What are the Key Facts of Madagascar?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Madagascar |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Antananarivo |
|
Largest City |
Antananarivo |
|
Coordinates |
-20.000000, 47.000000 |
|
Area |
226,658 sq mi ( 587,041 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Coastline |
3,000 mi ( 4,828 km) |
|
Currency |
Malagasy ariary (MGA) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
No land neighbors. Nearby island countries include Comoros, Seychelles and Mauritius |
|
Population |
24,894,551 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Malagasy, French |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity, indigenous religions |
|
National Day |
26 June |
|
National Anthem |
“Ry Tanindraza nay malala o” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary semi-presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Andry Rajoelina |
|
Prime Minister |
Christian Ntsay |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$1,558.3 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 449.7 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
HDI |
0.519 (2017), Rank: 161 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
128 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+261 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3(EAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.mg |
Where is Madagascar?
Madagascar is an island country that is located around 400 kilometers (250 miles) off the coast of East Africa in the Indian Ocean. Geologically, this country is located within the Somali plate. Besides the main island of Madagascar, there are numerous smaller peripheral islands.
What is the Geography of Madagascar?
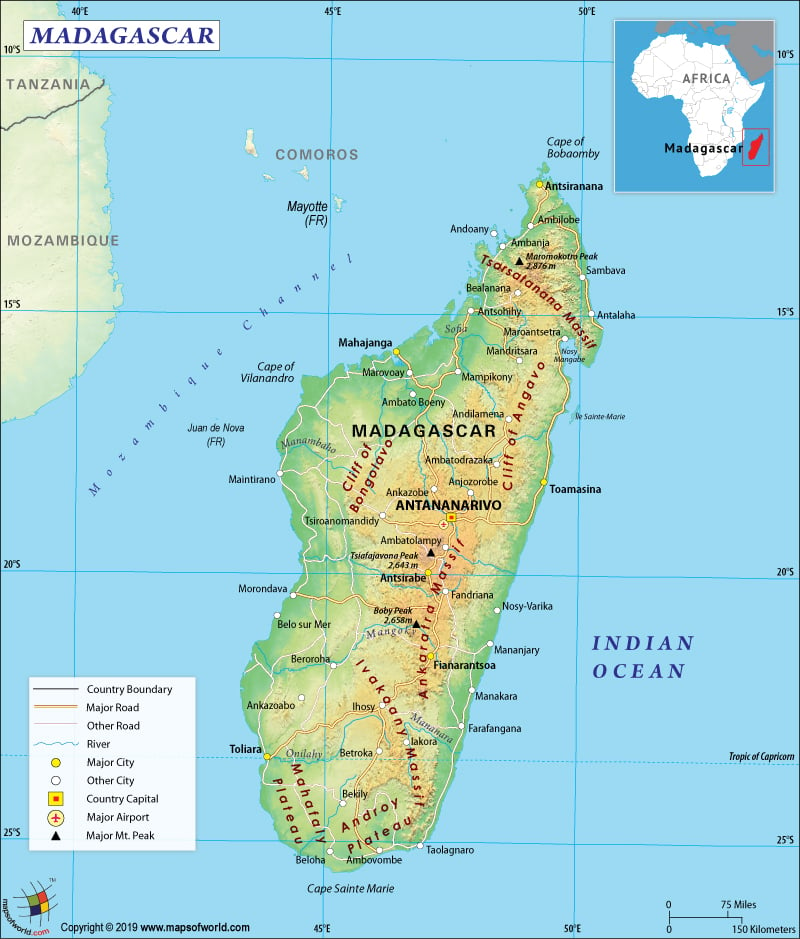
Madagascar is a southern African country that is spread over 226,658 square miles or 587,041 sq. km in area, making it the fourth largest island of the world. While the island country has a narrow coastal plain, at the center of the island a high plateau and mountains can be found. Madagascar has a huge coastline, spread over 4,828 km (3,000 miles). Here is Madagascar Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
The highest mountain of Madagascar is Maromokotro, whose height is 2,876 meters or 9,436 feet. It is located in the island’s northern part, inside the Tsaratanana Reserve. Besides, the other main mountains of this island country are Massif du Tsaratanana, Andringitra, and Ankaratra. The major rivers of Madagascar are Mangoky, Onilahy, Betsiboka, Sofia, Ihosy, and others.
