What are the Key Facts of Guinea-Bissau?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Guinea-Bissau |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Bissau |
|
Largest City |
Bissau |
|
Coordinates |
12.000000, -15.000000 |
|
Area |
13,948 sq. mi ( 36,125 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
473 mi ( 762 km) |
|
Coastline |
217 mi ( 350 km) |
|
Currency |
West African CFA franc (XOF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Senegal, Guinea |
|
Population |
1,815,698 (2016 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Portuguese |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
24 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Esta e a Nossa Patria Bem Amada” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary semi-presidential republic |
|
President |
Umaro Sissoco Embalo |
|
Prime Minister |
Baciro Dja |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 778.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,795.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.455 (2017), Rank: 177 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+245 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+0 (GMT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.gw |
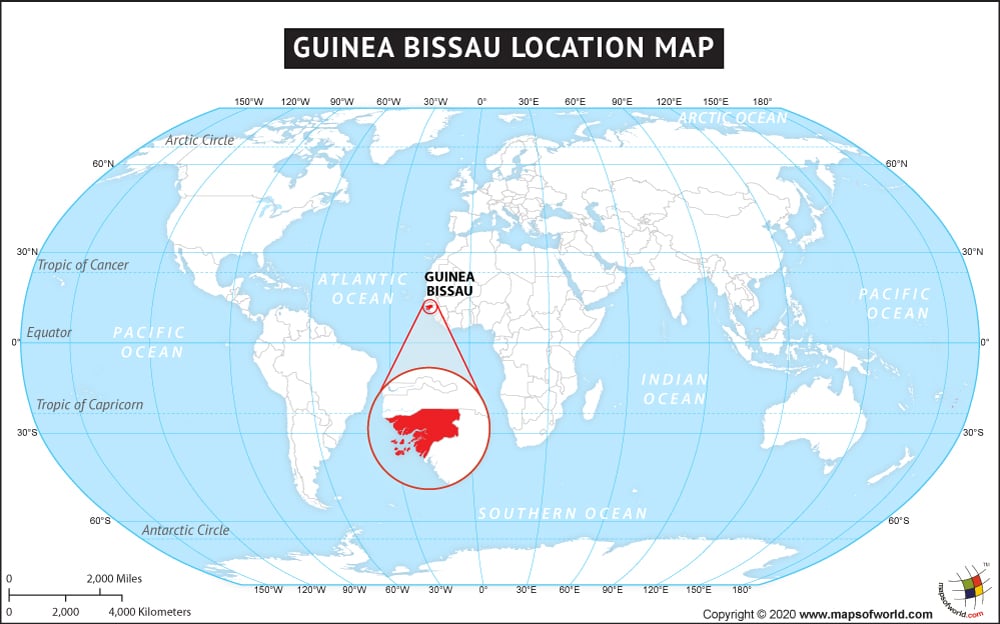
Where is Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau is a West African country that is located between Senegal and Guinea, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean.
What is the Geography of Guinea-Bissau?
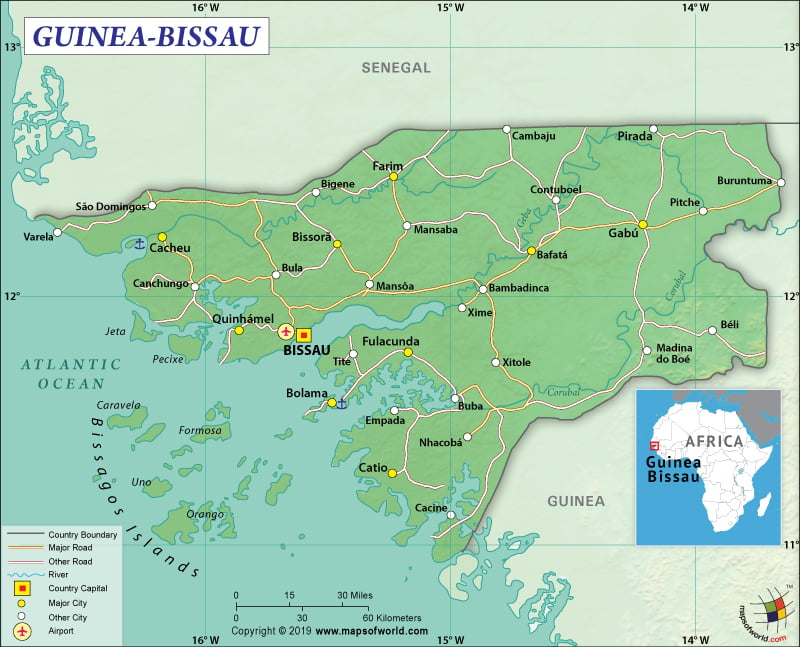
To begin with, Guinea-Bissau has a total area of 36,125 sq. km (13,948 sq. mi), out of which 28,120 sq. km (10,857 sq. mi) is land area and 8,005 sq. km (3,091 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 762 km (473 mi) long land boundary that is shared with two neighboring countries: Guinea (421 km or 262 mi) and Senegal (341 km or 212 mi). Guinea-Bissau has a 350 km (217 mi) long coastline.
Further, the mean elevation of Guinea-Bissau is 70 m (230 ft). While the highest elevation point is at 300 m (984 ft), the lowest point is sea level at the Atlantic Ocean. The major peaks of the country are Kakoulima, Kambo, Belakaniare, Bonkoui, Kankhare, Moinahi, and many more. There are many rivers and tributaries in Guinea-Bissau, and some of them are Cacheu River, Mansoa River, Rio Petu, Geba River, Rio Grande de Buba, Tombali, Cumbijã River, Como River, Cacine River, etc.
Furthermore, the landforms of Guinea-Bissau consist of low-lying plains including flat savanna and rain forests in the interior. A group of 18 major islands along with dozens of smaller islands in the Atlantic Ocean near Guinea-Bissau create the Bijagos Archipelago, where the main tourist attraction is the Orango Islands National Park. The coastline of the mainland includes many scattered beaches as well as swamps of mangroves.
As a matter of fact, the climatic condition of Guinea-Bissau can be characterized as tropical. It is usually hot and humid almost throughout the year. The dry season lasts from November to May. The rainy season lasts for five months, from June to October. Guinea-Bissau experiences maximum temperature just before the rainy season, usually during February-to-May. The temperature comes down slightly as the rain starts but still it remains muggy. The interior parts of the country get intense heat. However, the breeze along the coastal areas relieves the place from intense heat.
Heavy monsoon rain starts from July and continues till September. The heavy downpour usually causes a widespread flood. The rainiest month is August. The central-southern part of the coastal belt gets more than 2,000 mm (79 in) rainfall per year. However, the north-eastern parts receive less than 1,500 mm (60 in) rainfall per year. The sky remains cloudy during this time of the year.
Harmattan (a wind blowing from the desert) prevails during the winter season, keeping the weather good and dry. The dust brought by the wind causes the sky to remain whitish. Generally, the daytime temperature revolves around 30 °C (86 °F). However, the temperature may reach 40 °C (104 °F) too.
The temperature, as well as humidity, starts increasing gradually from February. It reaches a peak during March-to-May and the temperature surpasses 40 °C (104 °F) easily. The temperature starts decreasing as the rainy season starts, when the temperature usually revolves around 28/30 °C (82/86 °F). The heat gets muggy because of the increased moisture in the air.
What is the Economy of Guinea-Bissau?
In reality, Guinea-Bissau is predominantly a poor country where 2 out of 3 citizens remain below the absolute poverty line. The economy is highly dependent upon subsistence agriculture, fishing, foreign assistance, and export of cashew nuts. The nominal GDP of the country was US$1.458 billion and it grew by 3.8% in 2018. However, the important economic indicators such as GDP per capita and Human Development Index (HDI) are one of the lowest in the world. All these factors make Guinea-Bissau one of the ten poorest countries in the world.
Nonetheless, in cashew production, it is one of the leading countries in the world. Other important export items earning them foreign currency are seafood, non-fillet frozen fish, palm kernels, peanuts, and timber. The country also earns from license fees for providing permission to fish in the Gulf of Guinea sea-zone.
The rate of unemployment was 6.10% in 2017. The average unemployment rate during 1979-2017 was 6.52%. In fact, lack of political stability has led to lack of development in the country and the subsequent high levels of poverty. Reports say around 70% of the population lives in poverty, with more than 25% suffering from chronic malnutrition.
What is the Transportation System of Guinea-Bissau?
The transportation system in the country is not well developed. It has 4,400 km (2734 mi) of roadways, of which 453 km (281 mi) is paved and 3,947 km (2453 mi) is still unpaved. There are 8 airports in the country. While two airports have paved runways, six have unpaved runways. The waterways are also partially developed. The rivers are partially navigable, and the interiors of the country can be accessed through navigation of many inlets and creeks. There are four important seaports of Guinea-Bissau and they are Bissau, Farim, Cacheu, and Buba. The country has 9 merchant marine ships (5 general cargo and 4 other vessel types).
What International Organizations is Guinea-Bissau part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, ILO, Interpol, ACP, AfDB, AOSIS, AU, CPLP, ECOWAS, FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINUSMA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WAEMU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), WADB (regional)