What are the Key Facts of Cambodia?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Cambodia |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Phnom Penh |
|
Largest City |
Phnom Penh |
|
Coordinates |
13.000000, 105.000000 |
|
Area |
69,898 sq. mi ( 181,035 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,572 mi ( 2,530 km) |
|
Coastline |
275 mi ( 443 km) |
|
Currency |
Riel (KHR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Vietnam, Laos, Thailand |
|
Population |
15,288,489 (2019 Census ) |
|
Official Languages |
Khmer |
|
Major Religion |
Buddhism |
|
National Day |
9 November (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Nokoreach” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
King |
Norodom Sihamoni |
|
Prime Minister |
Hun Sen |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 4,354.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,512.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.582 (2017), Rank: 146 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
80.53(UNESCO, 2015) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
84 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+855 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+07:00 (ICT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.kh |
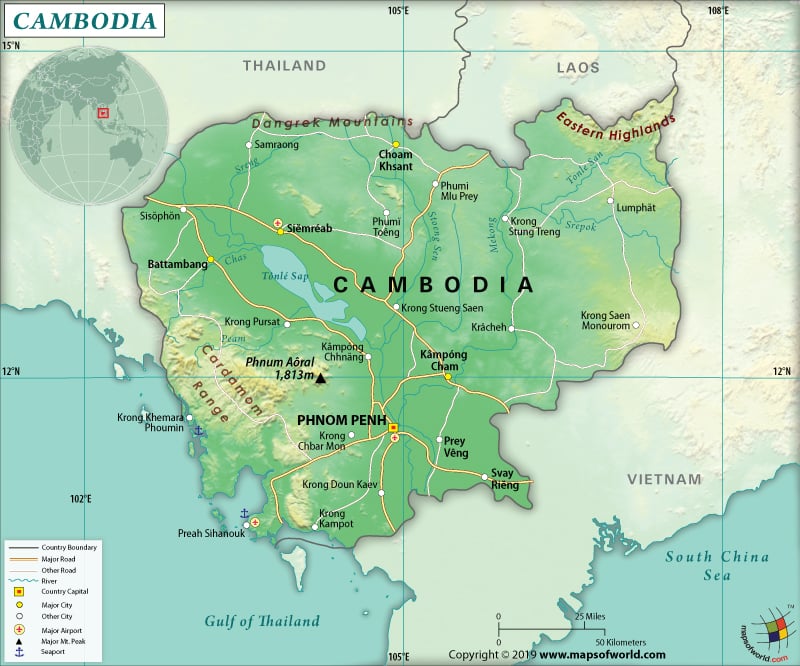
Where is Cambodia?
Cambodia is a Southeast Asian country that is bordered by the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest, Vietnam to the east, Thailand to the northwest, and Laos to the north.
What is the Geography of Cambodia?
The total area of Cambodia is 181,035 sq. km (69,898 sq. mi), out of which 176,515 sq. km (68,153 sq. mi) is land area and the rest 4,520 sq. km (1,745 sq. mi) is water area. Cambodia has a 2,530 km (1,572 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with Vietnam (1,158 km or 720 mi), Thailand (817 km or 508 mi), and Laos (555 km or 345 mi). The country also has a 443 km (275 mi) long coastline.
Lowland plain dominates the Cambodian landscape, covering around 3/4th of the total area. This plain (including both Mekong River Basin and Tonle Sap) slightly slopes towards the southwest. The landform includes mountains too.
The Cardamom Mountains are located in the southwest, the Elephant Range in the south, a high plateau in the northeast, and the Dangrek range in the northwest.
The Cambodian mountains are not much high in altitude. The highest elevation point of the country is Phnum Aoral at 1,810 m (5,938 ft). The Gulf of Thailand at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Cambodia is 126 m (413 ft). The major mountains in Cambodia are Phnom Aural, Phnom Samkos, Krachau, Chrey Mlu, Khmaoch, etc. The major rivers in Cambodia are Tonlé Sap, the Bassac River, Boribo River, Chinit River, the Kah Bpow, the Kong River, etc.
The climate in Cambodia is tropical in nature. It remains hot around the year. The rainy season (mainly because of the south-west monsoon) in this Southeast Asian country starts in May and continues till mid-November.
There are two dry seasons in Cambodia. During the first dry season, the weather remains least hot during the year. The second dry season is the hottest time of the year. It starts in mid-February and continues till May.
The monsoon starts withdrawing from the northern parts of the country in early-November. However, in the center-southern parts, the monsoon withdraws either from the middle or end of November. While the month of December is the coldest month of the year, April-May is the hottest time of the year. The climate remains more or less the same throughout the country as the country size is small.
The inland areas get 1,300-1,800 mm (51-70 in) of rainfall. However, maximum rainfall takes place in the coastal areas of the Gulf of Thailand. This place gets more than 2,000 mm (80 in) precipitation per year because vast areas are covered with forest. The highlands and mountainous areas remain a bit cooler. December-to-mid-February is the best time to visit Cambodia.
What is the Economy of Cambodia?
The Cambodian economy has a significantly high growth rate since 1995. The nominal GDP of the economy grew at 7.52% in 2018 to reach US$ 24.572 billion. The average growth rate of the economy was more than 8% during 2000-2010. The growth rate is steadily increasing at an average rate of 7% since 2011. The economy is mainly dependent on tourism, construction, real estate, garments, agricultural sector, and others.
The garment and footwear sector industry employ around 700,000 people, out of which most are women. While the tourism sector employs around 500,000 people, construction employs around 200,000 people. Around 5.6 million tourists visit the country every year. The mining sector (for extraction of gems, iron, gold, and bauxite) is also expanding.
In 2017, Cambodia exported US$15.8 billion value of goods and imported US$12 billion value of goods, generating a positive balance of trade of around US$3.82 billion. The main export items are Knit Sweaters, Knit/Non-Knit Women’s Suits, Non-Knit Men’s Suits, Knit T-shirts, etc. The major import items are Gold, Pile Fabric, Rolled Tobacco, Refined Petroleum, Light Rubberized Knitted Fabric, etc.
Unemployment rate was 0.1% in 2017, less than 0.2% in 2016. The average unemployment rate from 1994 to 2017 was 0.98%. Official data shows that the rate of poverty came down from 47.8% in 2007 to 13.5% in 2014. Around 4.5 million people are vulnerable to falling back to poverty in case of fluctuations because they remain near-poor.
What is the Transportation System of Cambodia?
There are 47,263 km (29,368 mi) long roadways in Cambodia, out of which 12,239 km (7,605 mi) is paved and 35,024 km (21,763 mi) is unpaved. 642 km (399 mi) long railway tracks are available in the country and all of them are narrow-gauge ones. Around 3,700 km (2,299 mi) of waterways are also available and they are mainly concentrated on the Mekong River. While Sihanoukville (Kampong Saom) is the main seaport, Phnom Penh (Mekong) is the main river port. There are 364 merchant marine vessels in Cambodia. A total of 16 airports are present in this Southeast Asian country, out of which just 6 have paved runways and the rest 10 have unpaved runways. One heliport is also there in Cambodia.
What International Organizations is Cambodia part of?
UN, ILO, IMF, UNESCO, NAM, ADB, ARF, ASEAN, CICA, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, MINUSMA, MIGA, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, CICA (observer), ISO (correspondent), WFTU (NGOs)