What are the Key Facts of Serbia?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Serbia |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Belgrade |
|
Largest City |
Belgrade |
|
Coordinates |
44.000000, 21.000000 |
|
Area |
29,913 sq. mi (77,474 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,443 mi (2,322 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi (0 km) Landlocked |
|
Currency |
Serbian dinar (RSD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Kosovo |
|
Population |
6,945,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Serbian |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
15 February (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Boze pravde” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Aleksandar Vučić |
|
Prime Minister |
Ana Brnabić |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 18,989.0 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 7,402.4 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.799 (2019), Rank: 63 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
98.84 (UNESCO, 2016) |
|
Space Agency |
Serbian Office for Space sciences, Research and Development (SERBSPACE) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
68 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
15 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
381 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.rs |
Where is Serbia?
Serbia (whose official name is the Republic of Serbia) is a Southeast European country located between Hungary and Macedonia. This landlocked country is at the intersection of Central Europe and Southeast Europe in the southern Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans.
What is the Geography of Serbia?
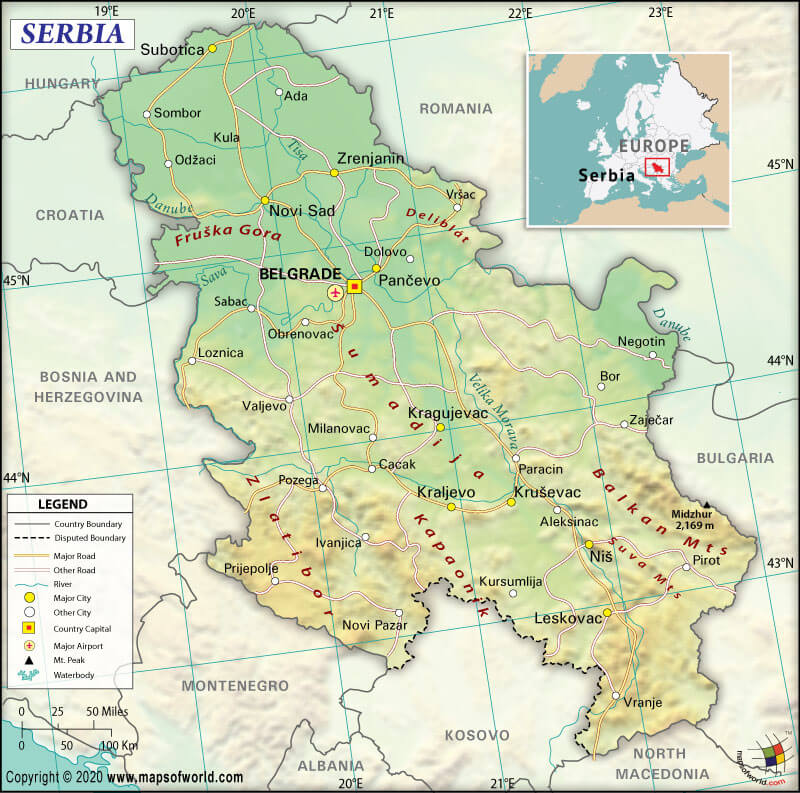
Serbia spreads across a total area of 29,913 sq. mi (77,474 sq. km). Out of the total area, 29,913 sq. mi (77,474 sq. km) is land area and 0 sq. mi (0 sq. km) is the water area.
The Republic of Serbia’s total land boundary is 1442.8 mi (2,322 km) long. It shares its border with Romania 330 mi (531 km) to the northeast, Kosovo 227.4 mi (366 km), Bosnia and Herzegovina 214.3 mi (345 km) to the west, Bulgaria 213.7 mi (344 km) to the southeast, Croatia 195 mi (314 km) to the west, Hungary 102 mi (164 km) to the north, Montenegro 97.5 mi (157 km) to the southwest, and North Macedonia 62.7 mi (101 km) to the south. Serbia has no coastline.
The mean elevation of Serbia is 1450.13 ft (442 m). While the highest point is Midzor at 7116.1 ft (2,169 m), the lowest point is the Danube and Timok Rivers at 114.8 ft (35 m).
Serbia has an extremely varied terrain. You will find rich fertile plains in the northern parts of the country, limestone ranges and basins in the eastern regions, and ancient mountains and hills in the southeast section.
There are several mountain ranges present in Serbia. They are Dinaric Alps in the southwest, Rila-Rhodope Mountains’ northwestern corner in the southeast, Srednogorie mountain chain system’s easternmost section in the east, Balkan Mountains in the east, and the Carpathian Mountains in the northeast.
The highest peaks (mountains) in Serbia are Midžor (Stara planina), Pogled (Mokra Gora), Dupljak (Stara planina), Pančić’s Peak (Kopaonik), Suvo Rudište (Kopaonik), etc.
Major rivers of Serbia are Danube, Tisa, Velika Morava (Great Morava), Drina, and many more. Famous lakes include Đerdap, Đerdap II, Vlasina Lake, Ečka fish pond, Perućac Lake, Gazivoda Lake, Zasavica, Carska bara, and others.
What is the Climate of Serbia?
The climate in Serbia varies as you move from the north to the south. While northern Serbia has a continental climate, southern Serbia experiences a more Mediterranean climate.
The continental climate in the northern part of the country is characterized by cold and dry winters and warm and humid summers. The more Mediterranean climate in southern Serbia experiences hot and dry summers & autumns and relatively colder and rainier winters. Heavy snowfall takes place in the mountains.
Climatic changes happen because of 3 factors: elevation, winds, and proximity to the Adriatic Sea, Aegean Sea, and large river basins. The great air masses shape the climatic profile of northern Serbia from Northern and Western Europe. Strong Mediterranean currents influences affect the climatic conditions of South and Southeast Serbia.
The presence of mountain ranges, especially the Dinaric Alps, cools down a large part of the warm air masses. As the mountains encircle the Raška (region), winters are quite harsh.
Throughout southern Serbia, Mediterranean micro-regions exist. Some of the most important ones are the Pčinja District around the valley, Zlatibor, and river Pčinja.
The average annual temperature as per altitude varies.
- The average yearly temperature up to an altitude of up to 300 m (984 ft) hovers around 52.9 °F (11.6 °C).
- The average yearly temperature at altitude in the 300-500 m (984-1,640 ft) altitude range hovers around 51.8 °F (11.0 °C).
- The average yearly temperature at altitude over 1,000 m (3,281 ft) altitude hovers around 45.5 °F (7.5 °C).
In Serbia, the lowest temperature is −24.5 °F (−31.4 °C) in Pešter’s Karajukića Bunari (recorded on January 26, 2006) and the highest recorded temperature is 113.4 °F (45.2 °C) in Leskovac (recorded on July 24, 2007).
What is the Economy of Serbia?
The economy of Serbia is an upper-middle-income economy, which is primarily dependent upon the services sector. The tertiary sector accounts for 2/3rd of the Serbian GDP.
The main pillars of the Serbian economy are the automotive industry, energy, mining, machinery, and agriculture. Belgrade (the capital of Serbia) and Novi Sad are the country’s most important economic hubs.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Serbia increased by 4.187% to US$51.409 billion. The economy is primarily based on free-market principles. Serbia’s export and import values in 2018 were US$19.7 billion and US$26.6 billion, respectively. It has a negative trade balance of -US$6.94 billion in 2018.
Major export items are Insulated Wire, Cars, Rubber Tires, Hot-Rolled Iron, and Electric Motors. Significant imports of Serbia are Crude Petroleum, Packaged Medicaments, Cars, Petroleum Gas, and Refined Petroleum.
The unemployment rate in this Southeast European country has dropped significantly from 24% in 2012 to 12.69% in 2019. Data from the National Statistical Office of Serbia (RZS) shows that 25.7% of Serbia’s population lived below the poverty line in 2017. 50.6% of the unemployed persons in Serbia are poor.
What is the Transportation System of Serbia?
Serbia has 26 airports. While ten have paved runways, 16 have unpaved runways. The major airports of Serbia are Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport (Belgrade), Niš Constantine the Great Airport (Niš), Morava Airport (Kraljevo), etc. two heliports are also there in the country.
There is 27,494.4 mi (44,248 km) long roadways available, out of which 17398.4 mi (28,000 km) are paved and 10,096 mi (16,248 km) are unpaved. 2366.8 mi (3,809 km) long standard-gauge railway tracks are there in Serbia.
Waterways are around 364.7 mi (587 km) long (concentrated mainly on the Danube and Sava Rivers). Belgrade (Danube) is the principal river port.
What International Organizations is Serbia Part of?
IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, BIS, BSEC, CD, CE, CEI, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, G-9, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO ICCT, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MONUSCO, NSG, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, SELEC, UNCTAD, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), EU (candidate country), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), NAM (observer), OIF (observer), OAS (observer).
Related Links: