What are the Key Facts of Oman?
|
Official Name |
Sultanate of Oman |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Muscat |
|
Largest City |
Muscat |
|
Coordinates |
21.000000, 57.000000 |
|
Area |
119,500 sq. mi ( 309,500 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
970 mi (1,561 km) |
|
Coastline |
1300 mi ( 2,092 km) |
|
Currency |
Rial (OMR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
U.A.E, Yemen, Saudi Arabia |
|
Population |
4,829,473 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
18 November (National Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Nashid as-Salaam as-Sultani” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary absolute monarchy |
|
Sultan |
Haitham Bin Tariq |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 41,434.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 16,418.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.821 (2017), Rank: 48 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
95.65 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
29 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code+ |
+968 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+4 (GST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.om |
Where is Oman?
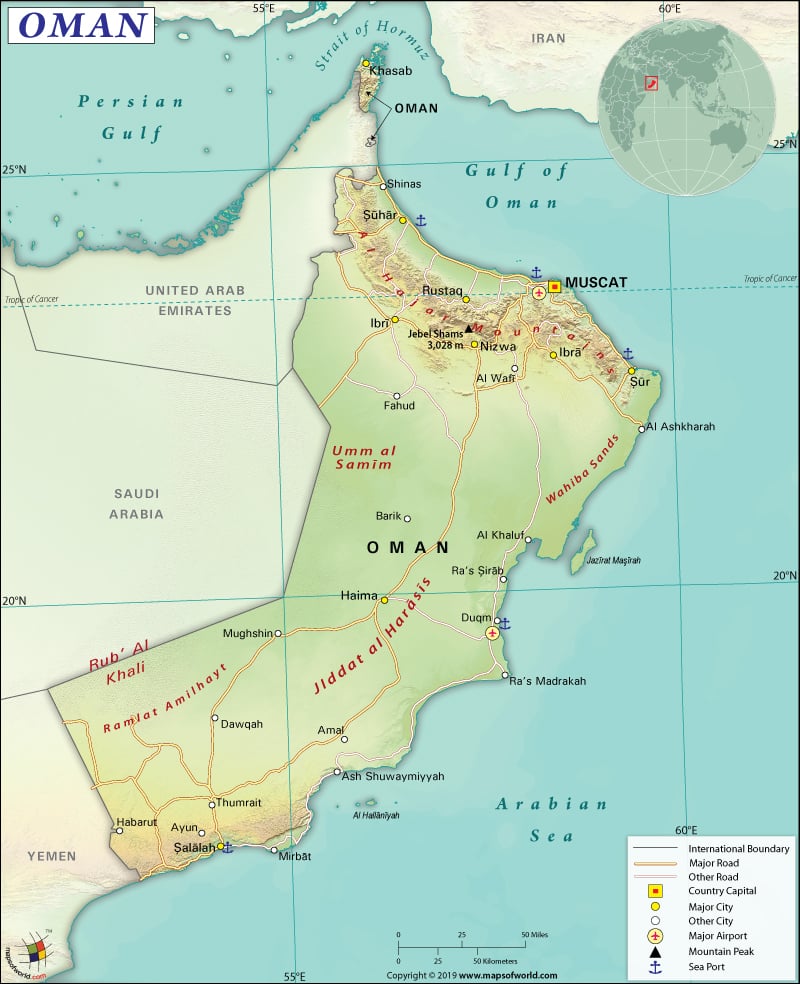
Oman is a west Asian country that borders the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Oman (on the northeast), and the Arabian Sea (on the southeast). The Sultanate of Oman shares its land boundary with UAE to the northwest, Yemen to the southwest, and Saudi Arabia to the west.
What is the Geography of Oman?
The total land area of Oman is 309,500 sq. km (119,500 sq. mi), out of which 309,500 sq. km (119,499 sq. mi),) is land area and 0 sq. km (0 sq. mi) is water area. Oman has a 1,561 km (970 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with three countries: Saudi Arabia (658 km or 409 mi), UAE (609 km or 378 mi), Yemen (294 km or 183 mi). The country also has a coastline of 2,092 km (1,300 mi).
A strip of land belonging to UAE separates Oman’s northernmost part from the Musandam Peninsula. Low hills and mountains are mostly located there.
A narrow and fertile coastal plain in the northern part of the company is located in front of the Gulf of Oman. The land starts rising from this region and goes on to the rugged Hajar Mountains. Both the coastal area and the desert landscape in the central and southeastern regions of the country have some low mountains and scrubby hills. The west of Oman has land slopes that are similar to deserts and are pebbly in nature. This slope of land goes gently into the Rub’ Al Khali Desert’s sands.
The major mountains in Oman are Jabal Shams, Qarn al Ḩammām, Ra’s al Ḩaraq, Jabal Ghubrah, Ra’s al Kabūl, etc. The mean elevation of the country is 310 m (1,017 ft). While Jabal Shams at 3,004 m (9,856 ft) is the highest elevation point, the lowest elevation point is the Arabian Sea at 0 m (0 ft). No noteworthy rivers or lakes are there.
Oman’s climate is a subtropical dry, hot desert climate. It gets low annual rainfall and the summertime has very high temperatures. There is a huge difference in the maximum and minimum temperatures, especially in the inland regions.
June to September is the summertime in Oman. Very low rainfall takes place during this time. During summer, the daily maximum temperature can easily reach 40 °C (104 °F) or even more. Wintertime remains cooler. However, rainfall takes place occasionally. Pleasant weather prevails mostly during autumn and spring. The weather mostly remains dry and warm. The maximum temperature varies within 25-35 °C (77-95 °F). Nighttime remains cooler with temperature varying within 15-22 °C (59-71.6 °F).
Both during summer and spring (March-August), a hot and dust-laden wind (called Shamal) blows. Sometimes these winds can become extremely strong and can also take the form of the sandstorms. In winter, the rainfalls mainly take place suddenly. They take place in short spells. However, they mainly take place in the form of thunderstorms and cloudbursts.
What is the Economy of Oman?
The economy of Oman is mainly dependent upon oil and gas resources. The oil industry contributes to around 68-85% of the government revenue. Low global oil prices have adversely affected the economy but the government has started using enhanced oil recovery techniques for boosting production.
Oman is now stressing on diversification of the economy. The industries on which it is stressing are tourism, aquaculture, manufacturing, mining, logistics, and shipping. In Oman, tourism is the fastest growing industry currently.
The World Bank data shows that the nominal GDP of Oman has increased by 2.125% to reach a figure of US$ 79.295 billion. The main exports are crude/refined petroleum, petroleum gas, acyclic alcohols, iron ore, etc. The main imports are cars, helicopters, planes, spacecraft, gas turbines, gold, refined petroleum, etc. In 2018, the export value was US$31.2 billion and the import value was US$29.8 billion, resulting in a positive balance of trade of US$1.34 billion.
The unemployment rate in Oman was 3.11% in 2018. Lack of economic diversification, unemployment, and underpayment are the main reasons for poverty in the country despite the fact that it has large reserves of oil. However, due to good work from the government, the rate of poverty has fallen significantly in the last decade.
What is the Transportation System of Oman?
The major transportation system in Oman developed post-1970. The transportation is mainly dependent upon highway network, two international airports, two modern deepwater ports, and an oil port. All significant populated places have a modern transportation system.
Oman has 60,230 km (37,425 mi) long roadways, out of which 29,685 km (18,445 mi) is paved and 30,545 km (18,980 mi) unpaved. There are 132 airports in the country, out of which only 13 have paved runways and the rest 119 have unpaved runways. 3 heliports are also there. Some of the major airports in the country are Muscat International Airport, Salalah International Airport, Khasab Airport, Duqm Jaaluni Airport, etc.
The major seaports in Oman are Suhar, Salalah, and Mina’ Qabus. While Qalhat is a major LNG terminal, Salalah is a major container port. 51 merchant marine ships are there in Oman.
What International Organizations is Oman part of?
WTO, UN, NAM, IMF, ILO, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, OIC, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)