What are the Key Facts of Equatorial Guinea?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Equatorial Guinea |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Malabo |
|
Largest City |
Bata |
|
Coordinates |
2.000000, 10.000000 |
|
Area |
10,830 sq. mi ( 28,050 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
328 mi ( 528 km) |
|
Coastline |
184 mi ( 296 km) |
|
Currency |
Central African CFA franc (XAF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Cameroon, Gabon, Nigeria, São Tomé and Príncipe |
|
Population |
1,222,442 (2015 Census) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish, French, Portuguese |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
12 October (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Caminemos pisando la senda” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary dominant-party presidential republic |
|
President |
Alpha Conde |
|
Prime Minister |
Ibrahima Kassory Fofana |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 23,472.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 10,174.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.591 (2017), Rank: 141 |
|
Literacy Rate |
95.00 % (2014, UNESCO) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+240 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (WAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.gq |
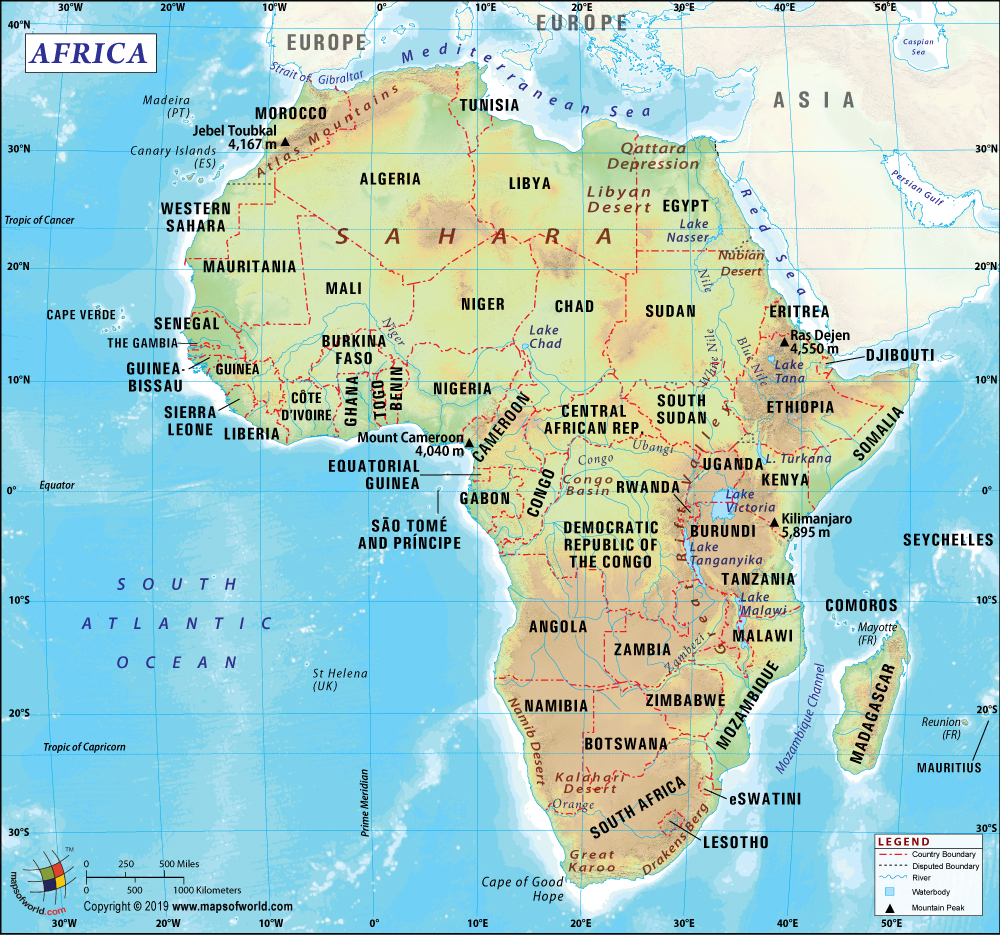
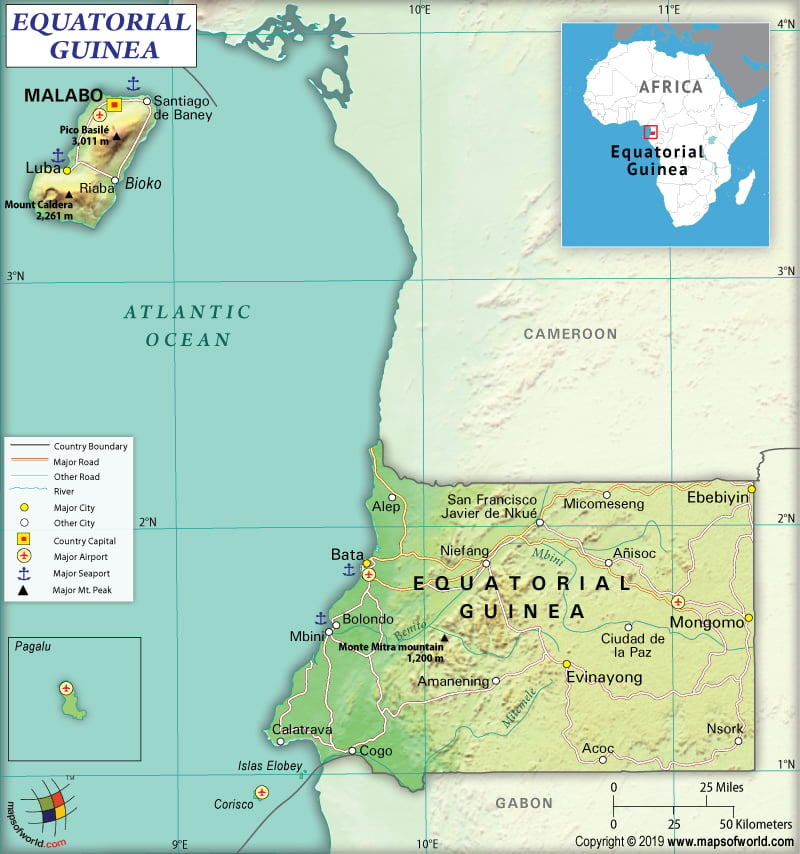
Where is Equatorial Guinea?
Equatorial Guinea is a Central African country that borders the Bight of Biafra and is located between Gabon and Cameroon.
What is the Geography of Equatorial Guinea?
The total area of Equatorial Guinea is 28,050 sq. km (10,830 sq. mi), out of which 28,050 sq. km (10,830 sq. mi) is land area and no water area. It has a 528 km (328 mi) long land boundary. The country also has a 296 km (184 mi) long coastline.
Equatorial Guinea’s mainland consists of a narrow coastal plain having mangrove swamps as edges. Towards its border with Gabon, the land rises from the coastal plain to an elevated plateau having thickly forested hills. In some places, the elevation also goes above 4,000 ft or 1,219 m above sea level. Uola is the major river in the country, which moves through the center of Equatorial Guinea like a snake.
Three extinct volcanoes dominate the offshore Bioko Island, whose landscape has a volcanic origin and therefore is very fertile. In the southern parts of the country, the coastline is both rugged and steep. The country has a picturesque northern coast, which has scenic beaches as well as harbors.
Pico Basile is the highest elevation point in Equatorial Guinea at 3,008 m (9,869 ft) and the Atlantic Ocean 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation is 577 m (1,893 ft). The major mountains in the country are Clarence Peak on Bioko Norte, Pico Biaó, Pico Quioveo, Pico Lago, Pico Do Fogo, and Quepuchin. The major rivers are Benito River (Mbini River), the Campo River (Ntem River), and the Muni River, Komo River, etc.
The equatorial climate is mainly found in the continental region (Rio Muni) as well as the islands (including Bioko and Annobón). This climatic condition is characterized by high temperatures and heavy rainfall with cloud cover remaining most of the time throughout the year.
Local variation mainly takes place due to proximity to the sea, on one hand, and differences in elevation, on the other. Slight cool weather prevails during June-to-September, especially when the south-west currents prevail.
From January to May, the temperature remains higher. However, it gets lower during July-September. In the continental region, the temperature drops to around 27-28 °C (81-82 °F). The temperature in the islands remains a bit higher.
The wet season takes place twice during the year: February-to-June and September-to-December. The coastal areas get more rainfall than in the inland areas. The pattern of rainfall in the mainland and Bioko Island are the opposite.
What is the Economy of Equatorial Guinea?
The economy of Equatorial Guinea is dependent mainly on oil and gas deposit exploitations. The GDP has been rebased recently, resulting in an increase in the economic size by around 30%. Farming and forestry also contribute to the GDP but they are only minor factors.
This middle-income economy actually contracted in 2018. The nominal GDP’s growth rate dropped by -2.9% (slightly higher than the -4.7% growth rate in 2017) to reach the figure of US$13,318 million. In 2017, the country had a positive balance of trade of $3.96 billion. It exported $4.72 billion value of goods and imported $755 million of goods. The main export items are petroleum gas, crude petroleum, acyclic alcohol, rough wood, special purpose ships, etc. The main imports are poultry meat, beer, large construction vehicles, refined petroleum, machinery having an individual function, etc.
The rate of unemployment (percentage share of the workforce that is without work) in Equatorial Guinea was 9.16% in 2018, the same as 2017. Despite having one of the highest per capita incomes among the Sub-Saharan African countries, extremely fertile soil, and extraordinarily low debt, World Bank data shows that the country has an extremely high poverty rate (76.8%). Around 42% of the children are not even registered in the primary schools as per the 2016 data.
To contain poverty, the government has chalked out a medium-term National Economic Development Plan: Horizon 2020. It aims to reduce poverty and also expand the diversification of the economy. The government allocates 2-3% of the revenue to both health and education.
Reports say most of the revenue earned by the country is distributed mostly among the political elite. Infrastructure development gets around 80% of the fund. The improvement in living conditions of the general populace is slow because of corruption, lack of economic diversification, and a decline in revenue from the production of hydrocarbon.
What is the Transportation System of Equatorial Guinea?
Equatorial Guinea has 2,880 km (1,790 mi) long roadways. There are 7 airports in the country. While 6 have paved runways, 1 has an unpaved runway. The most important airports are Bata Airport, Malabo International Airport, Corisco International Airport, President Obiang Nguema International Airport, and Annobón Airport.
The major seaports in the country are Malabo, Luba, and Bata. An LNG terminal in Bioko Island is also present for export purposes. 36 merchant marine ships are there in Equatorial Guinea.
What International Organizations is Equatorial Guinea part of?
UN, WHO, ILO, IMF, UNESCO, ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, CEMAC, FAO, FZ, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WIPO, WTO (observer), CPLP (associate), OAS (observer)
Related Maps: