What are the Key Facts of Hungary?
|
Official Name |
Hungary |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Budapest |
|
Largest City |
Budapest |
|
Coordinates |
47.000000, 20.000000 |
|
Area |
35,920 sq. mi ( 93,030 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,248 mi ( 2,009 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Forint (HUF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, Austria |
|
Population |
9,772,756 (2019 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Hungarian |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
20 August (Saint Stephen’s Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Himnusz” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary republic |
|
President |
János Áder |
|
Prime Minister |
Viktor Orbán |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 30,978.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 15,938.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.838 (2017), Rank: 45 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
99.10 (UNESCO, 2014) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
65 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
498 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+36 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1(CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.hu |
Where is Hungary?
Hungary is a central European country that is located in both the northern and eastern hemispheres. It shares 2,106 km (1,309 mi) long land border with 7 countries – Slovakia (627 km or 390 mi), Romania (424 km or 263 mi), Croatia (348 km or 216 mi), Austria (321 km or 199 mi), Serbia (164 km or 102 mi), Ukraine (128 km or 80 mi), and Slovenia (94 km or 58 mi).
What is the Geography of Hungary?
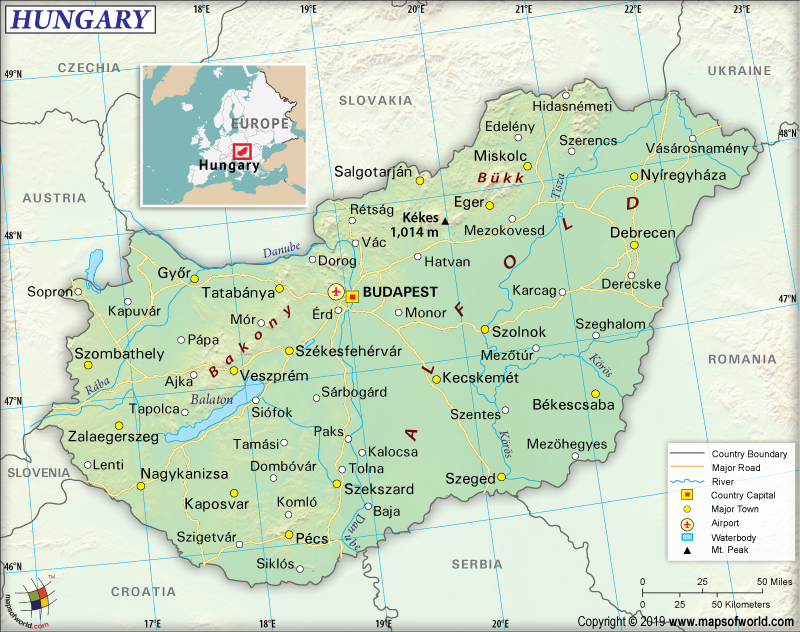
Hungary is spread across a total area of 93,030 sq. km (35,920 sq. mi), out of which 89,608 sq. km (34,598 sq. mi) is land area and 3,420 sq. km (1,320 sq. mi) is water area. It is a landlocked country and has no coastline. While Kekes is the highest elevation point at 1,014 m (3,327 ft), Tisza River is the lowest point at 78 m (256 ft). The mean elevation of Hungary is 143 m (469 ft).
Broadly, the Danube and Tisza rivers define the traditional geography of the country. Geographically, Hungary is divided into 3 sections: Dunántúl (means beyond the Danube river; also called Transdanubia), Tiszántúl (means beyond the Tisza river), and Duna-Tisza köze (means between the Danube and Tisza rivers).
Generally, Dunántúl or Transdanubia region stretches towards the west (in the direction of Austria) from the center of Hungary. The landform of this region is mainly hilly, and the terrain has low mountains. This terrain includes Alpokalja (the eastern stretch of the Alps) that is located in the western part of Hungary. The Transdanubian Mountains are located in this region’s central part. The southern part of Transdanubia is characterized by the Villány Mountains and the Mecsek Mountains. Írott-kő is a part of the Alps and is the highest elevation point in the Dunántúl region. In the northern parts of the region, Kisalföld or the Little Hungarian Plain can be found. The largest thermal lake in the world, Lake Hévíz, and the largest lake in Central Europe, Lake Balaton, is situated in the Transdanubia region.
Further, Alföld or the Great Hungarian Plain is located in both Tiszántúl and Duna-Tisza köze regions. This plain is located mainly in the eastern and southeastern areas of Hungary. Near the Slovakian border, the foothills of the Carpathians can be found, which are located mainly in the northern parts of the plain. The tallest mountain in Hungary, Kékes, is located in this region.
In addition, a temperate seasonal climate is found in Hungary. This climate is characterized by warm summers having low overall humidity levels and frequent summers. The winters are cold and snowy. The average annual temperature revolves around 9.7 °C (49.5 °F). During summer, the average temperature revolves within 23-to-28 °C (73-to-82 °F). In winter, the average temperature ranges from −3 to −7 °C (27 to 19 °F). The average annual rainfall remains around 600 mm (23.6 in).
What is the Economy of Hungary?
In 2018, the Hungarian economy’s nominal GDP was US$155.70 billion and the growth rate was 4.9%. The most important sector of the economy is the services sector, whose contribution to the GDP is around 65%. Industrial and agricultural sectors contribute around 31% and 4% respectively. Most of the labor force is also employed in the services sector (around 65%) and the industrial sector (around 21%). Only 5% of the workforce is employed in agriculture.
Moreover, the main industries of Hungary are pharmaceuticals, food processing, IT, motor vehicles, machinery, metallurgy, chemicals, mobile technology, information security, and electrical goods. Tourism plays an important part in the economy. In Central and Eastern Europe, Hungary is the largest producer of electronics. The Hungarian economy has a trade surplus.
During 2018, the rate of unemployment was 3.7% (World Bank). However, the Hungarian population at the risk of poverty is 19.6% (as per the Eurostat data of 2018).
What is the Transportation System of Hungary?
The transport system in Hungary is highly developed. The total length of roadways available in Hungary is 203,601 km (126,512 mi), out of which 77,087 km (47,900 mi) is paved and 126,514 km (78,612 mi) is unpaved. 1,582 km ( 983 mi) of expressways are also there in the country.
Besides, Railways are also significantly well established. In fact, 8,049 km (5,001 mi) long railway network is present in Hungary. While most of the railway track (7,794 km or 4,843 mi) is standard gauge, 219 km (136 mi) is a narrow gauge, and 36 km (22 mi) is the broad gauge. There are 41 airports in Hungary, out of which 20 have paved runways and 21 have unpaved runways. Three heliports are also there.
1,622 km (1,008 mi) of waterways are present in Hungary and most of them are part of the Danube River. There are 4 major river ports in this landlocked country, and they are Csepel, Baja, Mohacs, Gyor-Gonyu, and Dunaujvaros.
What International Organizations is Hungary part of?
NATO, Australia Group, CERN, IMF, BIS, UN, CD, UNESCO, CE, UNCTAD, CEI, UNHCR, EAPC, Interpol, EBRD, ECB, UNFICYP, EIB, Schengen Convention, EU, FAO, G-9, IAEA, WHO, IBRD, ICAO, ILO, ICCt, WMO, ICRM, WIPO, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, SELEC, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WTO, ZC, WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), ESA (cooperating state), OAS (observer), OIF (observer), ICC (national committees)
Related Links: