What are the Key Facts of Liechtenstein?
|
Official Name |
Principality of Liechtenstein |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Vaduz |
|
Largest City |
Schaan |
|
Coordinates |
47.266667, 9.533333 |
|
Area |
62 sq. mi ( 160 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
47 mi ( 76 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Swiss franc (CHF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Switzerland, Austria |
|
Population |
38,547 (2017 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
German |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
15 August |
|
National Anthem |
“Oben am jungen Rhein” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Hans-Adam II |
|
Prime Minister |
Adrian Hasler |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$98,432 (2013 est.) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$143,151 (2010 est.) |
|
HDI |
0.916 (2017), Rank: 17 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
10 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+423 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.li |
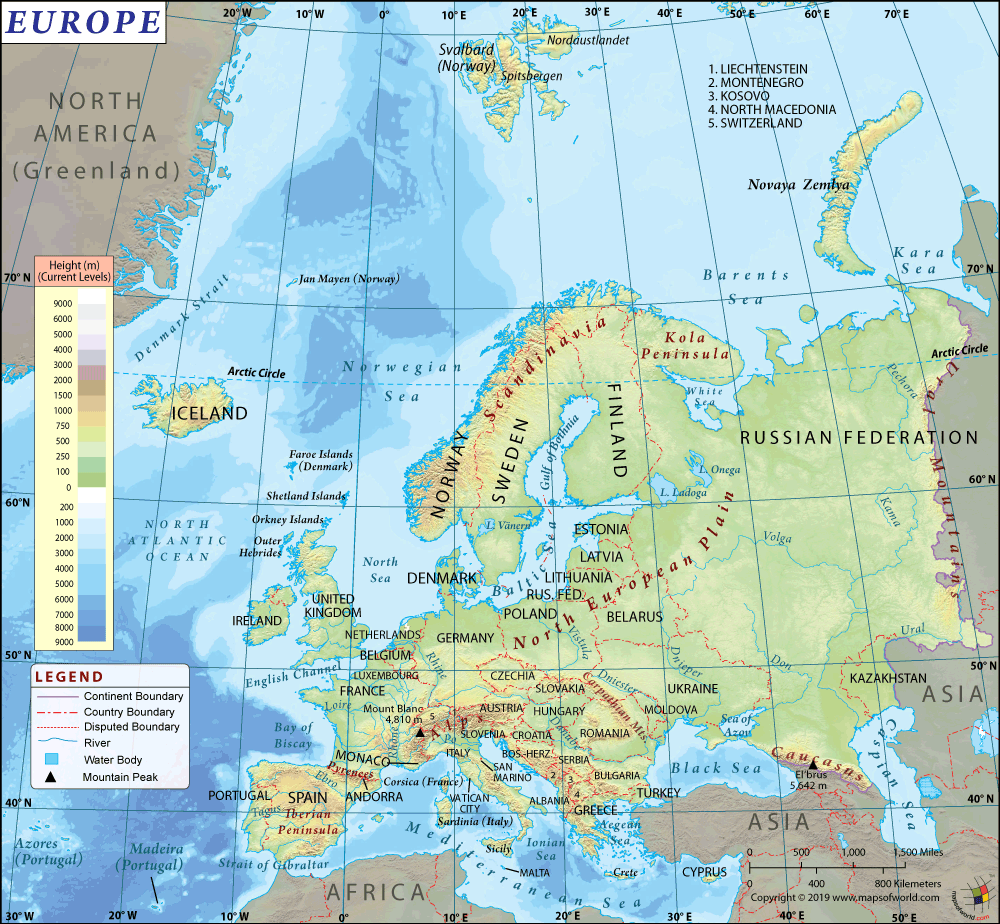
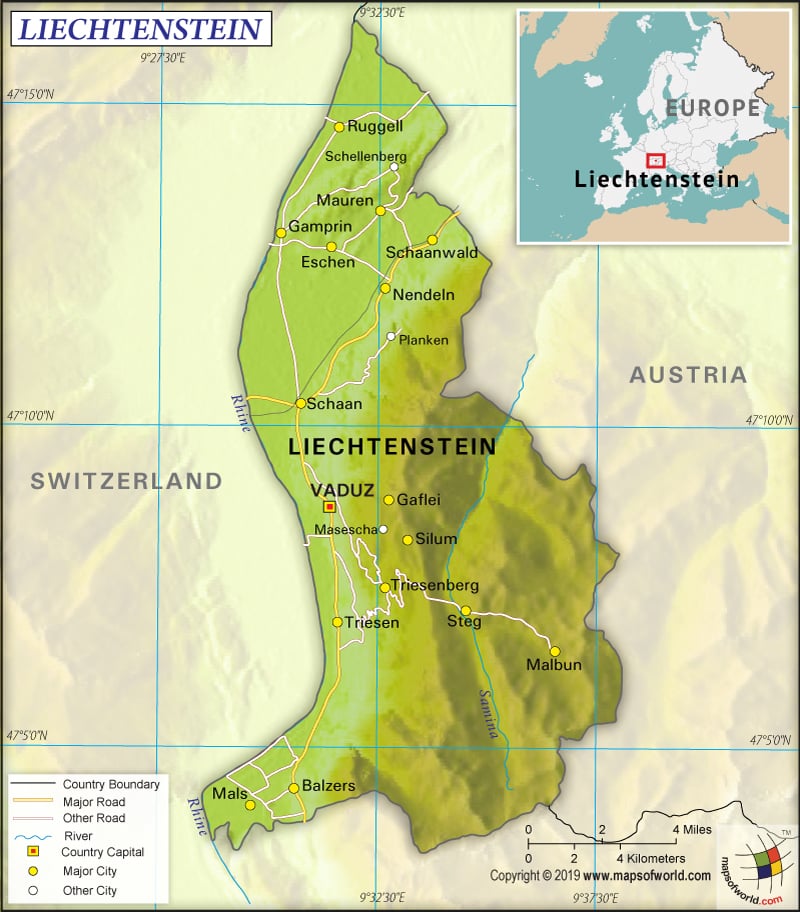
Where is Liechtenstein?
Liechtenstein is located in Alpine Central Europe. While Austria is located to the east and north of the country, Switzerland is located to the west.
What is the Geography of Liechtenstein?
Liechtenstein is one of the smallest countries of Europe as well as the world. This landlocked country is spread over a total area of 160 sq. km (62 sq. mi). It has no coastline and 75 km (47 mi) of land boundaries. Liechtenstein shares 41 km (25 mi) border with Switzerland and 34 km (21 mi) border with Austria. Vorder-Grauspitz is the highest point of the country at 2,599 m (8,527 ft) and Ruggeller Riet is the lowest point at 430 m (1,411 ft).
In fact, the country is located in the European Alps’ Upper Rhine valley. The Rhine forms the entire western border of the country. Liechtenstein is one of the two doubly landlocked countries of the world (the other being Uzbekistan), which means that other landlocked countries surround this country.
Further, major mountains of Liechtenstein are Schwarzhorn, Naafkopf, Falknis, Mazorakopf, and others. The most important river in the country is the Rhine. The second largest river is Samina, located in the Alps. The country has a natural lake called Gampriner Seele.
Broadly, the climate of Liechtenstein is characterized as temperate and alpine. The country gets mild winter season and wet summer. In January, the average temperature revolves around -1 °C (30.2 °F). In July, the average temperature hovers around 21 °C (69.8 °F).
Furthermore, the average yearly rainfall of the country revolves around 1,000 mm (39.37 in). The amount of rainfall is almost evenly distributed throughout the year. A warm, dry southerly wind known as Föhn modifies the climate. The rainy season usually lasts from June to August. Heavy thunderstorms are the characteristic feature of the rainy season. Heavy hail during this season causes a lot of damage.
In the valleys, snow cover remains from late December to March. At altitudes around 1,800 m (5,906 ft), snow cover lasts from November to May.
What is the Economy of Liechtenstein?
To begin with, Liechtenstein is a prosperous and highly industrialized economy despite a lack of natural resources. Financial services play a pivotal role in the economy. In 2016, the nominal GDP was US$6.21 billion and the economy expanded at the rate of 3.8% in 2017. It is one of the very few countries that have a per capita GDP of over US$100,000. The country has more listed companies than its population, which is just above 38,000.
Moreover, highly diversified small-to-medium-sized businesses are also thriving in Liechtenstein. The agricultural sector is small but significant. Around 30% of the revenues of the country come from the nominal offices established by the holding companies in the country due to low business taxes. The country has a flat 12.5% income tax. Almost all of its energy requirements are imported. More than half of its workforce comprises cross-border commuters, mainly from Switzerland, Germany, and Austria.
The main industries of the country are electronics, metal manufacturing, precision instruments, textiles, pharmaceuticals, calculators, anchor bolts, and food products. Tourism plays an important part in the economy. Most of the workforce is employed in the services sector (over 60%), followed by industry (around 40%). Not even 1% of the population works in agriculture. Strong standard of living has ensured that poverty is almost non-existent in Liechtenstein.
What is the Transportation System of Liechtenstein?
Roadways are the main transport system within Liechtenstein. 630 km (391 mi) of roadways are there in the country. LIEmobil buses are the main means of transport around the country. These buses are really reasonably priced. As this service traverses throughout the country, you can reach any part with LIEmobil buses. At every stop, you will find the timetable of the bus. Other popular means of road transport include cars, motorcycles, and bicycles.
9 km (6 mi) of railway network is present in Liechtenstein and all of it is in the form of electrified, standard gauge lines. These are most suitable for cross-country movement, especially from Austria to Switzerland. This railway network is run by the Austrian rail company ÖBB. Not all trains stop at Liechtenstein and that’s why it’s not a convenient mode of transport to get around the country.
There is no air transport system in the country. The closest international airport in Liechtenstein is Zürich Airport. Just 28 km (17 mi) of waterways are present in the country.
What International Organizations is Liechtenstein part of?
WTO, CD, UN, CE, Interpol, UNCTAD, EBRD, ITU, UPU, EFTA, WIPO, IAEA, ICCt, Schengen Convention, ICRM, IFRCS, IOC, IPU, ITSO, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer)