What are the Key Facts of Norway?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Norway |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Oslo |
|
Largest City |
Oslo |
|
Coordinates |
62.000000, 10.000000 |
|
Area |
125,020 sq. mi (323,802 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,594 mi (2,566 km) |
|
Coastline |
62,705 mi (100,915 km) (including mainland and islands) |
|
Currency |
Norwegian krone (NOK) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Finland, Russia, Sweden. Maritime neighbors: Denmark, Iceland, United Kingdom |
|
Population |
5,348,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Bokmal Norwegian, Nynorsk Norwegian |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
17 May (Constitution Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Ja, vi elsker dette landet” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Harald V |
|
Prime Minister |
Erna Solberg |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 66,831.9 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 75,419.6 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.954 (2019), Rank: 1 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Norwegian Space Agency |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
30 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
520 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
47 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST)UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.no |
Where is Norway?
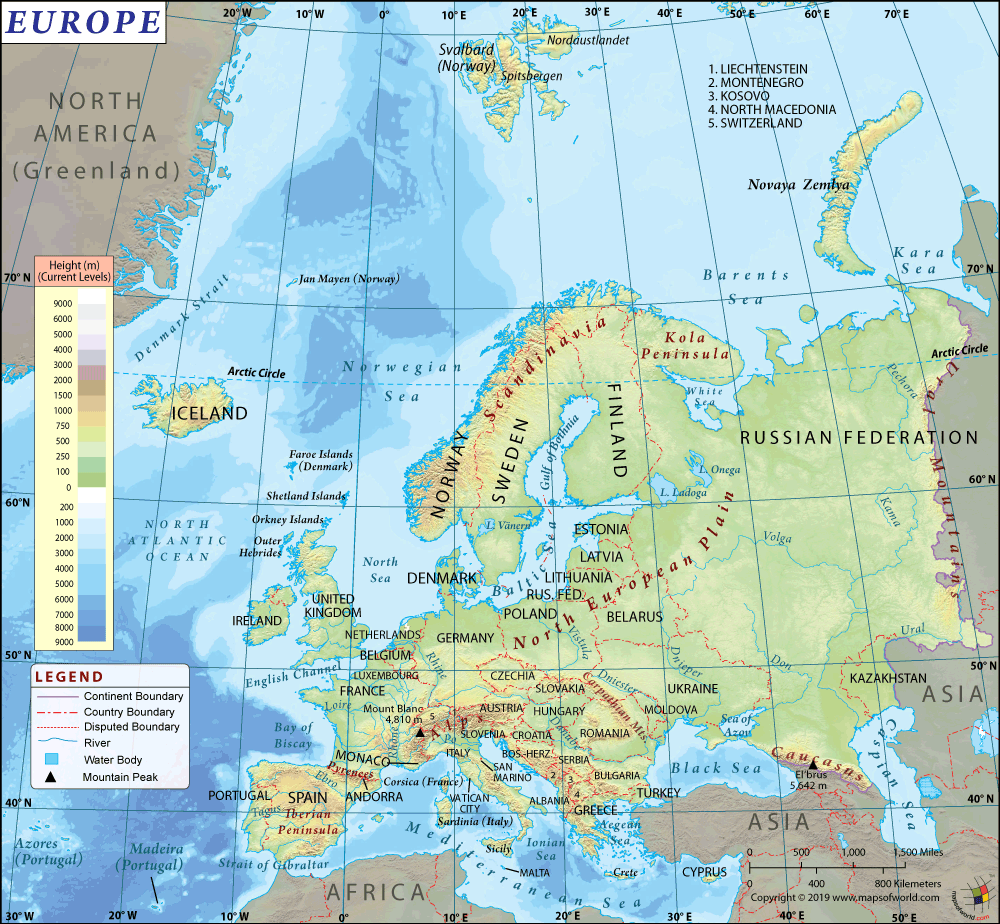
Norway (whose official name is the Kingdom of Norway) is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. While the mainland territory includes the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Norway also consists of the remote island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard.
What is the Geography of Norway?
Norway spreads across a total area of 125,020 sq. mi (323,802 sq. km). Out of the total area, 117,484 sq. mi (304,282 sq. km) is land area and 7,537 sq. mi (19,520 sq. km) is the water area.
The Kingdom of Norway’s total land boundary is 7,808.2 mi (2,566 km) long. It shares its border with Sweden 1035.2 mi (1666 km) to the east, Finland (440.6 mi or 709 km) to the north-east, and Russia (118.7 mi or 191 km) to the north-east.
Norway has a 15,626.2 mi (25,148 km) long coastline (including 1,646.6 mi or 2,650 km coastline of mainland and 13,979.6 mi or 22,498 km coastline of fjords, numerous small islands, and minor indentations).
The mean elevation of Norway is 1509.2 ft (460 m). While the highest point is Galdhopiggen at 8100.4 ft (2,469 m), the lowest point is the Norwegian sea at 0 ft (0 m).
The terrain of Norway is glaciated, consisting mostly of high plateaus and rugged mountains, which are broken by fertile valleys. There are also small, scattered plains located in the country. Fjords have deeply indented the coastline. Arctic tundra is present in the northern part of the country.
The highest mountains in Norway are Galdhøpiggen, Glittertind, Store Skagastølstinden, etc. Major rivers of Norway are Glomma, Pasvikelva and Ivalo, Numedalslågen, Gudbrandsdalslågen and Vorma, etc. Famous lakes include Mjøsa, Røssvatnet, Femund, Randsfjorden, etc.
What is the Climate of Norway?
Norway has a milder climate than any other region in the north, especially along the western coast. Even when snow falls, they melt immediately. Almost all the seaports (even the ones in the northern regions) in the country remain ice-free, thanks to the warm North Atlantic Current of the Gulf Stream.
As per Koeppen-Geiger classification, there are three climatic conditions in Norway:
- Southern Norway has a warm temperate humid climate (a Cfb Climate). The average temperature in the warmest month is lower than 71.6 °F (22 °C) over average. For four or more months, the temperature remains above 50 °F (10 °C) over average.
- Mid and northern regions of Norway has a humid Snow Climate (a Dfc Climate) where the temperature remains above 50 °F (10 °C) over the average for less than four months.
- The northern coastal areas and the mountainous regions in Norway have an Ice climate (an E Climate) where the temperature remains below 50 °F (10°C) in the warmest month.
As the mountains block the warm west winds from the sea, the inland regions of Norway remain colder than the coast during winter. For at least 3-months, the ground stays covered by snow.
When the sea remains cooler than the land during summer, the west winds cool the coast more than the inland. That’s why the southeast Norway’s inland valleys get the warmest summers. The average temperature varies from 14 °F (-10 °C) in January (in Spitzbergen) to 60.8 °F (16 °C) in July (in Oslo).
The level of precipitation in Norway varies from 19.69 inches (500 mm) to 118.1 inches (3000 mm) per year. While the coastal areas get most rainfall, the Inland areas and eastern Norway get less rain.
As Northern Norway is in the Land of the Midnight Sun, it gets continuous daylight during part of the summer. As you go farther north in Norway, the number of days of constant daylight increases. The sun remains above the horizon for around 2.5 months in northernmost Norway. Daylight doesn’t remain continuously in Southern Norway. On average, it gets 19 hours of sunlight per day during midsummer.
During winter, northernmost areas of Norway get periods of continuous darkness for around 2-months. However, Southern Norway doesn’t get constant darkness during winter. It gets around 6-hours of daylight per day in mid-winter. Aurora Borealis or northern lights (a brilliant display of lights) are a common sight in the sky during winter nights.
What is the Economy of Norway?
The economy of Norway is characterized by the presence of a large public sector, well supported by a vibrant private sector, and the provision of an extensive social safety net.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Norway increased by 1.155%, and it grew to US$403.336 billion. It has a stable economy. Norway’s export and import value in 2018 were US$127 billion and US$89.5 billion, respectively. It has a positive trade balance of US$37.8 billion.
Major export items are Petroleum Gas, Crude Petroleum, Refined Petroleum, Non-fillet Fresh Fish, and Raw Aluminum. It is the 2nd largest exporter of seafood. Significant imports of Norway are Cars, Refined Petroleum, Special Purpose Ships, Broadcasting Equipment, and Passenger and Cargo Ships. The petroleum sector accounts for around 37% of exports, 13% of Norway’s revenue, 12% of GDP, and 9% of jobs.
The unemployment rate in this Nordic country has shot up from 3.4% before COVID-19 pandemic to 13.2% as of June 23, 2020. As per OECD data, the poverty rate in Norway was 0.084% in 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Norway?
Norway has 95 airports. While 67 are paved, 28 are unpaved. The major airports are Oslo Airport (Gardermoen), Bergen Airport (Flesland), Trondheim Airport (Værnes), etc.
There is 58969.4 mi (94,902 km) long roadways available, out of which 282.7 mi (455 km) are expressways. 2609.8 mi (4,200 km) long standard-gauge railway tracks are there in Norway. Waterways are around 979.9 mi (1,577 km) long. Major seaports are Bergen, Sture, Narvik, Maaloy, Haugesund, and Mongstad.
What International Organizations is Norway part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, ILO, Paris Club, NSG, UNESCO, Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, EFTA, ESA, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINUSMA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), EITI (implementing country), ICC (national committees), IGAD (partners), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer)
Related Link: