What are the Key Facts of Jordan?
|
Official Name |
Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
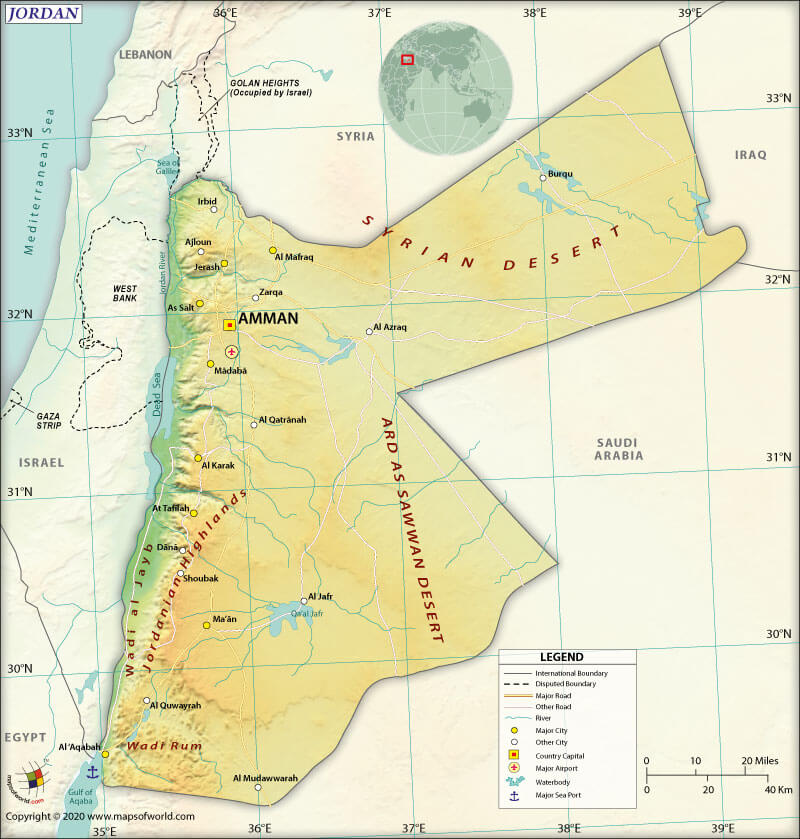
Capital |
Amman |
|
Largest City |
Amman |
|
Coordinates |
31.000000, 36.000000 |
|
Area |
34,495 sq. mi (89,342 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,084 mi (1,744 km) |
|
Coastline |
16 mi (26 km) |
|
Currency |
Jordanian dinar (JOD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Iraq, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Palestine. |
|
Population |
10,102,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
25 May (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“As-salam al-malaki al-urdoni” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
King Abdullah II |
|
Prime Minister |
Omar Razzaz |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 10,316.6 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 4,330.3 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.723 (2019), Rank: 102 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
98.23 (UNESCO, 2018) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
57 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
1 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
962 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (EET); DST: UTC+3 (EEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.jo |
Where is Jordan?
Jordan (whose official name is the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan) is an Arab country in Western Asia that is located at the Jordan River’s East Bank.
What is the Geography of Jordan?
Jordan spreads across a total area of 34,495 sq. mi (89,342 sq. km). Out of the entire area, 34,287 sq. mi (88,802 sq. km) is land area and 208 sq. mi (540 sq. km) is the water area.
The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan’s total land boundary is 1083.7 mi (1,744 km) long. It shares its border with Saudi Arabia (454.2 mi or 731 km) to the south, Syria (235.5 mi or 379 km) to the north, Israel (190.8 mi or 307 km) to the west, Iraq (111.2 mi or 179 km) to the north-east, and West Bank of Palestine (92 mi or 148 km) to the west. Jordan’s coastline is just 16.2 mi (26 km) along the Red Sea in its extreme south-west.
The mean elevation of Jordan is 2664.04 ft (812 m). While the highest point is Jabal Umm ad Dami at 6082.7 ft (1,854 m), the lowest point is the Dead Sea at -1414.04 ft (-431 m).
The terrain of Jordan mostly consists of the arid desert plateau. A dominant topographical feature along the western part of Jordan is the great north-south geological rift. It includes the Jordanian Highlands, the Jordan River Valley, and the Dead Sea.
The highest mountains in Jordan are Jabal Umm ad Dāmī (Aqaba), Jabal Ramm (Aqaba), Jabal Mabrak (Ma’an), Jabal an Nabī Hārūn (Ma’an), Mount Maqta’ al Qurmeya (Jerash), etc. Major rivers, tributaries, and wadis of Jordan are Jordan River, Yarmouk River, Wadi al-Yabis, Wadi Arabah, Wadi Rum, Zarqa River, etc.
What is the Climate of Jordan?
Jordan has a hot and dry climate. While the summers are hot, dry, and long, the winters are cool and short. Both the Arabian desert’s subtropical aridity and the eastern Mediterranean area’s subtropical humidity influence climate in different locations of Jordan.
As per the Koeppen-Geiger classification, Jordan’s climate can be classified as a BSh climate, which is characterized by a predominantly hot and dry climate across the year. The yearly average temperature remains above 64.4 °F (18 °C).
BWh Climate is found in the eastern and southern parts of Jordan. This climatic condition is characterized by a hot, dry desert climate, where the yearly average temperature remains above 64.4 °F (18 °C).
While August is the hottest month in the country (with temperature ranging within 68-95 °F or 20-35 °C), January is the coldest month (with temperature ranging within 41-50 °F or 5-10 °C).
Especially during summer, the daily temperature can get very hot. The temperature can remain 104 °F (40 °C) or more on some days, especially when a hot, dry southerly wind (called Shirocco) blows. These strong winds can sometimes gain momentum and may cause Sandstorms.
Most of the rainfall (70% of the total yearly rainfall) takes place within November-March. However, it remains often rainless during June-August. In Jordan, precipitation usually takes place along with violent storms during winter and causes erosion as well as local flooding.
What is the Economy of Jordan?
The economy of Jordan is one of the smallest economies in the Middle East. It suffers from insufficient supplies of natural resources, including water and oil. That’s why the Jordanian economy has to depend heavily on foreign assistance.
Significant economic challenges of the country include extremely high rates of unemployment and underemployment, increasing government debt, and significantly high budget and current account deficits.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Jordan increased at an annual rate of 2% to US$43.744 billion. Jordan’s export and import value in 2018 were US$8.28 billion and US$22.3 billion, respectively. It has a high negative trade balance of – US$14.1 billion.
Major export items are Potassic Fertilizers, Calcium Phosphates, Packaged Medicaments, Knit Sweaters, and Mixed Mineral or Chemical Fertilizers. Significant imports of Jordan are Cars, Refined Petroleum, Petroleum Gas, Crude Petroleum, and Packaged Medicaments.
The unemployment rate in this Middle Eastern country has shot up from 11.9% in 2014 to 15.28% as in 2016 but again decreased to 14.72% in 2019.
Unicef’s “Geographic Multidimensional Vulnerability Analysis – Jordan” report shows that the absolute poverty rate in Jordan increased from 14.4% in 2010 to 15.7% in 2018. This means that more than 1 million Jordanian people live below the poverty line.
Jordan’s poverty situation has been aggravated by the Syrian crisis in 2019 as around 660,000 Syrian refugees fled Syria and registered in Jordan till August 2019. An estimated 81% of these refugees live out of camps, which only worsens the situation.
What is the Transportation System of Jordan?
Jordan has one of the best infrastructures in the world. As it is a transit country between Iraq and Palestine for goods and services, the high infrastructural development was necessitated.
There is 4475.7 mi (7,203 km) long roadways are available in Jordan, and all of them are paved ones. 316.3 mi (509 km) long narrow-gauge railway facility is also available.
The country has 18 airports, out of which 16 have paved runways, and 2 have unpaved runways. Eight airports have more than 9996.7 ft (3,047 m) long paved runways, five airports have 7998.7-9996.7 ft (2,438-3,047 m) long paved runways, two airports have 5,000-7,995.4 ft (1,524-2,437 m) long paved runways, and two airports have under 914 m (under 2,999 ft) long unpaved runways.
Al’ Aqabah is the principal seaport in Jordan, and the total merchant marine vessels available in the country are 32 (7 are general cargo, 1 is an oil tanker, and 24 are other types of vessels).
What International Organizations is Jordan Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, NAM, ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, CD, CICA, EBRD, FAO, G-11, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, MINUSTAH, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), OSCE (partner)