What are the Key Facts of Azerbaijan?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Azerbaijan |
|
Continent |
Asia, Europe |
|
Capital |
Baku |
|
Largest City |
Baku |
|
Coordinates |
40.500000, 47.500000 |
|
Area |
33,436 sq. mi (86,600 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,533 mi (2,468 km) |
|
Coastline |
443 mi (713 km) (Coastline with Caspian Sea) |
|
Currency |
Manat (₼) (AZN) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Armenia, Georgia, Iran, Russia, Turkey. |
|
Population |
10,023,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Azerbaijani |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
28 May (Republic Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Azerbaijan Marsi” |
|
Form of Government |
Presidential republic |
|
President |
Ilham Aliyev |
|
Prime Minister |
Ali Asadov |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 15,000.8 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 4,793.6 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.754 (2019), Rank: 87 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
99.79 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
Azerbaijan National Aerospace Agency |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
61 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
42 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
994 |
|
Time Zone |
AZT (UTC+04) |
|
Internet TLD |
.az |
Where is Azerbaijan?
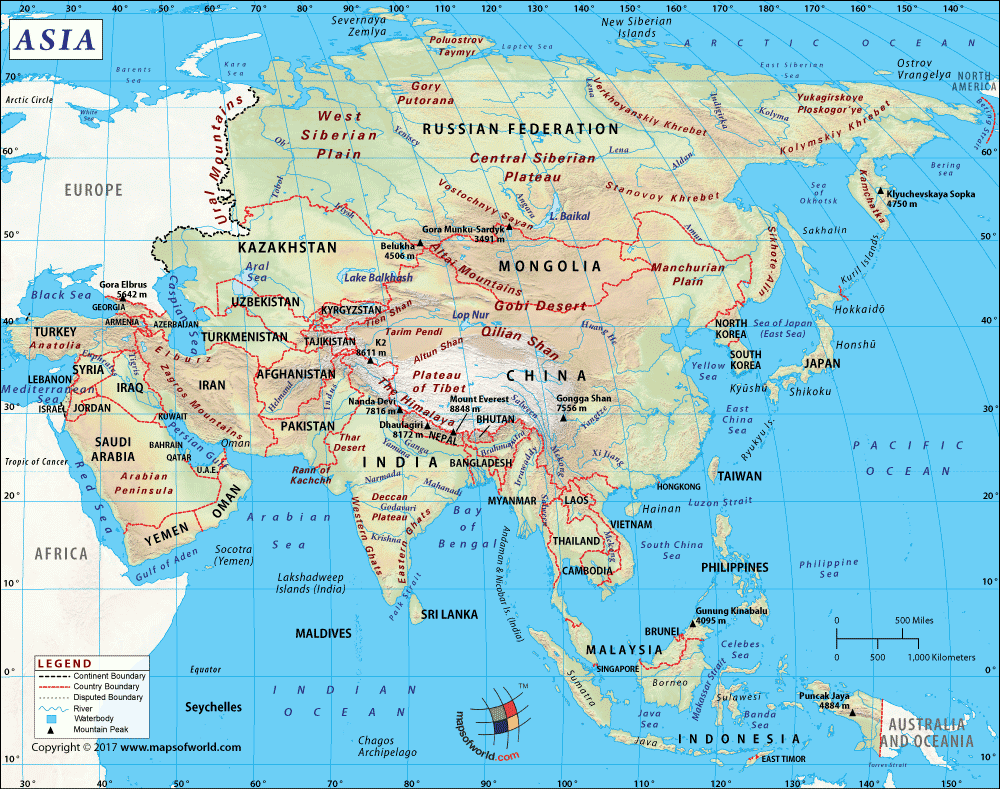
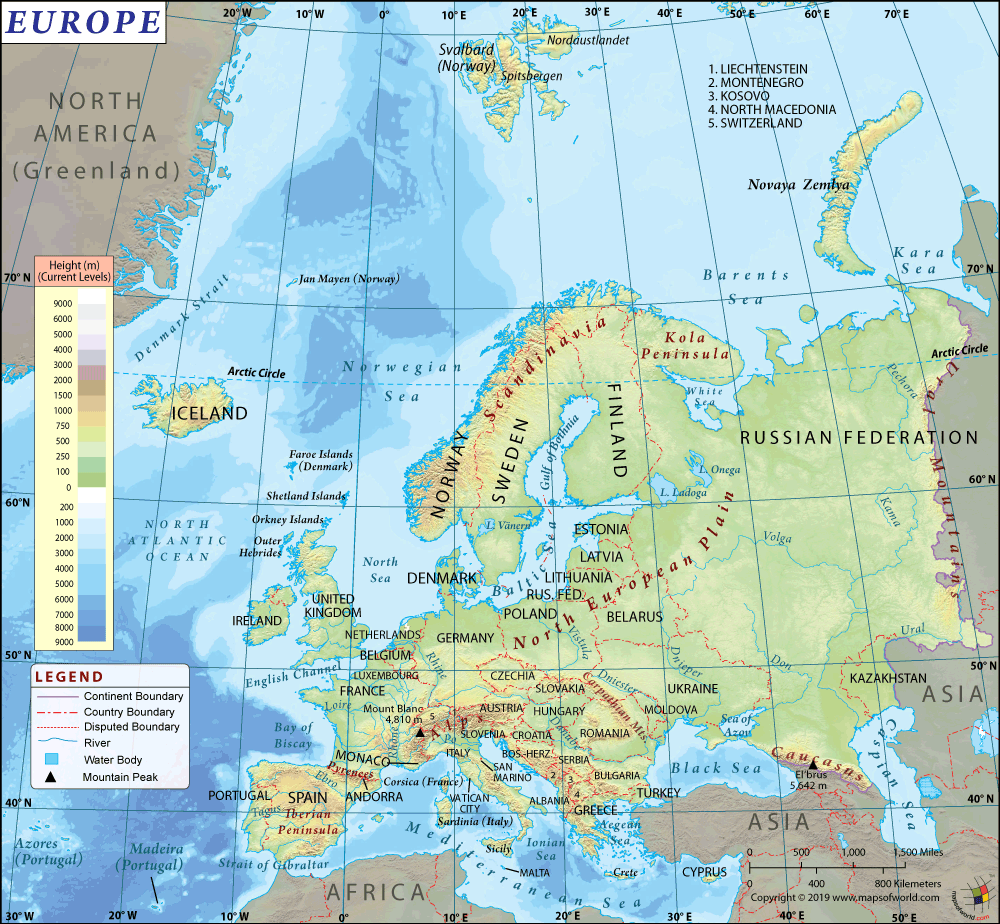
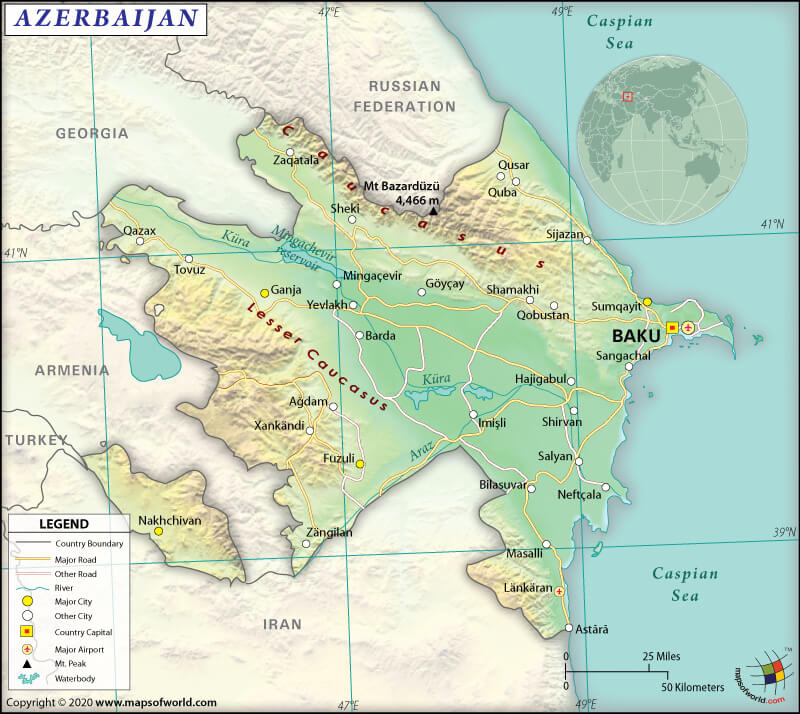
Azerbaijan (whose official name is the Republic of Azerbaijan) is a Eurasian country that is in the Caucasus region (at the intersection of Western Asia and Eastern Europe). Most parts of the country are in South West Asia, with a small portion located north of the Caucasus range. It borders the Caspian Sea and lies between Iran and Russia.
What is the Geography of Azerbaijan?
Azerbaijan spreads across a total area of 33,436 sq. mi (86,600 sq. km). Out of the total area, 31,903 sq. mi (82,629 sq. km) is land area, and 1,533 sq. mi (3,971 sq. km) is the water area.
The Republic of Azerbaijan’s total land boundary is 2,468 km (1,533.5 mi) long. It shares its border with Armenia (618.9 mi or 996 km), Iran (689 km or 428.1 mi), Georgia (265.9 mi or 428 km), Russia (210 mi or 338 km), and Turkey (106 mi or 17 km). Azerbaijan is a landlocked country and has no coastline. It is important to note that the country has a 443 mi (713 km) long border with the Caspian Sea.
The mean elevation of Azerbaijan is 1259.8 ft (384 m). While the highest point is Bazarduzu Dagi at 14652.2 ft (4,466 m), the lowest point is the Caspian Sea at -91.9 ft (-28 m).
The terrain of Azerbaijan is characterized by the Kura-Araks Lowland (called Kur-Araz Ovaligi, locally), much of it is below sea level. While the Great Caucasus Mountains are towards the north of Kura-Araks Lowland, the Karabakh Upland (called Qarabag Yaylasi, locally) is to its west. Baku (the capital of Azerbaijan) is on Apsheron Peninsula (called Apsheron Peninsula, locally), which extends into the Caspian Sea.
Almost 60% of the landforms of the country are mountains. There are three main mountain ranges in Azerbaijan, and they are the Talysh Mountains, the Lesser Caucasus, and the Greater Caucasus.
The highest mountains are Bazardüzü, Shahdagh, Tufandag, Yarudag, Raqdan Dagi, etc. There are three main river systems in the country, and they are the Kur basin, Araz basin, and the rivers flowing directly to the Caspian Sea. Major rivers of Azerbaijan are Kura, Aras, Alazani, Lori, Samur, Tartar, etc.
Besides the most significant inland water body in the world, the Caspian Sea, the other major lakes in Azerbaijan are Mingachevir Reservoir, Shamkir Reservoir, Lake Sarysu, Lake Ağgöl, and many more.
What is the Climate of Azerbaijan?
Azerbaijan has a continental influenced climate, characterized by warm summer and freezing, dry winters. Three different climate zones are found in the country:
- The climate in the north of the mountainous regions.
- The climate in the south of the mountainous regions.
- The climate along the coast of the Caspian Sea.
As per the Koeppen-Geiger classification, Azerbaijan’s climate is classified as a Dfb climate. The country has a humid snow climate.
- During the warmest month, the average temperature remains below 71.6 °F (22 °C).
- For around four or more months, the temperature remains above 50 °F (10 °C).
- During the coldest month of the year, the temperature remains below 26.6 °F (-3 °C).
The temperature during the summer season in Azerbaijan remains within 68-86 °F (20-30 °C). It usually remains warm, sunny, and dry. However, sometimes heavy cloudbursts and severe thunderstorms can take place, causing local flashfloods and damage.
It remains significantly cold during December-March. The daily temperature during these months dip far below zero and causes small snowfall. Severe weather conditions are found in the mountainous regions. It remains icy with powerful winds and snowstorms.
The Sheki Zakataly region is just south of the mountains. It has a significantly different type of climate in comparison to the northern regions. Sheki Zakataly region’s climate is characterized by warmer summers, a bit milder winters, and less rain. Due to the tempering effect of the Caspian Sea, the coastal areas remain significantly warmer than that of the mountainous areas.
What is the Economy of Azerbaijan?
The economy of Azerbaijan is heavily dependent upon oil export, thanks to the presence of vast oil reserves. After the completion of the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan Pipeline, it became a major oil-based economy.
With remarkable transition brought by increasing oil production, the GDP of Azerbaijan jumped from 9.254% in 2004 to 27.962% in 2005 and 34.466% in 2006. However, it came down to 4.789% in 2010, followed by -1.573% in 2011. In 2019, the nominal GDP grew at a rate of 2.219% to US$48.048 billion.
The values of export and import in 2018 were US$19.9 billion and US$11.9 billion, respectively, resulting in a positive trade balance of US$8.01 billion. Major export items are Crude Petroleum, Petroleum Gas, Refined Petroleum, Tomatoes, and Gold. Major imports of Azerbaijan are Gold, Cars, Iron Pipes, Petroleum Gas, and Gas Turbines.
The unemployment rate in this Eurasian country has remained more or less stable during 2016-19. It had increased marginally from 5% in 2016 to 5.51% in 2019. As per ADB data, the poverty rate in Azerbaijan was 5.1% in 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Azerbaijan?
Azerbaijan has 37 airports. While 30 have paved runways, 7 have unpaved runways. The major airports are Heydar Aliyev International Airport (Baku), Ganja International Airport (Ganja), Lankaran International Airport (Lankaran), Qabala International Airport (Qabala), Nakhchivan International Airport (Nakhchivan), Zaqatala International Airport (Zaqatala), etc.
There are 24,981 km (15,522.5 mi) long roadways and 2,944 km (1,829.3 mi) long broad-gauge railways available. Baku on the Caspian Sea is the principal seaport in Azerbaijan. There are 305 merchant marine vessels available in the country, out of which 40 are general cargo, 48 are oil tankers, and 217 other types of vessels.
What International Organizations is Azerbaijan part of?
ADB, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, BSEC, CD, CE, CICA, CIS, EAPC, EBRD, ECO, FAO, GCTU, GUAM, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer), EITI (compliant country), ICC (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), SELEC (observer), WFTU (NGOs)