What are the Key Facts of Papua New Guinea?
|
Official Name |
Independent State of Papua New Guinea |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Port Moresby |
|
Largest City |
Port Moresby |
|
Coordinates |
-6.369750, 144.069022 |
|
Area |
178,700 sq. mi ( 462,840 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
512 mi ( 824 km) |
|
Coastline |
3,201 mi ( 5,152 km) |
|
Currency |
Papua New Guinean kina (PGK) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Indonesia Maritime neighbors: Australia, Solomon Islands |
|
Population |
8,084,999 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
English, Hiri Motu, Tok Pisin |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
16 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“O Arise All You Sons” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Elizabeth II |
|
Prime Minister |
James Marape |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 4,298.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 2,722.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.544 (2017), Rank: 153 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
131 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+675 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+10:00, +11:00 (AEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.pg |
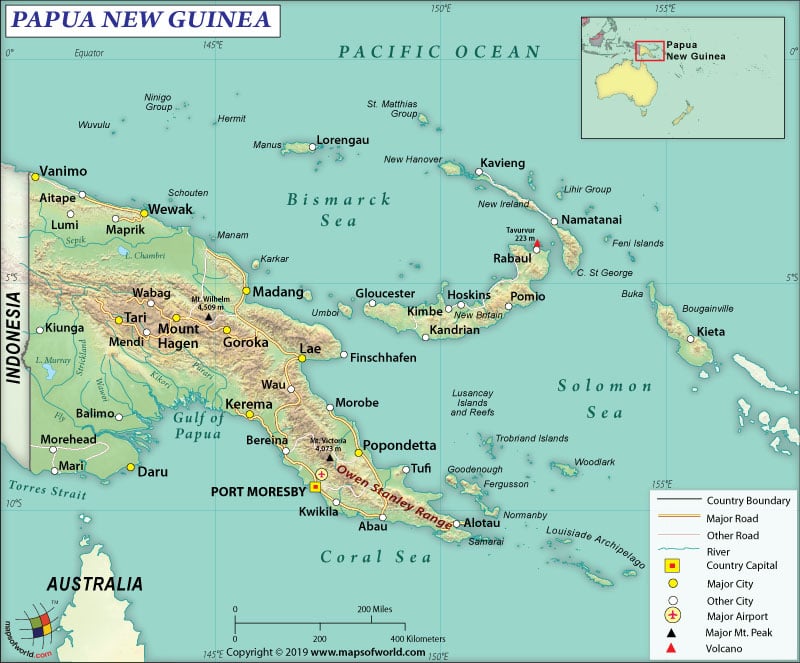
Where is Papua New Guinea?
Papua New Guinea is part of Oceania and is located between the South Pacific Ocean and the Coral Sea. It is situated to the north of Australia and east of Indonesia.
What is the Geography of Papua New Guinea?
The total area of the country is 462,840 sq. km (178,700 sq. mi), out of which 452,860 sq. km (174,850 sq. mi) is land area and 9,980 sq. km (3,853 sq. mi) is water area. It has 824 km (512 mi) long land boundary, which is entirely shared with Indonesia. The coastline is 5,152 km (3,201 mi) long.
Papua New Guinea occupies the eastern part of New Guinea, which is a West Pacific Island. Papua New Guinea also includes many smaller islands such as New Ireland, New Britain, and the Autonomous Region of Bougainville. Around 600 additional smaller islands/atolls are also part of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
The terrain of Papua New Guinea mainly contains mountains. However, it also has rolling hills and coastal lowlands. The mean elevation of the country is 667 m (2,188 ft). While Mount Wilhelm at 4,509 m (14,793 ft) is the highest elevation point of the country, the Pacific Ocean at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point.
As the country is located along the Pacific Ring of Fire, there are several volcanoes. In fact, that’s the reason why Papua New Guinea is also prone to both tsunamis and earthquakes. Some of the main rivers are the Sepik River and the Fly River. Some of the major mountains here are Wilhelm, Giluwe, Bangeta, Victoria, Albert Edward, and many more.
The climatic condition of Papua New Guinea can be described as tropical. The average temperature in the coastal plains, inland/mountain areas, and higher mountain regions are 28 °C (82.4 °F), 26 °C (78.8 °F), and 24 °C (75.2 °F) respectively. The relative humidity of the country remains pretty high, ranging within 70-90%.
Though temperature and air pressure remain the same across the year, extreme variations are seen in case of rainfall. While June-September is the dry season, December-March is the rainy season. Most precipitation takes place in the northern and western parts of Papua New Guinea. December-mid-March is the time when typhoons hit the country every year.
What is the Economy of Papua New Guinea?
Papua New Guinea (PNG) is endowed with natural resources such as copper, oil, natural gas, and gold. The economy is mainly dependent upon the export of these natural resources. Export of copper, oil, and gold account for around 2/3rd of the export earnings. It has a small formal sector. Most of the population is employed in the informal sector, mainly agriculture, fishing, and forestry. Around 87% of the inhabitants of the country live in rural areas.
The nominal GDP grew at a rate of 3.6% in the last two decades. In 2018, it increased at a rate of 0.43% to become a US$23.432 billion economy. Since mid-2000, the real GDP per capita increased at an average of 4% consistently.
In 2017, PNG had a US$5.35 billion positive trade balance. The country exported US$8.9 billion of items and imported US$3.55 billion of items. The major export items are copper ore, gold, petroleum gas, crude petroleum, and rough wood. The items mostly imported by Papua New Guinea are refined petroleum, excavation machinery, delivery trucks, broadcasting equipment, and crude petroleum.
The unemployment rate in the country was 2.40% in 2018. During 1991-2018, it averaged 2.58%. Around 37.5% of the PNG population was below the National Poverty Line in 2017, thereby making it one of the poorest countries in the Pacific region. The country has severe rural poverty.
What is the Transportation System of Papua New Guinea?
As PNG has highly mountainous terrain, the transportation system is very limited. That’s why air travel has come up as the most important form of transport for carrying both passenger and freight. There are 561 airports in this country. While 21 of them have paved runways, 540 have unpaved runways. There are two heliports too in Papua New Guinea. Jacksons International Airport is the main airport of the country.
There is around 9,349 km (5,809 mi) long roadway available, out of which 3,000 km (1,864 mi) is paved and 6,349 km (3,945 mi) is unpaved. Highlands Highway, linking the Highlands region with Lae and Madang is the longest road in PNG. Kiunga-Tabubil, Boluminski Highway, and Wewak-Vanimo highways are the other main highways.
Papua New Guinea has around 11,000 km (6,835 mi) of waterways. The main seaports are Wewak, Rabaul, Madang, Lae, and Kimbe. 173 merchant marine ships are there in PNG.
What International Organizations is Papua New Guinea part of?
UN, WHO, WTO, IMF, UNESCO, ACP, ADB, AOSIS, APEC, ARF, C, CD, CP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, EITI (candidate country), WFTU (NGOs), ISO (correspondent), ASEAN (observer)

