What are the Key Facts of Nepal?
|
Official Name |
Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Kathmandu |
|
Largest City |
Kathmandu |
|
Coordinates |
28.000000, 84.000000 |
|
Area |
56,827 sq. mi (147,181 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,963 mi (3,159 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi (0 km) Landlocked |
|
Currency |
Nepalese rupee (Rs, रू) (NPR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
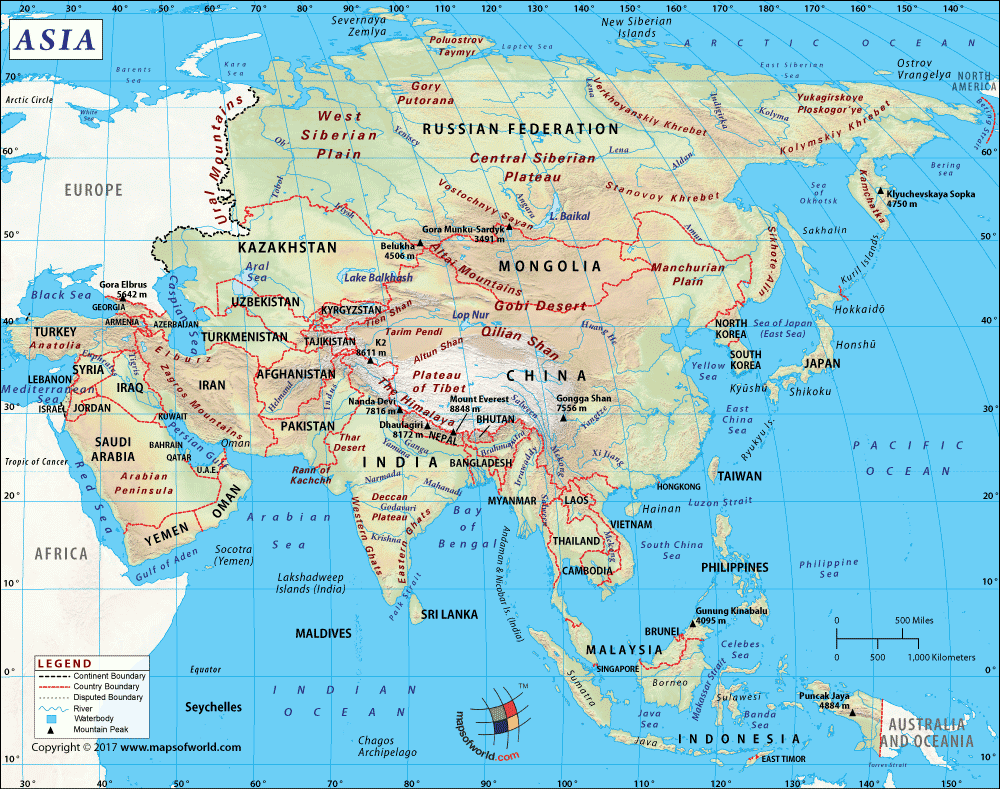
India, China |
|
Population |
28,609,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Nepali |
|
Major Religion |
Hindu |
|
National Day |
20 September (Constitution Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Sayaun Thunga Phool Ka” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Bidhya Devi Bhandari |
|
Prime Minister |
Khadga Prasad Sharma Oli |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 3,558.4 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,071.1 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.579 (2019), Rank: 147 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
67.91 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
90 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
977 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+05:45 (Nepal Standard Time) |
|
Internet TLD |
.np |
Where is Nepal?
Nepal (whose official name is the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal) is a South Asian country that is located mainly in the Himalayas but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It is a landlocked nation that lies in the Indian subcontinent between India and China.
What is the Geography of Nepal?
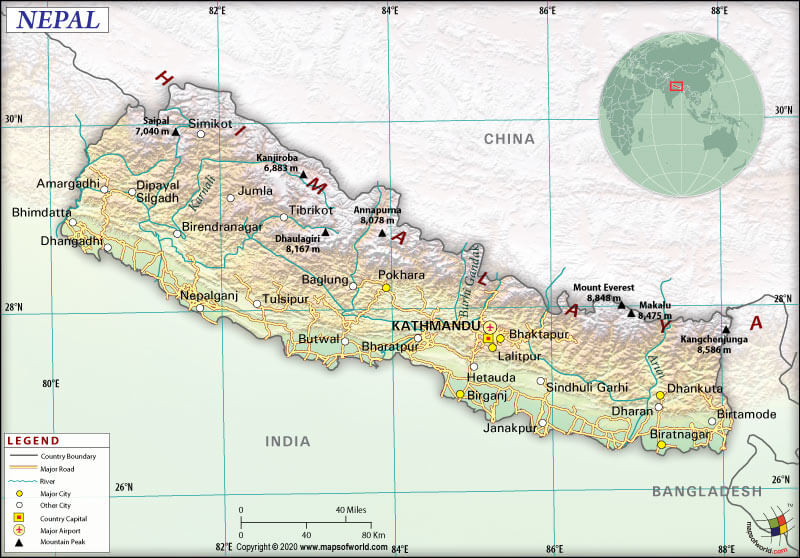
Nepal spreads across a total area of 147,181 sq. km (56,827 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 143,351 sq. km (55,348 sq. mi) is land area and 3,830 sq. km (1,480 sq. mi) is the water area.
The Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal’s total land boundary is 3,159 km (1,962.9 mi) long. This landlocked country shares its border with India (1,770 km or 1,099.8 mi) in the south, east, and west, and China (1,389 km or 863 mi) in the north. Nepal doesn’t have any coastline.
The narrow Siliguri Corridor or Chicken’s Neck (just 27 km or 17 mi) in West Bengal separates Nepal and Bangladesh. The Indian state of Sikkim separates Nepal from Bhutan.
The mean elevation of the country is 2,565 m (8,415.4 ft). While the highest point is Mount Everest at 8,848 m (29,028.9 ft), the lowest point is Kanchan Kalan at 2,670 m (229.7 ft).
The terrains of Nepal include rugged Himalayas (called “himal”) in the north, flat river plain (called “tarai” or “terai”) in the south, and hill region (called “pahad”) in the central part of the country. Nepal has a trapezoidal shape. It is around 800 km (500 mi) in length and 200 km (120 mi) in width.
From east-to-west, the country has three major river systems: Koshi, Gandaki/Narayani, and Karnali (tributaries of the Ganges River). Along the Nepal-Tibet border, the Ganges-Yarlung Zangbo/Brahmaputra watershed is present.
The tall mountains of the country are Mount Everest (Khumbu Mahalangur), Kanchenjunga (Northern Kanchenjunga), Lhotse (Everest Group), Makalu (Makalu Mahalangur), Cho Oyu (Khumbu Mahalangur), Dhaulagiri I (Dhaulagiri), Manaslu (Mansiri), and Annapurna I (Annapurna).
Major rivers in the country are Ghaghara (Karnali), Koshi, Gandaki, West Rapti, and Bagmati. Famous lakes of Nepal are Gokyo Lake, Shey-Pokshundo Lake, Panch Pokhari Lake, Rara Lake, Gosaikunda Lake, and Tilicho Lake.
What is the Climate of Nepal?
Varied climatic conditions are found in the country, depending upon the location, altitude, and influence of maritime and continental factors. The average temperature in Nepal drops by 6 °C (42.8 °F) with every 1,000 m (3,280.8 ft) rise in altitude.
Spring (March-May) remains warm along with occasional rain showers. During the spring season, the temperature hovers around 22 °C (71.6 °F).
Summer (June-August) is also the monsoon season in Nepal, turning the hills lush green. During heat waves, the temperature can reach up to 30 °C (86 °F).
Autumn (September-November) remains predominantly cold, and the sky remains clear. It is the most popular season for trekking in Nepal. Daily maxima hover around 25 °C (77 °F) and the night’s stay cool with minima of 10 °C (50 °F). It rains for a maximum of one- or two-days during autumn in Nepal.
Winter (November-February) remains cold at night, and the temperature may sometimes dip below 0 °C (32 °F). However, the maximum temperature can reach up to 20 °C (68 °F). In some high hills and mountain tops, they get covered with snow in this season.
Autumn and Spring are the best time to visit Nepal. While rhododendrons bloom in Spring, the skies remain clearest during October-November.
The average rainfall in the country is around 1,600 mm (163 inches). Approximately 80% of rain takes place during monsoon (June-September). While Pokhara gets 3,345 mm (131.7 inches), Mustang gets below 300 mm (11.8 inches) of rainfall in a year.
What is the Economy of Nepal?
The country is one of the least developed economies in the world. Around 1/4th of its population lives below the poverty line. Its economy heavily depends on remittance income, which accounts for 30% of the GDP.
Agriculture is still the principal employer in the country. Almost 2/3rd of the population is dependent on the agricultural sector, contributing to less than 1/3rd of their GDP. Industrial activity is limited, revolving around the processing of farm products, such as tobacco, sugarcane, jute, pulses, and grains.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Nepal was US$ 30.641 billion, and the GDP growth rate was 6.99%. The economic condition is strengthening, evident from the increasing GDP growth rate from 0.58% in 2016 to 6.99% in 2019.
The country suffers from a negative trade balance, which was -$ 9.39 billion in 2018. While the export value was $10.1 billion, the import value was $723 million. The major export items of Nepal are Non-Retail Synthetic Staple Fibers Yarn, Knotted Carpets, Flavored Water, Nutmeg, Mace and Cardamoms, and Other Plastic Products. The major import items are Refined Petroleum, Semi-Finished Iron, Planes, Helicopters, and Spacecraft, Gold, and Petroleum Gas.
The unemployment rate in this South Asian country was 1.41% in 2019. It is the 12th poorest country in the world. However, poverty has come down significantly in the last decade. While urban poverty fell from 22% to 10%, rural poverty fell from 43% to 35%. As per the World Bank, the rate of poverty came down from 15% in 2010 to 8% in 2019.
What is the Transportation System of Nepal?
The country has 47 airports, out of which 11 have paved runways, and 36 have unpaved runways. Some of the major airports are Tribhuvan International Airport (Kathmandu), Gautam Buddha International Airport (Siddharthanagar), Tenzing-Hillary Airport Airport (Lukla), Pokhara Airport (Pokhara), Bharatpur Airport (Bharatpur), Biratnagar Airport (Biratnagar), etc.
27,990 km (17,383.2 mi) long roadways are there in Nepal, out of which 11,890 km (7,388.1 mi) are paved and 16,100 km (10,004.1 mi) are unpaved. 59 km (36.7 mi) of narrow-gauge railway tracks are also available.
What International Organizations is Nepal part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, NAM, ADB, BIMSTEC, CD, CP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, OPCW, SAARC, SACEP, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNDOF, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs), ICC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links: