What are the Key Facts of Cuba?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Cuba |
|
Continent |
North America (Caribbean) |
|
Capital |
Havana |
|
Largest City |
Havana |
|
Coordinates |
21.892392, -78.792052 |
|
Area |
42,426 sq. mi ( 109,884 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
18 mi ( 28.5 km) |
|
Coastline |
2,321 mi ( 3,735 km) |
|
Currency |
Peso (CUP), Convertible peso (CUC) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Maritime neighbors: United States, The Bahamas, Haiti, Mexico, Cayman Islands (UK), Jamaica |
|
Population |
11,209,628 (2018 Census ) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
10 October (Independence Day), 1 January (Triumph of the Revolution Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“La Bayamesa” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic |
|
President |
Miguel Díaz-Canel |
|
First Vice President |
Salvador Valdés Mesa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
NA (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 8,541.2 (World Bank, 2017) |
|
HDI |
0.777 (2017), Rank: 73 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
226 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+53 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−5 (CST), Summer (DST): UTC−4 (CDT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.cu |
Where is Cuba?
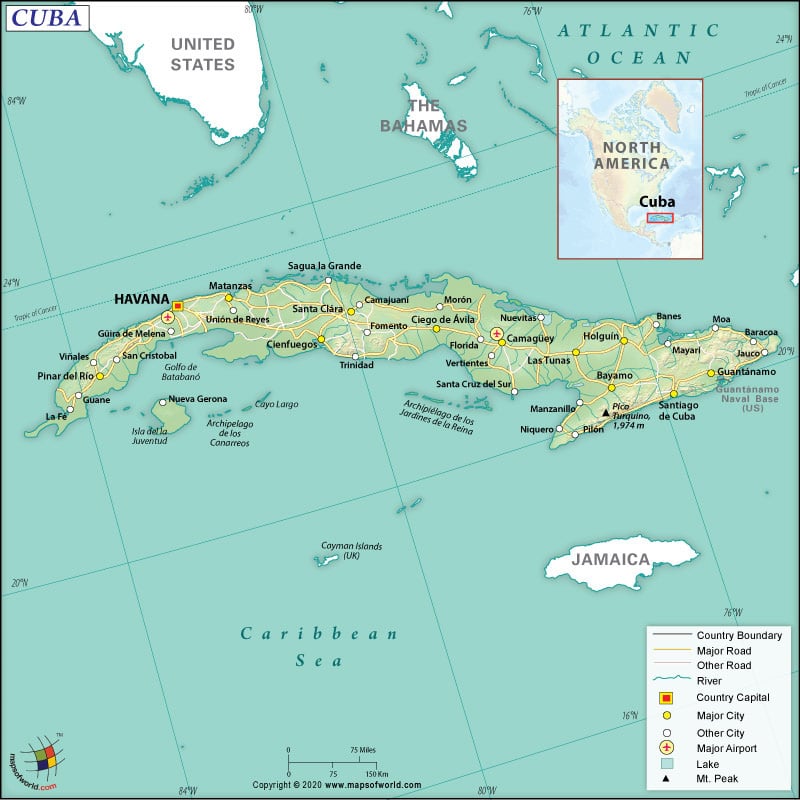
Cuba comprises of the island of Cuba, the second-largest Cuban island Isla de la Juventud, and many minor archipelagos. The Republic of Cuba is located at the confluence of the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea. This north Caribbean archipelago is situated 150 km (93 mi) south of the USA’s Florida, south of the Bahamas, north of Cayman Islands, north of Jamaica, and east of Mexico’s Yucatán Peninsula.
What is the Geography of Cuba?
Cuba is spread across a total area of 109,884 sq. km (42,426 sq. mi), out of which 109,820 sq. km (42,402 sq. mi) is land area and 1,040 sq. km (402 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 28.5 km (18 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with Guantanamo Bay (currently a US Naval Base) which is still a part of Cuba and has been leased by the United States. Cuba has a 3,735 km (2,321 mi) long coastline.
The terrain of Cuba mostly consists of flat to rolling plains. The mountainous parts, as well as the rugged hills, are situated mainly in the southeast region. The mean elevation of this North Caribbean country is 108 m (354 ft) from the sea level. Pico Turquino is the highest elevation point of the country at 1,974 m (6,476 ft), and the Caribbean Sea at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point.
Some of the significant mountains beside Pico Turquino are Gran Piedra, Pico Mogote, Pico San Juan, etc. There are around two hundred small rivers. The principal rivers are Rio Cauto, Rio Almendares, and Rio Yurimi. Some of the vital inland water areas are Laguna de Leche and the man-made Zaza Reservoir.
What is the Climate of Cuba?
Cuba has a tropical climate, and it has two distinct seasons. The rainy and muggy season starts in late-April and continues till early-November. The other season is a dry and relatively cool one, which begins in late-November and continues till mid-April. A fairly stable climate is found throughout the country with some notable differences in certain areas.
The annual rainfall level in this country is 1,000-1,500 mm (40-60 in). In the southern areas (including the Guantanamo Bay), the yearly rainfall level is below 700 mm (27.5 in). In the northern part, the weather is pleasantly warm during winter. However, in the southern region, the weather is even hotter.
In Havana (the capital city of Cuba), the temperature hovers around 26 °C (79 °F) in the daytime during December-February. The southernmost areas get temperatures around 28 °C (82 °F). The short cold outbreaks can drive down night temperature in the north-western region to around 10 °C (50 °F) or even below that.
July and August are the hottest months of the season when the daytime temperature can sometime exceed 33-34 °C (91-93 °F). High moisture content makes the heat sweltering in Cuba. Rainfall generally takes place in late-afternoon in the form of showers or thunderstorms.
For a beach holiday, late-March-to-April is the best time to visit the northwest part of Cuba. The southwest part of the country can also be visited during the winter season.
What is the Economy of Cuba?
The nominal GDP of Cuba in 2017 was US$96.851 billion, and the annual growth rate was 1.8%. The main exports of the country are raw sugar, nickel mattes, rolled tobacco, crustaceans, hard liquor, and many more. Some of the major import items of Cuba are crude/refined petroleum, wheat, poultry meat and concentrated milk. In 2017, they had a US$4.8 billion value of the negative balance of trade.
Cuba is a developing country that is growing decently despite heavy US-sanctions. Around 76% of the population is employed in the public sector. Tourism is the primary service sector in the country. After the reform, self-employment has been allowed in this socialist economy. There are over 500,000 self-employed registered Cuban workers in the country. In 2018, 4.78 million tourists visited Cuba. The Cuban tourism ministry announced that they are expecting more than 5 million tourists in 2019, and the tourism income is expected to be more than US$3 million.
Venezuela is a significant trading partner of Cuba. It gets petroleum products from Venezuela on preferential terms. Cuba repays for the oil by offering Cuban professionals, especially medical professionals to the country. There are around 30,000 medical professionals/doctors working in Venezuela.
The unemployment rate in this north Caribbean country was 2.26% in 2018. The rate of poverty (in terms of income of internationally accepted US$2 per day) is complicated to quantify in Cuba because every Cuban citizen gets free social services in addition to the mere $20 per month state government salary.
Over 1/3rd of the workforce in the country is self-employed, especially after implementing the reforms in 2016. The poverty rate varies from 5% to 26%, depending upon the parameter chosen for estimating the poverty level. The level of poverty has come down drastically in Cuba since the extended period of the economic crisis that started in 1991, especially after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Human Development Index (HDI) has improved in the country by 15% (from 0.676 to 0.777) during 1990-2017. It is currently categorized among the high-HDI countries. In 2017, its ranking was 73 out of 189 countries and territories, in terms of HDI.
What is the Transportation System of Cuba?
Cuba has over 60,000 km (37,282 mi) long roadway system, out of which 20,000 km (12,427 mi) is paved and 40,000 km (24,855 mi) is unpaved. Some 240 km (149 mi) long waterway system is there in the country. The main seaports here are Antilla, Santiago de Cuba, Cienfuegos, Nuevitas Bay, Matanzas, Guantanamo, Mariel, and Havana. Forty-one merchant marine ships are there in Cuba.
An extensive railway network is present in this country. The entire railway network is 8,367 km (5,199 mi) long, out of which 8,195 km (5,092 mi) is standard-gauge (124 km or 77 mi is electrified) and 172 km (107 mi) is narrow-gauge. There are 133 airports, out of which 64 have paved runways, and 69 have unpaved runways.
What International Organizations is Cuba part of?
UN, WTO, WHO, Union Latina, UNESCO, Petrocaribe, ACP, ALBA, AOSIS, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IAEA, ICAO, ICRM, IFAD, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, NAM, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), IOM (observer), OAS (excluded from formal participation since 1962), PIF (partner), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links: