What are the Key Facts of Benin?
| Official Name | Republic of Benin |
| Continent | Africa |
| Capital | Porto-Novo |
| Largest City | Cotonou |
| Coordinates | 9.500000, 2.250000 |
| Area | 44,310 sq. mi ( 114,763 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,319 mi ( 2,123 km) |
| Coastline | 75 mi ( 121 km) |
| Currency | West African CFA franc (XOF) |
| Neighboring Countries | Togo, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria |
| Population | 10,872,298 (2016 est. ) |
| Official Languages | French |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 1 August (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | “L’Aube Nouvelle” |
| Form of Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| President | Patrice Talon |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 2,420.5 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 902.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.515 (2017), Rank: 163 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | NA |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 124 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 0 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +229 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1 (WAT) |
| Internet TLD | .bj |
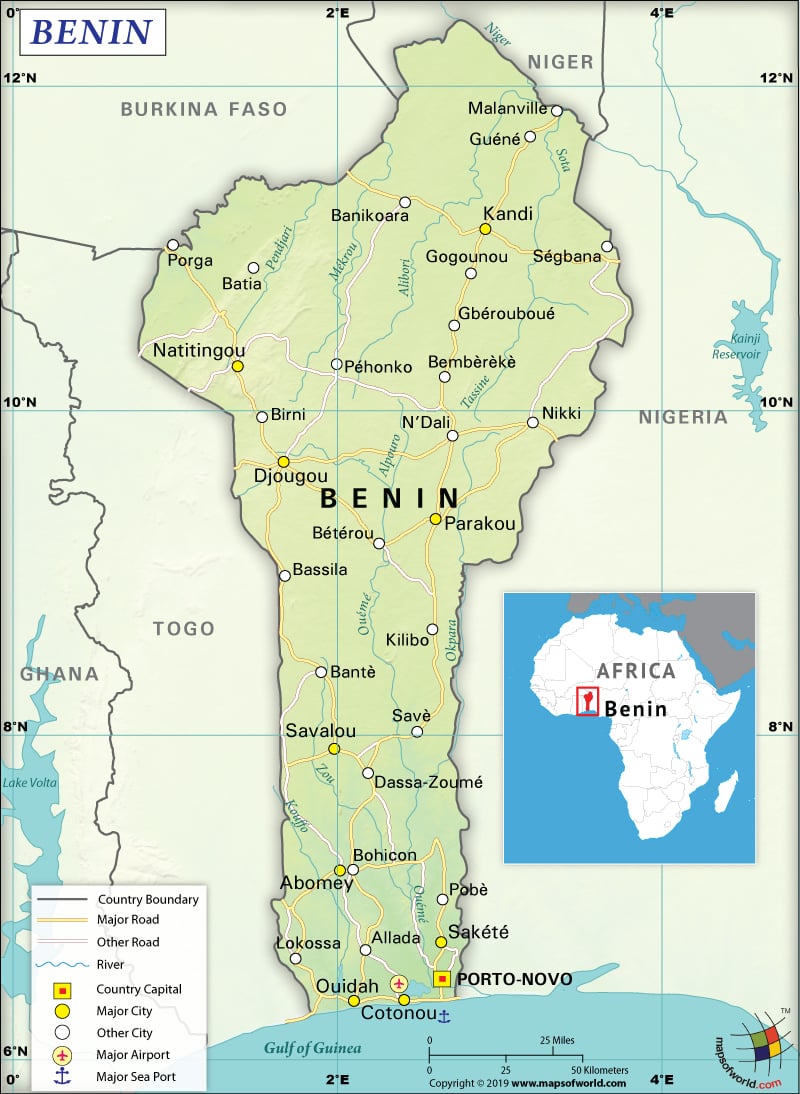
Where is Benin?
Benin (formerly known as Dahomey) is a West African country that shares 2,123 km (1,319 mi) of land boundaries with its neighboring countries. It shares its borders with Nigeria (809 km or 503 mi) to the east, Togo (651 km or 405 mi) to the west, and Burkina Faso (386 km or 240 mi) and Niger (277 km or 172 mi) to the north.
What is the Geography of Benin?
To begin with, Benin is spread across a total area of 114,763 sq. km (44,310 sq. mi), out of which 110,622 sq. km (42,711 sq. mi) is land and 2,000 sq. km (772 sq. mi) is water. The total coastline of Benin is just 121 km (75 mi). Mont Sokbaro is the highest elevation point of the country at 658 m (2,159 ft). Sea level at Atlantic Ocean is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Benin is 273 m (896 ft). Here is Benin Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
Moreover, the country can be divided into four distinct geographical areas from the south to the north. The coastal plain having the highest elevation of 10 m (32.8 ft) is located in the southern part of Benin. It is predominantly low-lying and sandy. The maximum width of this coastal plane is 10 km (6.2 mi). This coastal plain is characterized by marshy lands with many lakes/lagoons connecting to the sea.
Further, as you move towards the north (just behind the coast), you will find southern Benin’s plateaus that are covered by the Guinean forest-savanna mosaic. The altitude of these plateaus varies from 20-200 m (66 -656 ft). Valleys along the rivers such as Ouémé River, Zou River, and Couffo River split the plateaus.
The third important geographical area includes flat land having rocky hills (maximum height is 400 m or 1,312 ft), extending around Nikki and Save. The fourth geographical area includes the mountainous range that is also known as the Togo Mountains or Atacora. They extend along the northwest border of Benin. Gbessa, Touloua Toundi, Boto, Deï Tondi, and Guéné Zéno are the main mountains of Benin.
The climatic condition of Benin is predominantly hot and humid. Every year, there are two rainy and dry seasons. April-to-late-July is the main rainy season followed by a short and cooler dry season from late-July-to-early-September. The second rainy season starts from September and continues till November. However, rainfall is less intense. The main dry season starts from December and continues till April.
The tropical coast has a higher temperature and humidity. The average maximum and minimum temperatures in Cotonou are 31 °C (87.8 °F) and 24 °C (75.2 °F). The average annual rainfall in Benin is around 1,300 mm (51 in). A dry wind called Harmattan blows from the Sahara during December-to-March.
What is the Economy of Benin?
The economy of Benin is underdeveloped. It is mainly dependent upon subsistence agriculture, regional trade and production of cash crop such as cotton. Benin’s nominal GDP was US$10.359 billion in 2018. The economic growth rate has also improved from 5.6% in 2017 to 6% in 2018.
The factors that accelerated the country’s economic growth include increased public sector investment in infrastructure, vibrant port activity, improved service sector performance, record production of cotton, and sound agricultural sector. The rate of unemployment stands at 2.1% in 2018.
However, rising food prices have increased inflation from -0.8% in 2016 to 0.1% in 2017 and further to 2.3% in 2018. There has been a slight improvement in the current account deficit (from 9.9% of GDP in 2017 to 8.9% of GDP in 2018), propelled by the higher agricultural exports. Consequently, the fiscal deficit has also improved from 5.9% of GDP in 2017 to 4.7% of GDP in 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Benin?
The main transportation systems of Benin include road, water, rail, and air transports. The total roadways available in the country are 16,000 km (9,942 mi), out of which most of them are unpaved. 6,787 km (4,217 mi) of highways are there in Benin. However, only 1,357 km (843 mi) are paved highways.
In addition, 10 expressways are there in the country. The Trans-West African Coastal Highway passes through Benin, thereby connecting it with other neighboring African countries including Nigeria, Ghana, Togo, and Ivory Coast. Another paved highway connects Benin with Burkina Faso, Niger, and Mali.
150 km (93 mi) of waterways are also present in Benin. Cotonou is the major seaport and there are six merchant marine ships in the country. The railway transport system is limited and is just 438 km (272 mi) long. While 6 airports are there is Benin, only 1 is paved.
What International Organizations is Benin part of?
IMF, ACP, WTO, AfDB, AU, UNESCO, CD, UN, ECOWAS, WHO, Entente, UNCTAD, FAO, UNHCR, FZ, Interpol, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UNAMID, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WAEMU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), WADB (regional), OAS (observer)