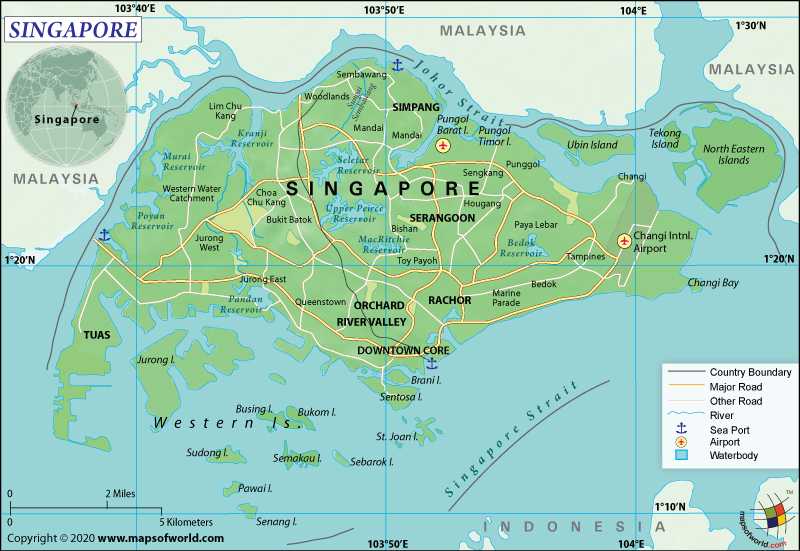
Singapore consists of the main island and 62 other islets. It is spread across a total area of 722.5 sq. km (279 sq. mi), out of which 709.2 sq. km (274 sq. mi) is a land area, and just 10 sq. km (4 sq. mi) is covered by water. This island nation has 193 km (120 mi) long coastline but no land boundaries.
While the main island is diamond-shaped, the farthest island is Pedra Branca. The comparatively larger islands are Pulau Tekong, Jurong Island, Sentosa, and Pulau Ubin. Most of the islands have an elevation within 15 m ( 49.21 ft) above sea level. Bukit Timah Hill (made up of granite igneous rocks) is the highest elevation at 165 m (538 ft) and sea level at Singapore Strait is the lowest elevation. Other major mountains of this island nation are Mount Serapong, Mount Faber, Bukit Gombak, Bukit Prigi Kling, Bukit Kalang, Bukit Batok, etc.
Broadly, while hills and valleys dominate the northwest part of the country made up of sedimentary rock, the eastern part mainly has sandy and flat land. The main rivers of the country are the Singapore River, Geylang, Rochor, Whampoa, and Kallang.
Further, a tropical rainforest climate is present in this country. Two distinct seasons are there. While northeastern monsoon remains from December-to-March, southwestern monsoon persists from June-to-September. Thunderstorms during the afternoon and early evening take place frequently.
As a result, there are no distinctive seasons in Singapore. While there is abundant rainfall in the country, the temperature and pressure remain high. Humidity remains significantly high. The tropical rainforest climate of this country is influenced by the Intertropical Convergence Zone (characterized by monotonous, windless weather).
This country doesn’t witness a significant temperature variation. The temperature revolves within 25 to 35 °C (77 to 95 °F). November-to-January is the monsoon season of this island country. During January-February, the sun rises at around 7:20 am and sets at around 7:25 pm. In July, the sun sets at 7.15 pm. During October-November, the sun rises at 6.45 am and sets at 6.50 pm. Rising sea levels due to climate change has seriously challenged the very existence of this country.
What is the Economy of Singapore?
To begin with, this country is a high-income market economy. Its nominal GDP has increased from US$338.41 billion in 2017 to US$364.16 billion in 2018. The economic growth had fallen slightly to 3.1% in 2018 from 3.7% in 2017. The most important reasons for the robust performance of the country are a pro-business attitude, low tax rate, extremely less corruption, and advanced infrastructure. Singapore’s key driver of growth is value-added manufacturing (including electronics and precision engineering sectors) and the services sector (mainly information and communications industries).
Moreover, the Singaporean economy is a major FDI outflow financier in the world. To keep up its economic pace, the government has emphasized on three crucial aspects: promotion of innovation, encouragement to entrepreneurship, and workforce re-training. The total number of Foreign Domestic Workers (migrant workers) is around 243,000, which accounts for 44% of the entire Singaporean workforce.
What is the Transportation System of Singapore?
Singapore’s transport system has been ranked as the overall best transportation system in the world by the Urban Transportation report of McKinsey.
Currently, there is 3,500 km (2,175 mi) of roadways available in this country, and all of them are paved. 164 km (102 mi) of expressways are available too. Roads can also access two islands (such as Sentosa and Jurong Island) of Singapore.
Besides, Woodlands 1st Link (Johor-Singapore Causeway) and Tuas 2nd Link (Malaysia-Singapore Second Link) bridges are the two man-made connections to Malaysia’s Johor. While the former is in the north, the latter is in the west.
Besides roadways, other major transit systems are the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) and the Light Rail Transit (LRT). They are mainly concentrated in specific neighborhoods only. The mainland Singapore remains connected to the other Singaporean islands, primarily with the help of ferryboat services.
Finally, there are 3,526 merchant marine ships/vessels in Singapore, out of which 732 are oil tankers, 603 are bulk carriers, 490 are container ships, 132 are general cargo ships, and 1,569 others. This country is a significant trans-shipment seaport.
The Singapore Changi Airport is not only the most important airport of the country but also one of the leading aviation hubs in Asia. There are nine airports in this country, and all of them have paved runways.
What International Organizations is Singapore part of?
WTO, ADB, WHO, AOSIS, IMF, APEC, ARF, UN, ASEAN, BIS, UNCTAD, Interpol, C, UNESCO, CP, UNHCR, EAS, FAO, WCO, FATF, WIPO, G-77, IAEA, UPU, IBRD, WMO, ICAO, NAM, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, OPCW, PCA, ICC (national committees), Pacific Alliance (observer), Arctic Council (observer), ITUC (NGOs)
Related Links: