What are the Key Facts of Canada?
|
Official Name |
Canada |
|
Continent |
North America |
|
Capital |
Ottawa |
|
Largest City |
Toronto |
|
Coordinates |
60.000000, -95.000000 |
|
Area |
3,855,100 sq mi ( 9,984,670 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
5,526 mi ( 8,893 km) |
|
Coastline |
125,570 mi ( 202,080 km) |
|
Currency |
Canadian Dollar ($) (CAD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
United States, Greenland (Denmark), Saint Pierre and Miquelon (France) |
|
Population |
35,151,728 (2016 ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, French |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
1 July (Canada Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“O Canada” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy, Commonwealth realm |
|
Monarch |
Elizabeth II |
|
Prime Minister |
Justin Trudeau |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 47,870.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 46,124.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.926 (2017), Rank: 12 |
|
Literacy Rate |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Canadian Space Agency / Agence spatiale canadienne (CSA/ASC) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
15 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
501 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+1 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−3.5 to −8, Summer (DST) UTC−2.5 to −7 |
|
Internet TLD |
.ca |
Where is Canada?
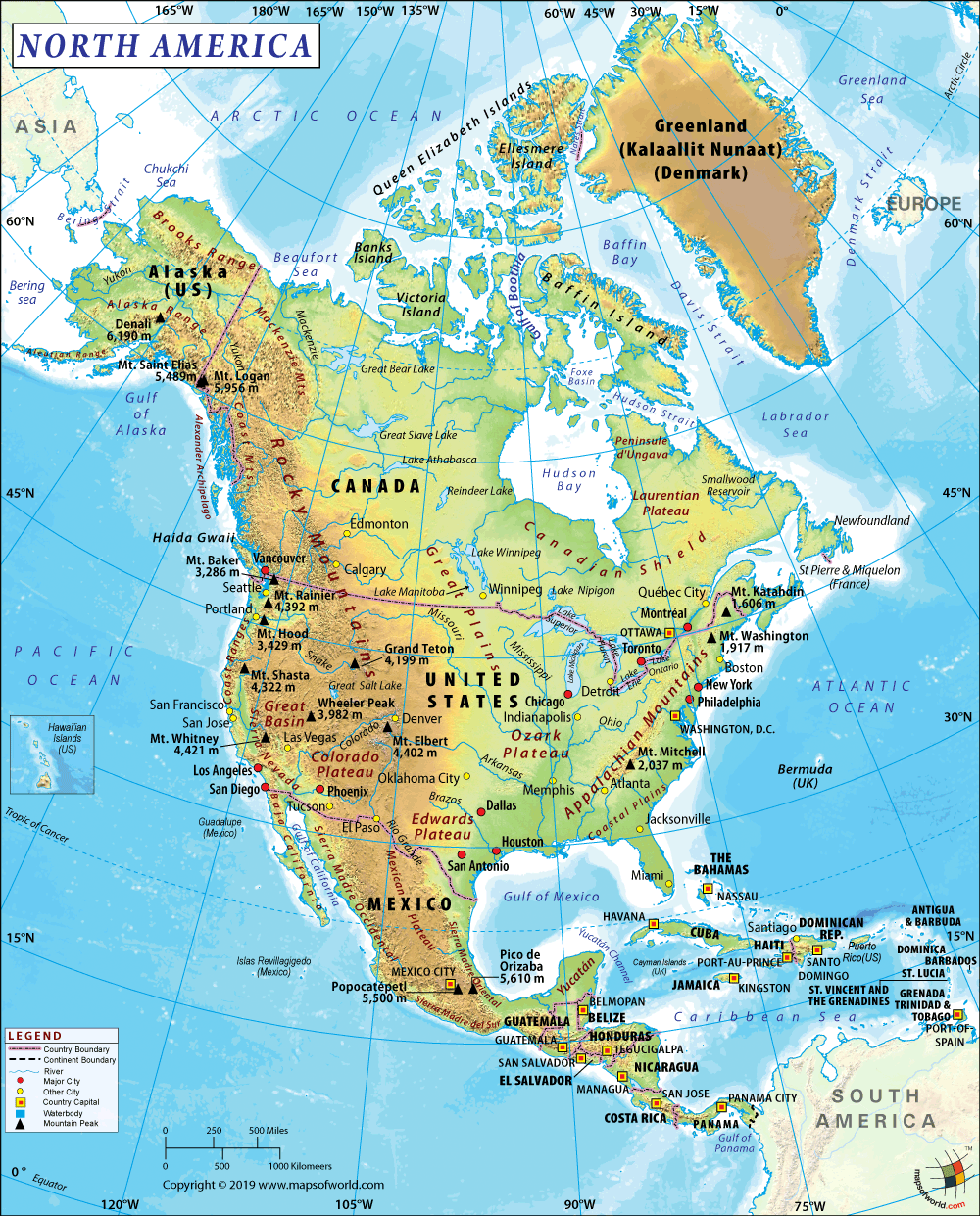
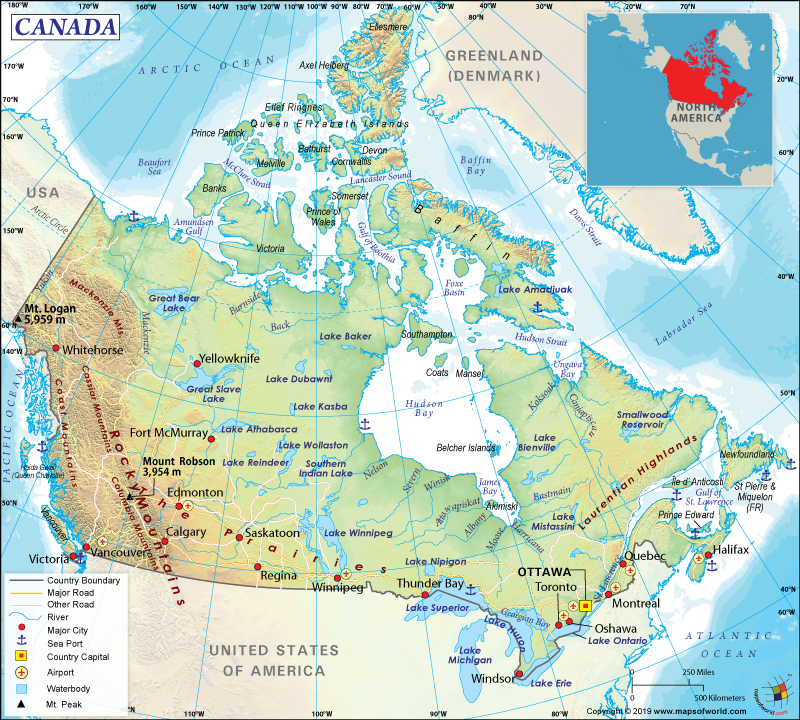
Canada is located in the northern part of North America. It is the second largest country in the world by area. Its provinces and territories are spread from the Atlantic to the Pacific. In the north, it extends into the Arctic Ocean. Canada has three ocean borders. The Atlantic Ocean is located in the east, the Pacific Ocean in the west, and the Arctic Ocean in the north direction. In the south and the northwest, Canada borders with the USA.
Canada is spread over almost the entire North American continent, north to the USA except Alaska as well as St. Pierre and Miquelon (small French islands). The country extends 5,187 km (3,223 miles) east-west from Cape Spear (Newfoundland) to the Yukon Territory’s Mount Saint Elias. It also extends 4,627 km (2,875 mi) north-south from Ellesmere Island’s Cape Columbia to Lake Erie’s Pelee Island. In the north, Canada is bounded by Arctic Ocean and in the east by the Atlantic Ocean, Davis Strait, Baffin Bay, Nares Strait, and Kennedy Channel. While on the south of Canada, the USA is located, on the western side of the country, the US state of Alaska and the Pacific Ocean are located.
What is the Geography of Canada?
Canada is spread over 9,984,670 sq km (3,855,103 sq. miles) area out of which 9,093,507 sq. km (3,511,023 sq. miles) is land and 891,163 sq. km (344,080 sq. miles) is water. In terms of total area, Canada is slightly larger than the United States of America and China. Southern border of Canada with the US stretches over 8,891 kilometers (5,525 miles), making it the longest bi-national land border of the world. Ottawa is the capital of Canada and the largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Here is Canada Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
The total land boundary length of Canada is 8,893 km (5,526 miles). A wide array of landforms is present in Canada including many maritime terrains, 36,563 islands, and more lakes/inland water bodies than any other country. Canada has the longest coastline on earth, which is 202,080 km (125,566 miles). This longest coastline has been possible thanks to the thousands of islands present in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago.
The country has four types of landscapes including prairie grasslands, high mountains, arctic tundra (permanently frozen ground), and a variety of forests. The wide array of landforms present in Canada are the Appalachian Mountains, Canadian Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Shield, St. Lawrence River, Great Plains, Hudson Bay, Great Lakes, Mackenzie River, Yukon River, Fraser, Columbia, Rocky Mountains, Great Slave Lake, Great Bear Lake, Canadian Cordillera, Rocky Mountains, and many volcanoes along the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Canada’s climate varies from subarctic and arctic in the north to temperate in the south. There are 4 different seasons found in Canada: winter, spring, summer, and autumn. Winter season is very cold in most of the places in Canada, often reaching many degrees below zero degrees Celsius (or 32°F). From December-to-March/April, the ground is covered by snow. In southwest British Columbia, rains are more predominant than snow.
Summer season lasts from June-to-September. The weather remains warm-to-hot. During daytime, temperature varies from 20°C-30°C (68°F-86°F) or sometimes higher. In some of the places such as Quebec and southern Ontario, the environment remains very humid. Both Fall and Spring seasons are transitional in nature. They are characterized by lots of rains and the weather starts getting colder or warmer.
The highest elevation in Canada is Mount Logan (in Yukon Territory), which is 5,959 meters (19,551 feet). The lowest point is sea level (Atlantic Ocean).
The top 10 summits in Canada are present in the earth’s highest coastal mountain range – Saint Elias Range. The steepest mountain range on earth is the Saint Elias, which rises 5,486 meters (18,000 feet) upwards from the sea level in just 6 miles. Other major mountains in Canada are Mount Lucania, King Peak, Mount Steele, Mount Slaggard, Mount Vancouver, Mount Wood, and Mount Fairweather.
Major rivers of Canada are St Lawrence, Ottawa, Saguenay, Saint John, Saskatchewan, Nelson, Athabasca, Peace, Slave, Mackenzie, Yukon, Fraser, Columbia, and many more. Throughout Canada, there are 31 lakes that are spread over an area of more than 1,300 sq km (500 sq miles). The largest lakes in the country are Great Bear, Baker, Dubawnt, Great Slave, Amadjuak, Nettilling, Athabasca, Wollaston, Reindeer, Winnipeg, Southern Indian, Winnipegosis, Manitoba, Lake of the Woods, Nipigon, Mistassini, Melville, and Smallwood Reservoir.
What is the Economy of Canada?
The Canadian economy is a highly developed mixed economy. Its nominal GDP stands at US$1.709 trillion, which was growing at 3 % (World Bank, 2018). This makes Canada the tenth largest economy in the world in terms of nominal GDP. Its top trading partners are the United States, EU, China, UK, Mexico and Japan. Canada’s unemployment rate is estimated at 5.4% in May 2019, which is the lowest level since 1976.
The service sector dominates the economy of Canada, contributing around 70% to the GDP and employing three quarter (3/4th) of the labor force of over 20 million. The country is endowed with huge natural resources, which is the 4th highest in the world in terms of total estimated value (US$33.2 trillion in 2016).
Canada is an energy superpower as it comes with the 3rd largest proven petroleum reserves in the world. It is the 4th largest exporter of both petroleum and natural gas. The manufacturing sector is also very developed in Canada. Some of the leading manufacturing industries of the country include aircraft and automobile industries (mainly located in Central Canada). Other important primary sector industries include oil and logging industries.
As the country has the largest coastline, the commercial fishing and seafood industry is also highly developed, which is the eighth largest in the world. Canada is also a revered name in the global entertainment software industry.
What is the Transportation System of Canada?
Canada has a high-capacity multimodal transportation system, which includes road of over 1,400,000 kilometers (870,000 miles), ten international airports, three hundred smaller airports, functioning railway tracks of 72,093 km (44,797 miles), and over three hundred commercial ports/harbors providing easy access to the Pacific/Atlantic/Arctic Oceans, the St. Lawrence Seaway, and the Great Lakes. The transport sector makes up 4.2% of Canada’s GDP.
What International Organizations is Canada Part Of?
WTO, ADB (nonregional member), UN, NATO, UNCTAD, UNESCO, AfDB (nonregional member), IMF, APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, ILO, NAFTA, BIS, C, CD, CDB, Interpol, CE (observer), EAPC, EBRD, WHO, EITI (implementing country), FAO, FATF, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, UNHCR, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS, OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), UNFICYP, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WIPO, WMO, ZC
Related Links: