What are the Key Facts of São Tomé and Príncipe?
|
Official Name |
Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
São Tomé. |
|
Largest City |
São Tomé |
|
Coordinates |
1.000000, 7.000000 |
|
Area |
386 sq. mi ( 1,001 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi (0 km) |
|
Coastline |
130 mi ( 209 km) |
|
Currency |
Dobra (STN) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
No land neighbours |
|
Population |
199,910 (2016 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Portuguese |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
12 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Independencia total” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary semipresidential republic |
|
President |
Manuel Pinto da Costa |
|
Prime Minister |
Jorge Bom Jesus |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 3,412.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 2,001.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.589 (2017), Rank: 143 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+239 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+0 (GMT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.st |
Where is São Tomé and Príncipe?
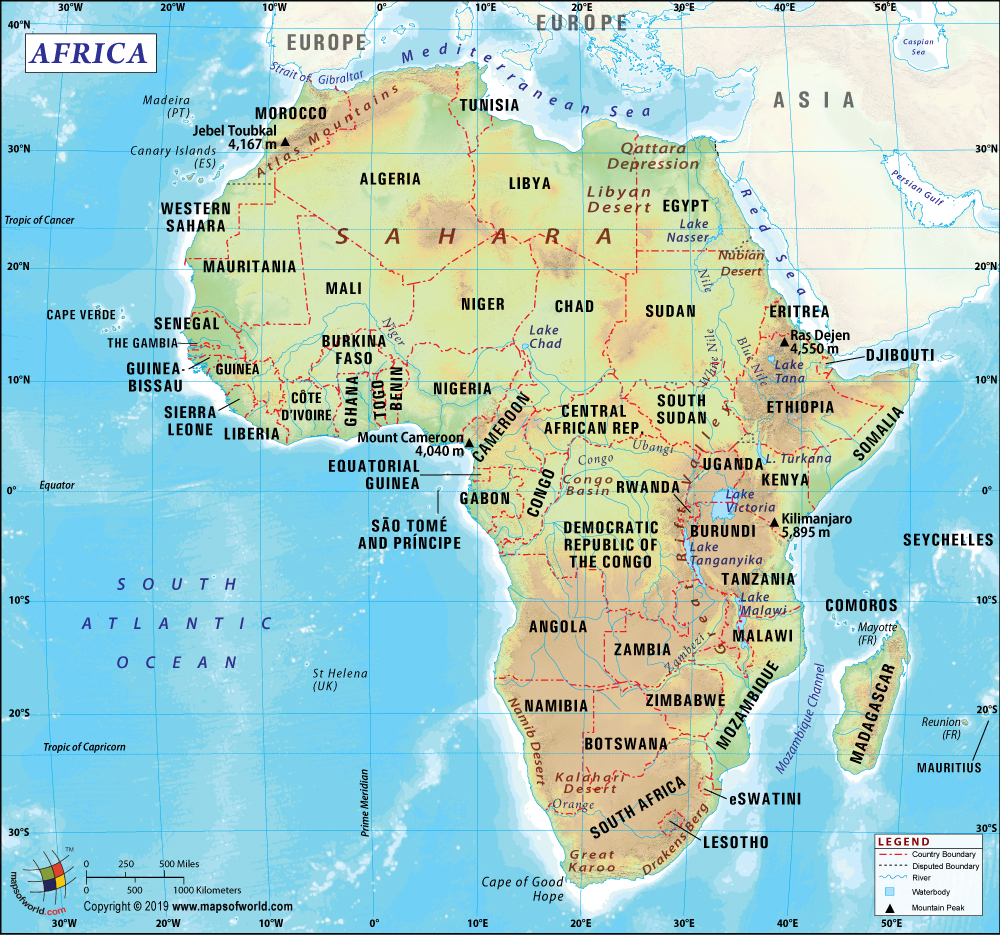
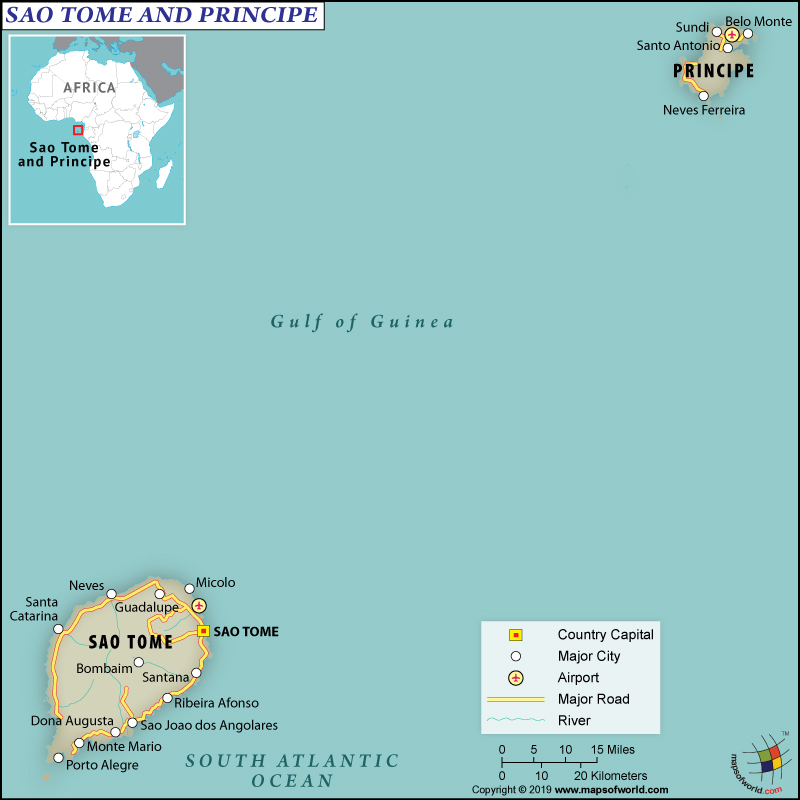
São Tomé and Príncipe is an island country consisting of two archipelagos around the São Tomé Island and Príncipe Island. Both of these islands are located around 140 km (87 miles) away from each other, in the north of the Equator and in the Gulf of Guinea. São Tomé and Príncipe islands are located around 250 km (155 miles) and 225 km (140 miles) away respectively off the northwestern coast of Gabon in the African continent.
What is the Geography of São Tomé and Príncipe?
São Tomé and Príncipe are spread across a total area of 964 sq. km (372 sq. miles). It is therefore the second smallest African country. Both the main islands of this country are mountainous and are a part of a chain of extinct volcanoes. They are part of the line of Cameroon volcanic mountain that includes Bioko to the northeast, Annobón to the southwest, and Mount Cameroon on the Gulf of Guinea coast. The total coastline of São Tomé and Príncipe is 209 km (130 miles).
São Tomé is more mountainous than Príncipe. While it is 50 km (30 miles) long and 30 km (20 miles) wide, Príncipe is around 30 km (20 miles) long and 6 km (4 miles) wide. While the highest peak of São Tomé is Pico de São Tomé (948 m or 3,110 feet high), Príncipe’s highest peak is Pico de Príncipe (948 m or 3,110 feet high). Atlantic Ocean (0 m) is the lowest point of the country.
The Pico Cão Grande or the Great Dog Peak, located in the southern São Tomé is a landmark volcanic plug peak. Above the surrounding terrain, it rises more than 300 m (1,000 feet). The summit is located 663 meters or 2,175 feet above sea level. Other major mountains in these islands are Pico Ana Chaves, Pico Kabumbe, Pico Mencorne, Pico Maria Fernandes, Pico Papagaio, Pico Cão Pequeno, and many more.
Both of the islands have mountains with swift streams running down to the croplands and lush forests. Major rivers of São Tomé and Príncipe are Io Grande, the Manuel Jorge, the Abade, Rio d’Ouro, Rio Papagaio, and others.
The climate is tropical at sea level. Daily variation of temperature is very little. The days are hot as well as humid. Average yearly temperature generally revolves within 27 °C (80.6 °F) and 32 °C (89.6 °F). However, at the higher elevations of the island’s interior, the average yearly temperature revolves around 20 °C (68 °F). Generally, the nights remain cool. October-to-May is the rainy season. On the southwestern slopes, the yearly rainfall level revolves around 5,000 mm (196.9 in). However, the same in the northern lowlands revolve around 1,000 mm (39.4 in).
What is the Economy of São Tomé and Príncipe?
São Tomé and Príncipe (STP) is categorized as a lower middle-income developing economy. This small island state has a fragile economy, which is highly vulnerable to exogenous shocks.
The economy of STP is mainly dependent on agricultural produce. Main growth factors of the economy are government expenditure (either through government borrowing or external aid), oil-fueled FDI, and tourism. It is increasingly getting dependent on cocoa beans export. However, mismanagement and drought have led to a substantial decline in the production of cocoa. The country exports around 80% of the total cocoa produced.
São Tomé and Príncipe are heavily dependent on imports of fuels, food, and consumer goods. The inflation rate of the economy is affected by the commodity price changes. The government is trying hard to reduce the controls on price as well as subsidies. For improving the business climate of the island, several laws related to business have been enacted.
The nominal GDP of the country grew at a rate of 4.5% between 2009-2017 and stood at US$422.29 million in December 2018. Additionally, in 2018, the economy was majorly impacted by an energy crisis. The unemployment rate of the economy was 12.2% in 2017. 66.2% of the total population lives in poverty. As this island country has 97% primary school enrolment and 69% literate population, its prospects are high in the coming years. However, due to the small population of 200,000 being scattered over a fragmented area, the cost of providing public goods and services is high.
What is the Transportation System of São Tomé and Príncipe?
São Tomé and Príncipe’s transportation system includes two paved airports, 15 merchant marine ships (12 general cargo and 3 others), and one major seaport (Sao Tome).
What International Organizations is São Tomé and Príncipe Part Of?
UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, ACP, WHO, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CD, Union Latina, CEMAC, CPLP, FAO, G-77, NAM, IBRD, Interpol, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IOC, IPU, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, IOM (observer), WTO (observer), EITI (candidate country)