What are the Key Facts of Maryland?
|
State |
Maryland |
|
State Capital |
Annapolis |
|
Largest City |
Baltimore |
|
Coordinates |
39°N 76.7°W |
|
Nickname(s) |
“Old Line State”, “Free State”, “Little America”, “America in Miniature” |
|
Postal Abbreviation |
MD |
|
Area |
12,407 sq. mi (32,133 sq. mi) |
|
Highest Point |
Hoye-Crest, 3,360 ft (1,024 m) |
|
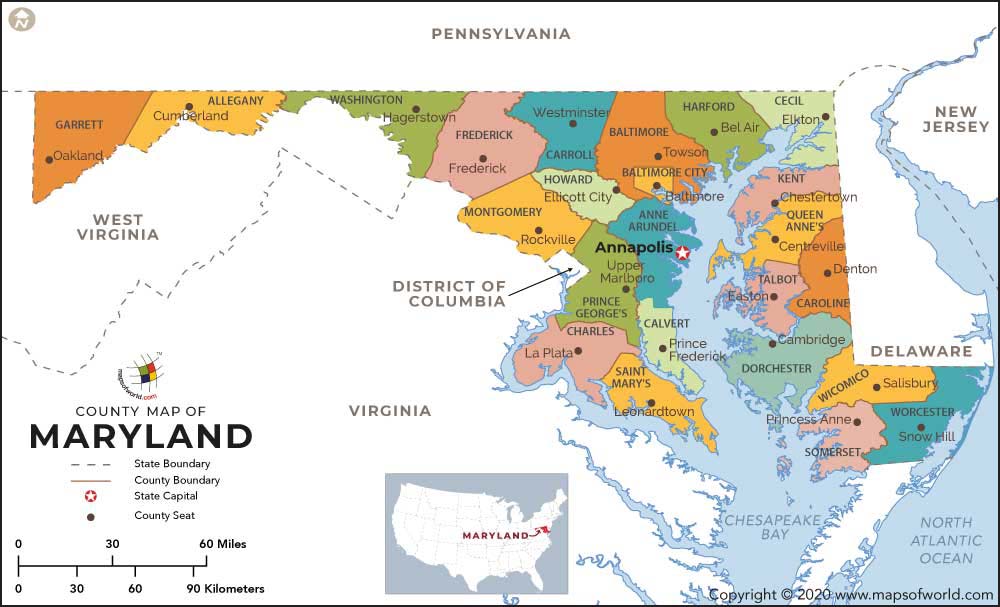
Number of Counties |
23 counties and 1 independent city |
|
Neighboring States |
Virginia, West Virginia, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Washington, D.C |
|
Population |
6,042,718 (2018) |
|
Date of Entering the Union |
April 28, 1788 |
|
State Anthem |
“Maryland, My Maryland” |
|
Governor |
Larry Hogan (Republican) |
|
Lieutenant Governor |
Boyd Rutherford (Republican) |
|
U.S. Senators |
Ben Cardin (Democratic Party), Chris Van Hollen (Democratic Party) |
|
U.S. House Delegation |
6 Democrats, 1 Republican, 1 Vacant |
|
GDP (Millions of Dollars) |
412584 |
|
Demonym |
Marylander |
|
Time Zones |
UTC-05:00 (Eastern), Summer (DST) UTC-04:00 (EDT) |
Where is Maryland?
Maryland (the 7th state admitted to the union on April 28, 1788) is located in the Mid-Atlantic region of eastern USA. Delaware borders this state to the east, Pennsylvania to the north, the District of Columbia to the south and west, West Virginia to the south and west, and Virginia to the south and west. The Atlantic Ocean is located to the east of Maryland.
What is the Geography of Maryland?
Maryland is spread across a total area of 12,407 sq. mi (32,133 sq. km), making it the 42nd largest state out of the 50 states of the United States. Out of the total area, the land area is spread across 9,776 sq. mi (25,314 sq. mi) and the water area occupies 2,633 sq. mi (6,819 sq. km). Water bodies occupy 21.8% of the total area.
Maryland is around 250 mi (402.3 km) long and 90 mi (144.8 km) wide. Its mean elevation is just 350 ft (106.7 m) above sea level. While Hoye-Crest on Backbone Mountain is the highest elevation point of Maryland at 3,360 ft (1,024.1 m) above sea level, the Atlantic Ocean at 0 ft (0 m) is the lowest elevation point.
The significant mountains in the state are Hoye-Crest, Roth Rock, Wild Turkey Rock, Pheasant Ridge, Allegheny Heights, Conneway Hill, Eagle Rock, Marsh Hill, Roman Nose Hill, Roman Nose Mountain, etc. The longest rivers are Susquehanna River, Potomac River, Youghiogheny River, Patuxent River, North Branch Potomac River, Conococheague Creek, Choptank River, etc.
Some of the significant lakes in Maryland are Deep Creek Lake, Liberty Reservoir, Loch Raven Reservoir, Prettyboy Reservoir, Jennings Randolph Lake, Little Seneca Lake, Savage River Reservoir, and Lake Needwood and Lake Frank.
The landscape of Maryland is characterized by five major land areas: Atlantic Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge Region, Appalachian Ridge and Valley, and Appalachian Plateau.
The Atlantic Coastal Plain (also known as Mid-Atlantic Coastal Plain) is located in the stretch from New Jersey to Florida. It is situated around the Gulf of Mexico and to the south of both the Yucatan Peninsula and Mexico. This land region covers this plain’s east shore and a part of the west shore.
The Atlantic Coastal Plain extends from the state’s northeastern tip to south and west across the state to near the Virginia border (Washington, D.C.). The entire plain mainly consists of flat and low land that rises to around 400 ft (121.9 m) on the West Shore. On the east shore of Maryland, marshy areas (including the Pocomoke Swamp) can be found. The west shore is used mainly for growing tobacco.
Piedmont is the second most crucial geographic region in Maryland. It extends southwest from New Jersey to Alabama. From the northeast through central Maryland, the state is around 50 mi (80.5 km) wide. Low rolling landscapes and fertile valleys are the characteristic features of the Piedmont region.
Two ridges extend in the southwest through Maryland, and they are the Dug Hill Ridge (1,200 ft or 365.8 m) and Pars Ridge (880 ft or 268.2 m). The rivers and streams to the west and east of these ridges flow into the Potomac River and the Chesapeake Bay respectively. A creamy dairy farming area is located to the east of these ridges along the Monocacy River, and it is known as Frederick Valley.
The Blue Ridge, the third important geographic region in northern Maryland, is located to the west of Piedmont. It starts from southern Pennsylvania and runs south to the north of Georgia. The region inside Mayland is characterized by a narrow, mountainous section of land that is located near the border of Pennsylvania. Two important mountains situated here are the South Mountain and Catoctin Mountain.
The fourth most important geographical region is the Appalachian Ridge and Valley, which is a northern strip of land separating West Virginia and Pennsylvania. The Great Valley (also called Hagerstown Valley), mainly consisting of orchards and farmland, dominates the eastern part of this geographic location. To the west of this valley, ridges from northeast to southwest are situated. The elevation of this region reaches around 2,000 ft (609.6 m).
The fifth most important region is the Appalachian Plateau, located to the west of the Blue Ridge. It encompasses a triangle of land in the western extreme of the state. The Allegheny Mountains cover most of its area. The highest elevation point of the state (the Backbone Mountain) is situated in the Appalachian Plateau. This region is heavily forested where rivers have cut deep valleys into the plateau.
What is the Climate of Maryland?
The Maryland climate usually comes with hot and humid summers as well as cool winters. Colder and longer winters, as well as more relaxed and shorter summers, are found in the uplands (located in the west) in comparison to the Eastern Shore and other lowlands.
The average temperature in July in western and eastern Maryland hovers around 18°C (65° F) and 24-27 °C (75-80 °F) respectively. The Baltimore region’s average temperature during July hovers with a high of 31 °C or 87 °F and a low of 19 °C or 67 °F.
The average temperature during January ranges within less than -2°C (28° F) in the western part of Maryland to more than 2 °C (35 °F) on the Eastern Shore. The average high and lows during January in Baltimore hover within 5 °C (40 °F) and -5° C (23° F) respectively. The western uplands get very cold winter.
Western Maryland gets more precipitation (including both rainfall and snowfall) than the east. The annual rainfall and snowfall level in the east are around 970 mm (38 in) and in the west is over 1,170 mm (46 in). However, the Hagerstown Valley in the west receives less than 910 mm (36 in) rainfall.
Most of the rainfall (sometimes accompanied by hailstorms and thunderstorms) takes place during summer. Snowfall generally takes place in the mountains. While the growing season on the Allegheny Plateau is less than 140 days, it is more than 210 days on the Delmarva Peninsula.
What is the Economy of Maryland?
The total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for Maryland increased from US$296,435.4 million in 2008 to US$412,584.2 million in 2018. The real median household income rose significantly in the last decade (from US$74,487 to US$86,223 during 2008-2018). The Per Capita, Personal Income in Maryland, has improved from US$49,428 in 2008 to US$63,354 in 2018. The real GDP grew at an annual rate of 1.6% in 2018.
Maryland ranked 29th, 19th, and 41st in terms of total exports, imports, and trade balance respectively in 2018. The total value of export was US$12,102,325,444, the total import value was $35,162,967,382, and the trade balance was -$23,060,641,938.
The principal exports of Maryland are Oil and Mineral Fuels, Industrial Machinery, Aircraft, Motor Vehicles and Parts, Chemical Products, Electrical Machinery, Precision Instruments, Plastics, Pharmaceuticals, and Nickel. The major imports of the state are Motor Vehicles and Parts, Industrial Machinery, Electrical Machinery, Aluminum, Furniture, Wood, Iron and Steel, Nickel, Coffee and Spices, and Precision Instruments.
The unemployment rate in Maryland increased drastically from 3.3% in January 2008 to 7.8% in January 2010. However, it has now come down to 3.6% in November 2019. The poverty rate in the state was 9.3% in 2018. The total number of people living below the poverty line was 549,171, out of the total population of 5,915,309.
What is the Transportation System of Maryland?
Maryland has a significantly complex roadway system, including US Highways, Interstate Highways, and State Highways.
There are around 14 US highways that pass through this state, and some of them are US 1, US 11, US 13, US 15, US 111, US 213, US 301, US 522, etc. Over 16 interstate highways are there in Maryland, and some of the most important ones are I-95, I-68, I-70, I-695, I-495, etc. Some of the significant state highways are MD 2, MD 4, MD 5, MD 16, MD 17, MD 27, MD 26, MD 28, MD 32, MD 36, and many more.
The major airports in Maryland are Baltimore or Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport (in Baltimore), Salisbury-Ocean City Wicomico Regional Airport (in Salisbury), Hagerstown Regional Airport (in Hagerstown), etc. The major ports and harbors in the state are Port of Baltimore, Inner Harbor, Londontowne, National Harbor, and Port Covington.
Why is Maryland called the “The Old Line State”?
The state nickname of Maryland is “the Old Line State”, which was bestowed by General George Washington in honor of the regular line troops (the Maryland Line) that fought many Revolutionary War battles courageously.
The other nicknames of the state are “the Free State”, “The Cockade State”, “The Monumental State”, “The Oyster State”, and “The Queen State”.
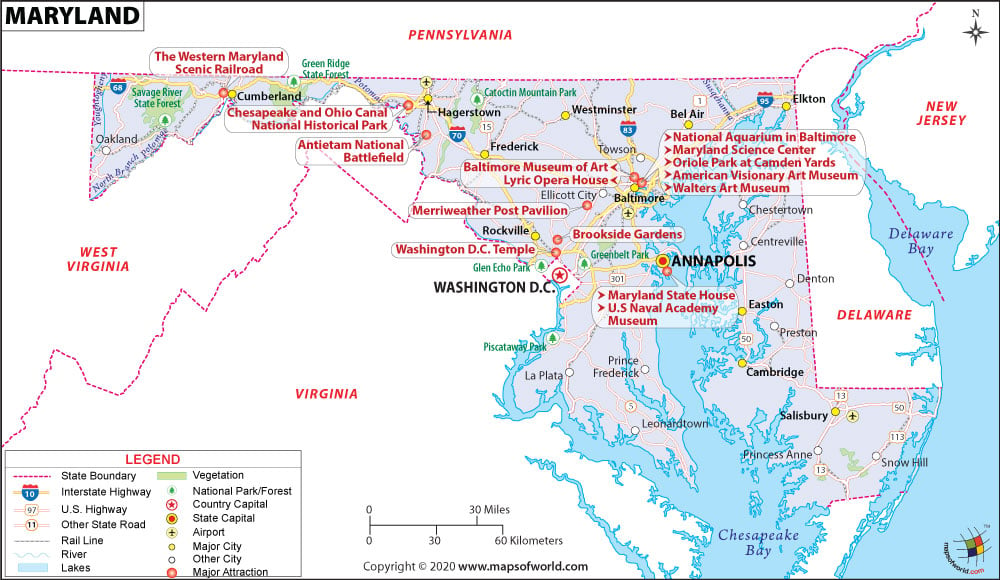
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Maryland?
Baltimore Inner Harbor, Fort McHenry National Monument, Old Town Annapolis and William Paca House, The Walters Art Museum, Ocean City, Antietam National Battlefield, National Aquarium, Baltimore and Ohio Railroad Museum, Chesapeake Bay Maritime Museum, Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park, Baltimore Museum of Art, Assateague State Park, American Visionary Art Museum, Blackwater National Wildlife Refuge
Facts About Maryland
- The state of Maryland has many nicknames such as the “Free State,” “Old Line State,” “America in Miniature,” and “Little America”.
- The capital city of Maryland is Annapolis and the biggest city is Baltimore.
- The demonym of the state of Maryland is Marylander.
- The tallest point in the state is the Backbone Mountain (elevation is 3,360 feet). The Backbone Mountain is also known as the Hoye Crest. The lowest point in the state is the Atlantic Ocean.
- Maryland shares its boundaries with Delaware, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Virginia, and Chesapeake Bay.
- The state of Maryland was admitted to the Union on April 28, 1788, and was the seventh state to ratify the US Constitution.
- The official motto is “Manly deeds, womanly words”.
- The official bird is the Baltimore Oriole.
- The official tree is the White Oak.
- The official flower is the Black-eyed Susan.
- The official fish is the Rockfish.
- The official song is “Maryland! My Maryland.”
- The state’s official mammal is the Chesapeake Bay Retriever and the official cat is the Calico Cat.
- Annapolis is nicknamed as the Sailing Capital of the World.
- Some of the famous people born in Maryland include Babe Ruth, Frederick Douglass, Frank Zappa, and Billie Holiday.
- The official flag of the state was adopted in 1904.
- The official reptile is the Diamondback Terrapin and the official crustacean is the Maryland Blue Crab.
- The official butterfly is the Baltimore Checkerspot.
- Fishing and shipping are the two major industries of the state.
- There are 47 state parks in Maryland. Fort Frederick State Park is one of the most famous state parks.
- Towards the end of the Revolutionary War, Annapolis served as the capital to the newly forming American nation.
- In 1969, Marylanders chose their first Jewish governor, in 1970 their first black congressman, and in 1986 their first female U.S. senator.
- In November 2012, the voters of Maryland approved a referendum that supported the same-sex marriage law that had been enacted earlier in the year.

![]()