What are the Key Facts of Finland?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Finland |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Helsinki |
|
Largest City |
Helsinki |
|
Coordinates |
64.000000, 26.000000 |
|
Area |
130,666 sq. mi ( 338,424 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,593 mi ( 2,563 km) |
|
Coastline |
777 mi ( 1,250 km) |
|
Currency |
Euro (€) (EUR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Norway, Sweden, Russia |
|
Population |
5,521,158 (2019 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Finnish, Swedish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
6 December (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Maamme” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Sauli Niinistö |
|
Prime Minister |
Sanna Marin |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 47,930.2 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 49,648.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.92 (2017), Rank: 15 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
46 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
470 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+358 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (EET), Summer (DST) UTC+3 (EEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.fi |
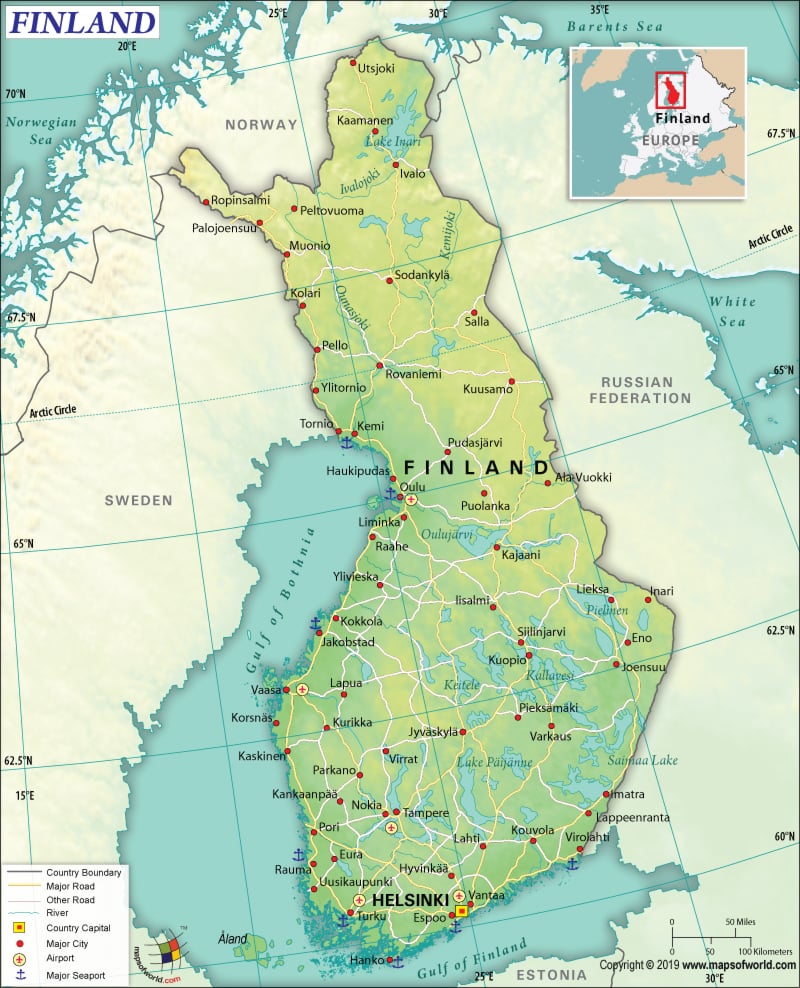
Where is Finland?
Finland is a Northern European country that borders the Gulf of Finland, Gulf of Bothnia, and the Baltic Sea. This Nordic country is bordered by Norway to the north, Russia to the east, and Sweden to the northwest.
What is the Geography of Finland?
Finland is spread across a total area of 338,424 sq. km (130,666 sq. mi), out of which 303,815 sq. km (117,304 sq. mi) is land area and 34,330 sq. km (13,255 sq. mi) is water area. The country has a 2,563 km (1,593 mi) long land boundary and 1,250 km (777 mi) long coastline. The land boundary is shared with three countries: Russia (1,309 km or 813 mi), Norway (709 km or 441 mi), and Sweden (545 km or 339 mi).
The terrain mostly consists of plains that are low and flat-to-rolling. Low hills and lakes intersperse these plains. Halti is the highest elevation point of the country at 1,328 m (4,357 ft) and the Baltic Sea at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Finland is 164 m (538 ft).
Most of the landscape in Finland is flat, 70% of which is covered by thick forest. Innumerable clear water lakes are present in the southern region of the country. Estimates say that there are around 188,000 lakes in this Nordic country, out of which 60,000 of them have over 200 m widths.
To the Arctic Circle’s north, the landscape rises into Lapland’s hills as well as low mountains. Haltiatunturi, the highest elevation point of the country is located on the edge of Norway’s border. The major mountains in Finland are Haltiatunturi, Saana, Aakenustunturi, Sauoiva, Sorsatunturi, Yllästunturi, etc.
Some of the largest lakes of the country are Lake Saimaa, Pielinen, Paijanne, Oulujarvi, Nasijarv, etc. The major rivers in Finland are Kemi, Torne, Teno, Oulu, Muonio, Luiro, etc.
An archipelago called the Aland Islands is located between Finland and Sweden in the middle of the Gulf of Bothnia. This archipelago consists of around 300 islands (out of them, 80 are inhabited) and more than 6,000 small/tiny rocky islands.
Tens of thousands of islands, most of them small in size, are located in the Archipelago Sea. They are located directly to the east and merge with the southwestern coastline of Finland and the Aland Islands. The larger islands are inhabited.
Many canals are also there in the country, especially in the southern parts, connecting one lake to another. Saimaa Canal, connecting Lake Saimaa with the Gulf of Finland, is the largest canal.
Finland’s climate comes with moderately rainy summers (that are short and mild) and cold winters that continue for a long period of time. Its proximity to Russia makes it one of the coldest Scandinavian countries.
The level of rainfall is not very high. In the extreme north-east, the average yearly precipitation level is 400 mm (15.5 in). In the eastern and southern areas, the annual rainfall level is 650 mm (25.5 in). The south-western tip of Finland gets around 700 mm (27.5 in) rainfall every year on an average. Rainfall happens quite frequently and is well distributed across the year.
Summer and autumn are the rainiest periods. The month of August gets a bit more rainfall than July in the centre-south region. February-April gets the least rainfall. Light snowfall takes place during winter.
Winter season lasts for around five months. Starting from mid-November to late-March, the temperature is around 0 °C (32 °F). Winter starts getting colder and longer as you move from the southern parts (say in the port of Helsinki) towards the northern and eastern parts. The seas also freeze there, especially in the Gulf of Bothnia and sometimes in the port of Helsinki.
When cold air masses from Russia starts blowing, the temperature can get below -20 °C (-4 °F). However, when the mild wind blows from the Atlantic Ocean, the temperature revolves around the freezing point (0 °C or 32 °F).
In the far north (in Lapland), the temperature can dip as low as -50 °C (-58 °F). The thaw normally takes place in southern Finland at the beginning of April and at the end of April in Lapland. While snowfall starts in Lapland in October, it takes place in the southern parts in November.
There are two transitional months in Finland and they are May and September, during which night temperature generally touches the freezing point. The months from June to August get mild weather. During the daytime, the weather remains hot.
During summer, the daytime temperature revolves around 20 °C (68 °F) in Lapland. However, it also reaches a high of around 30 °C (86 °F). The nighttime remains cold and usually remains below 10 °C (50 °F).
What is the Economy of Finland?
Finland has a highly industrialized, free-market based economy, where export plays an import role. Export accounts for more than 1/3rd of GDP currently. In 2018, the nominal GDP of the economy grew at a rate of 1.658% to reach a figure of US$273.961 billion.
The major exports of Finland are refined petroleum, kaolin coated paper, sulfate chemical wood pulp, cars, large flat-rolled stainless steel, etc. The major import items are packaged medicaments, vehicle parts, crude/refined petroleum, cars, etc. The Republic of Finland had a positive balance of trade of US$5.26 billion in 2017 as it exported US$70.7 billion value of items and imported US$65.4 billion value of items.
The rate of unemployment in Finland was 7.76% in 2018, less than 8.64% in 2017. Finland has one of the lowest rates of poverty in the world. It was 5.8%, as per the latest OECD report.
What is the Transportation System of Finland?
Finland has a developed transportation system. It has 454,000 km (282,103 mi) long roadway, out of which 78,000 km (48,467 mi) is highway, 350,000 km (217,480 mi) is private and forest roads, and 26,000 km (16,156 mi) urban roads. Out of the total 78,000 km (48,467 mi) highway, 50,000 km (31,069 mi) is paved (including 700 km or 435 mi of expressways), and 28,000 km (17,398 mi) is unpaved.
Over 8,000 km (4,971 mi) long waterways are present in Finland, including the 3,577 km (2,223 mi) Saimaa Canal system. And 8,200 km (5,095 mi) of coastal fairways are also maintained by Finland. The major seaports of the country are Helsinki, Rauma, Raahe, Porvoo, Naantali, and Kotka. The country has some 259 merchant marine vessels, out of which seven are bulk carriers, 88 are general cargo vessels, one in a container ship, four oil tankers, and 159 others.
Over 5,926 km (3,682 mi) long railway is there in Finland and all of them are broad-gauge tracks. There are 148 airports in Finland, out of which 74 have paved runways and 74 have unpaved runways. The major airports of the country are Helsinki-Vantaa Airport, Enontekiö Airport, Kokkola-Pietarsaari Airport, Tampere-Pirkkala Airport, etc.
What International Organizations is Finland part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, UNESCO, ILO, WHO, Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCT, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINUSMA, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, Schengen Convention, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNMOGIP, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, UNCTAD, WIPO, WMO, ZC, ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), EITI (implementing country),ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links:

3641 total views , 3 views today