Antananarivo is the capital (also the largest) city of the country, which is situated somewhat away from the coast. Madagascar has tropical rainforests as well as rich biodiversity. Around 5% of the total animal and plant species of the world are found in this country itself. Surface water is most abundant in the east coast region of Madagascar. However, it diminishes in the western and southern parts of the country. The southeastern trade winds dominate the climate of Madagascar.
The country predominantly has two seasons. November to April is the hot and rainy season, and May to October is the cooler and dry season.
Elevation and position of a place in Madagascar in relation to the dominant winds also brings great variation in climate. Its coastal regions are tropical, inlands are temperate, while southern portions are arid. East coast has the heaviest rainfall (3.5 meters on an average annually) as this part is directly exposed to the trade winds. This part of the island also has a hot and humid climate. East coast suffers from destructive cyclones (mainly coming from Mascarene Islands). Central highlands are cooler and significantly drier because of the higher altitude. During the rainy season, thunderstorms and lightning are common. West Coast is relatively drier. Semi-desert can be found in the southwest and the extreme south.
What is the Economy of Madagascar?
Madagascar is a market economy that is mainly dependent on agriculture (including fishing and forestry), textile, mining, and emerging tourism industry. Main cash crops of the country are vanilla, coffee, pepper, sugar, cloves, and cacao, which are among the top 12 exports in terms of value. 80% of the total vanilla production in the world takes place in Madagascar itself.
Around 80% of the population is still engaged in agriculture, fishing, and forestry. In fact, agriculture contributes 24% of GDP. However, lack of market connectivity, and modern farming techniques, hamper agricultural productivity. Around 56.4% is contributed by services and trade, while the share of industry is 19.5%. As per 2017 estimate, the nominal GDP of the country is US$11.5 billion and the GDP growth rate is 4.2% (World Bank, 2017).
The unemployment rate is hovering around 2.1%. Despite economic gains since 2013, the poverty rate is still relatively high. In 2017, 3-out-of-4 citizens of Madagascar lived on less than $1.90 per day. Only 35% of the total population has clean water access.
What is the Transportation System of Madagascar?
The main transport lifelines of Madagascar are roadways (paved and unpaved) and railways. Navigable waterways are also coming up fast as the preferred form of transportation.
- Six largest regional towns are mainly connected to Antananarivo by the national routes. In every district of the island country, minor paved and unpaved roadways provide the main transportation. During the rainy season, the unpaved roads (predominant in the country) become impassable.
- The railway is the next most important form of transport in Madagascar. While one rail connects Antananarivo with other important parts including Antsirabe, Ambatondrazaka, and Toamasina, another rail line connects Manakara and Fianarantsoa.
- Pirogues are used for covering smaller distances over Canal des Pangalanes and other isolated streams. Toamasina Autonomous Port is the main seaport (including cargo). The newest port is constructed at Port d’Ehola. Other ports in Madagascar are Antsiranana, Mahajanga, and Toliara.
- There are 133 airports in Madagascar including 29 airports (having paved runways) and 104 airports (having unpaved runways). Antananarivo’s Ivato International Airport is the main international airport in the country.
What International Organizations is Madagascar Part Of?
WTO, WHO, IMF, ACP, FAO, G-77, AfDB, UN, AU, UNESCO, CD, ILO, COMESA, EITI (candidate country), IAEA, UNHCR, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), UNCTAD, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, NAM, IFRCS, Interpol, IMO, InOC, IOC, IOM, WMO, IPU, ISO (correspondent), WIPO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), MIGA, OIF, WCO, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UPU, UNIDO, UNWTO
Related Link: