What are the Key Facts of Kazakhstan?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Kazakhstan |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Nur-Sultan |
|
Largest City |
Almaty |
|
Coordinates |
48.000000, 68.000000 |
|
Area |
1,052,100 sq. mi ( 2,724,900 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
8,304 mi ( 13,364 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Tenge (₸) (KZT) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Russia, Uzbekistan, China, Kyrgyzstan, and Turkmenistan |
|
Population |
18,448,600 (2019 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Kazakh, Russian |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
16 December (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Menin Qazaqstanim” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Kassym-Jomart Tokayev |
|
Prime Minister |
Askar Mamin |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 27,830.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 9,331.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.8 (2017), Rank: 58 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
KazCosmos |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
64 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
71 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+7 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+5 / +6 (West / East) |
|
Internet TLD |
.kz |
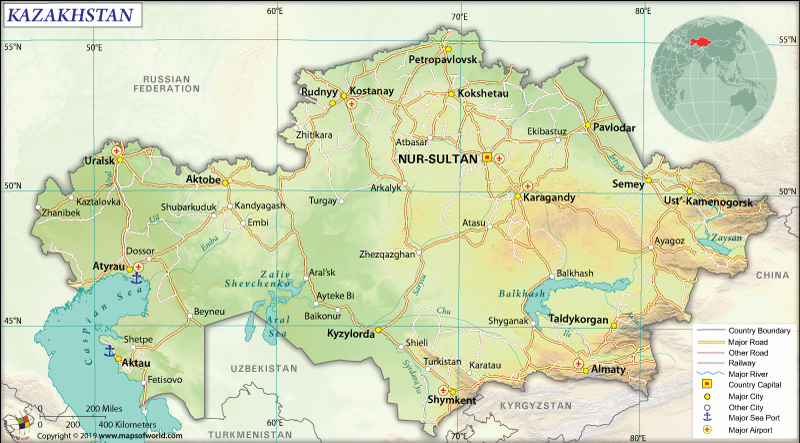
Where is Kazakhstan?
Kazakhstan is a Central Asian country whose small portion (to the west of the Ural or Zhayyq River) is also located in easternmost Europe. Kazakhstan shares 13,364 km (8,304 mi) long land boundaries with 5 countries including Russia (7,644 km or 4,750 mi), Uzbekistan (2,330 km or 1,448 mi), China (1,765 km or 1,097 mi), Kyrgyzstan (1,212 km or 753 mi), and Turkmenistan (413 km or 257 mi). It is a landlocked country as it is situated in the middle of the Asian continent. A large part of the country adjoins the landlocked Caspian Sea and the coastline (1,894 km or 1,177 mi) runs along the Caspian Sea.
What is the Geography of Kazakhstan?
The total area of Kazakhstan is 2,724,900 sq. km (1,052,100 sq. mi), out of which 2,699,700 sq. km (1,042,360 sq. mi) is land area and 25,200 sq. km (9,730 sq. mi) is water area. The landform of the country includes flatlands, deserts, snow-capped mountains, deltas, hills, rock canyons, taiga, and steppe.
Most of the landforms (70% of the total) in Kazakhstan are either desert or semi-desert. The semi-desert regions include sandy areas, eroded lowlands, and grasslands. The mountains are situated along the far eastern and southeastern borders. Altai and Tian Shan mountain ranges in these regions are predominantly forested and the snowcaps remain across the year.
Many of its elevated peaks exceed 6,500 m (21,325 ft). The highest elevation point of Kazakhstan is Khan Tangiri Shyngy (Pik Khan-Tengri) at 6,995 m (22,949 ft). The major mountains of the country are Khan Tängiri Shyngy, Pik Talgar, Gora Alagordy, Gora Belukha, etc.
The largest Steppe region of the world is located in Kazakhstan. It is known as the Kirgiz (Kaazakh) Steppe region, which is spread across 800,000 sq km (308,881 sq mi). The large stretch of land in this region generally remains very windy.
In some areas along the edges of the Caspian Sea, the land areas are located below the sea level. Along the borders of the Russian Federation (in the west of Kazakhstan), the landscape is dominated by rolling prairies as well as forests. Vpadina Kaundy is the lowest elevation point of the country at 132 m (433 ft). The Republic of Kazakhstan’s mean elevation is 387 m (1,270 ft).
Ishim, Ural, Tobol, Syr Dayra, and Irtush are the major rivers of the country. The largest water bodies are the Caspian Sea, the Aral Sea, and major lakes such as Alakal, Zaysan, Tengiz, and Balkhash.
Kazakhstan has an extreme continental climate, characterized by extreme dryness, cold winters, and hot summers. While July is the hottest month in the plains, August is the hottest in the mountains. The average summer temperature remains over 30 °C (86 °F) and the average winter temperature revolves around -20 °C (-4.0 °F). The temperature remains pleasant during April-to-June (Spring Season) and September-to-October (Autumn Season). Annual rainfall varies from arid to semi-arid conditions.
What is the Economy of Kazakhstan?
Kazakhstan has the largest economy (US$ 170.539 billion nominal GDP in 2018) in Central Asia. In 2018, the annual GDP growth was 4.1%. While the real GDP growth was 4.1% in 2017, it was 3.8% in 2018. World Bank believes that in the medium term, the real GDP will stabilize at about 3%.
The better-than-expected oil sector performance (with commendable growth in the service and agricultural sector) helped the economy to perform well. In 2017, the total oil production rose by 10.5%. However, the main challenges of the economy revolve around a lack of diversification and stagnation in productivity.
The country has a vast reserve of minerals, hydrocarbons, fossil fuel reserves, and metals (including uranium, zinc, and copper). The presence of vast steppe lands provides the country with huge potential in agriculture, livestock, and grain production. Apples and walnuts grow in the wild in the southern mountainous parts.
In recent years, the trade with the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) has improved. In 2017, the export and import with the EAEU countries increased by 30.2% and 24.1% respectively. Kazakhstan has a trade surplus (export was US$49.29 billion and the import was US$31.85 billion in 2017).
The unemployment rate was static at 5% in both 2016 and 2017. The rate of poverty was also hovering around 2.5%.
What is the Transportation System of Kazakhstan?
There are 95,409 km (59,284 mi) roadways in the country, out of which 81,814 km (50,837 mi) are paved and 13,595 km (8,448 mi) are unpaved. The total railway network available in Kazakhstan is 16,614 km (10,323 mi) and all of them are broad gauge network. 96 airports are currently available, out of which 63 have paved runways and rest 33 has unpaved runways. Three heliports are also present in the country. 4,000 km (2,485 mi) of waterways are there. Most of them are on Ertis (Irtysh) River and Syr Darya (Syrdariya) River. 121 merchant marine ships are also there.
What International Organizations is Kazakhstan part of?
IMF, UN, ADB, WHO, CICA, UNESCO, CIS, UNCTAD, CSTO, UNIDO, EAEU, UNWTO, EAPC, WIPO, EBRD, WMO, ECO, FAO, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMO, NSG, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, SCO, UPU, WCO, ZC, EITI (compliant country), ICC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), NAM (observer), OAS (observer), UN Security Council (temporary), WTO (observer)
Related Links: