What are the Key Facts of Malta?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Malta |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Valletta |
|
Largest City |
St. Paul’s Bay |
|
Coordinates |
35.894266, 14.439374 |
|
Area |
122 sq. mi ( 316 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Coastline |
122 mi ( 196.8 km) |
|
Currency |
Euro (€) (EUR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Maritime neighbors: Italy, Tunisia, Libya |
|
Population |
493,559 (2019 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Maltese, English |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
21 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“L-Innu Malti” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional republic |
|
President |
George Vella |
|
Prime Minister |
Joseph Muscat |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 42,567.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 30,074.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.878 (2017), Rank: 29 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
94.50 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
130 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+356 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.mt |
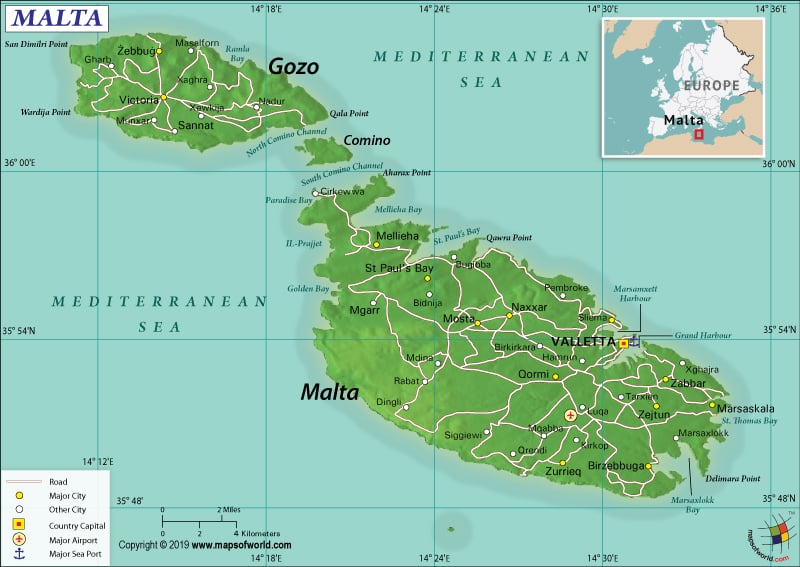
Where is Malta?
Malta is a group of islands in the Mediterranean Sea, located in the southern parts of Europe (south of Italy’s Sicily).
What is the Geography of Malta?
Malta is spread across a total area of 316 sq. km (122 sq. mi), out of which all of them are land area (316 sq. km or 122 sq. mi) and no water area (0 sq. km or 0 sq. mi). It has no land boundary. However, the country has a 196.8 km (122 mi) long coastline (excluding the 56 km or 35 mi for the island of Gozo).
The Malta archipelago has three large inhabited islands: Malta, Comino, and Gozo. This cluster of small islands is made up of coralline limestone. Most of its landscape is low, rocky, and rugged with flat to dissected plains. There are many steep coastal cliffs located in this island nation. Camino Island is known for having picturesque and gorgeous Blue Lagoons.
The highest elevation point of Malta is Ta’Dmejrek on Dingli Cliffs at 253 m (830 ft). The Mediterranean Sea at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point of the country. There are two high mountains in Malta: Għajn Abdul and Filfla. There are no rivers, streams or lakes.
The climate of Malta is Mediterranean, characterized by hot and sunny summers and mild, rainy winters. December-to-February is the winter season. The average temperature during December revolves around 14 °C (57 °F). The average temperature revolves around 12 °C or 53.5 °F during January-February.
The winter is mild and there is limited variation in daily temperature. The high temperature can drop below 10 °C (50 °F) in a handful of days. Freezing temperature or snowing never takes place. Bad weather persists for a few days with heavy rain and wind.
The temperature gradually rises in the spring season, which lasts from March-to-May. The average temperature in March, April, and May are 17 °C (63 °F), 19 °C (66 °F), and 23 °C (73 °F) respectively. The rainfall gets lesser and becomes rare in April. The climate remains sunny during spring and summer. The summer remains hot and sunny. It starts in June and continues till August. The highs revolve around 30 °C (86 °F). Summertime remains sultry, which is tempered by the sea breezes.
September-to-October is the autumn season. The temperature remains high in the first half of September but it decreases gradually. Thunderstorms start in the latter part of September. The temperature becomes pleasant in October when the highs revolve around 24 °C (75 °F).
What is the Economy of Malta?
The economy of Malta is an advanced, highly industrialized, and service-based. The strategic geographical position of the country makes it an important trading post, making it a leading center for the transshipment of container and freight. The main source of the economy is tourism.
In 2018, the nominal GDP of Malta grew at a rate of 6.6% to become a US$ 14.542 billion economy. The low debt-to-GDP ratio along with the financially sound banking sector helped Malta to maneuver the economy in a better manner than most of the European Union members.
The most imported products of the economy are fuel, raw material, boats, ships, integrated circuits, and chemical products. The major export items of the economy are manufactured goods, petroleum, integrated circuits, printed materials, pharmaceuticals, fish, and appliances.
The unemployment rate has dropped continuously from 2013 to 2017. The rate was 6.39% in 2013, which came down to 4.57% in 2017. It stagnated and increased marginally to 4.58% in 2018.
The Eurostat data shows that the total number of people at the risk of poverty or social exclusion has increased from 81,000 in 2008 to 83,000 in 2017. This trend is against that of the same in the European Union as the total number of people at the risk of poverty or social exclusion in the EU has dropped from 116 million in 2008 to 112.9 million in 2017. However, the percentage of people at the risk of poverty or social exclusion has dropped by around 1% in Malta during the last decade (from 20.1% in 2008 to 19.2% in 2017).
What is the Transportation System of Malta?
There is 2,254 km (1,401 mi) long roadway available in Malta. While most of the roads are present in the urban areas (1,422 km or 884 mi), around 832 km or 517 mi of roadway is present in the rural areas. Most of the roadways in the country are paved (1,973 km or 1,226 mi) and only 281 km (175 mi) are unpaved.
As Malta has come up as an important trading post for container and freight transshipment, there are a couple of major seaports/container ports available. Valletta and Marsaxlokk (Malta Freeport) are the major seaports of the country. Marsaxlokk is also the major container port of the country.
There is one airport in Malta (at Gudja), which has a paved runway. There are two heliports too in the country.
What International Organizations is Malta part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, ILO, Australia Group, Interpol, Schengen Convention, C, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NSG, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, PFP, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, OAS (observer), Union Latina (observer), ICC (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs)