What are the Key Facts of Luxembourg?
|
Official Name |
Grand Duchy of Luxembourg |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Luxembourg City |
|
Largest City |
Luxembourg City |
|
Coordinates |
49.750000, 6.166667 |
|
Area |
998.6 sq mi ( 2,586.4 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
203 mi ( 327 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) |
|
Currency |
Euro (EUR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Belgium, France, Germany |
|
Population |
602,005 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Luxembourgish, French, German |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
23 June |
|
National Anthem |
“Ons Heemecht” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Grand Duke Henri |
|
Prime Minister |
Xavier Bettel |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$107,640.6 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$104,498.7 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
HDI |
0.904 (2017), Rank: 21 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Luxembourg Space Agency (LSA) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
95 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
4 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+352 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.lu |
Where is Luxembourg located?
Luxembourg is one of the smallest countries in the world. It is located in northwestern Europe and is bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. Luxembourg City is its capital city.
What is the Geography of Luxembourg?
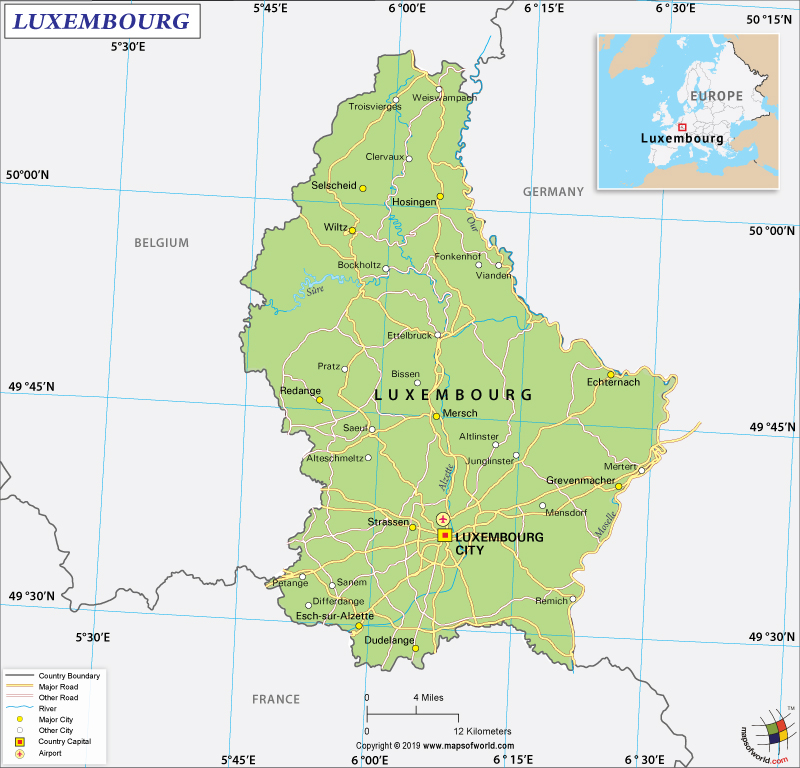
Covering an area of about 998.6 square miles or 2,586 square kilometers, Luxembourg is just about half the size of Delaware in the US. The northern mountainous part of the country, referred to as Oesling, is a continuation of the Ardennes Mountains of Belgium. This region is a forested plateau region and is home to most of Luxembourg’s castles. The plateau region is covered by oak and pine forests and has a number of nature parks. This region is home to the towns such as Clervaux, Vianden, and Wiltz. The southern region is referred to as the Bon Pays or Gutland and has more varied topography. The Moselle and the Sure valley regions provide Luxembourg most of its fertile pastures and farmlands. The Moselle valley is also famous for its sprawling vineyards. The weather in Gutland is comparatively milder than the northern parts of the Grand Duchy.
Luxembourg has mild cool summers and very cold harsh winters. The country experiences considerable amount of rainfall and a dry winter. The climate between May and October is temperate and May and June are the peak tourist months. There is also a slight variation of temperature between the north and the south.
What is the Economy of Luxembourg?
Luxembourg is one of the richest countries in the world, with one of the highest per capita incomes. The standard of living is very high, and it is also one of the safest countries in the world. The country’s iron and steel industry has been its major export revenue generator traditionally. The iron resources of the country, however, are now running low.
Additionally, through the later part of the 20th century, Luxembourg has become involved in international banking and financial services. The country’s nominal GDP was US$62.32 billion in 2017. In recent years the country has also capitalized on its information technology and e-commerce resources and provides services to the rest of the European Union. For its agricultural needs, however, Luxembourg depends largely on imports. Another major import is energy. The country’s hydropower projects power only about a fifth of the country’s growing needs as industrial development ramps up.
Of late, Luxembourg City has been witnessing an increase in the presence of international corporations due to the liberal tax policies practiced by the country. These companies prefer to build their headquarters in Luxembourg City rather than other major European cities where they may be taxed heavily. Its reputation as a tax haven and the country’s financial secrecy laws have also made Luxembourg a country for tax avoidance.
Following the global economic slowdown, the unemployment rate of Luxembourg has grown and is now at about 5.47 percent (2018). This may be lower than most other countries but is a high for the country.
What is the Transportation System in Luxembourg?
Luxembourg’s only commercial airport at Findel is serviced by the national carrier, Luxair, and by a number of other global air carriers. These connect Luxembourg with about 20 other destinations in the continent. Apart from this, the country has a very well-maintained network of highways connecting Luxembourg with Germany, Belgium, and France. The country’s internal rail network is well-maintained too. The seaport at Mertert is an important one and is used for cargo movement. Luxembourg is currently all set to become the first country in the world to have completely free public transport.
What International Organizations is Luxembourg Part of?
Australia Group, Benelux, BIS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NATO, NEA, NSG, OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNRWA, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO