What are the Key Facts of Austria?
| Official Name | Republic of Austria |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Vienna |
| Largest City | Vienna |
| Coordinates | 47.333333, 13.333333 |
| Area | 32,386 sq. mi ( 83,879 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 1,568 mi ( 2,524 km) |
| Coastline | 0 mi (0 km) landlocked |
| Currency | Euro (€) (EUR) |
| Neighboring Countries | Czech Republic, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, Slovenia, Switzerland |
| Population | 8,857,96 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | German |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 26 October (National day) |
| National Anthem | “ Bundeshymne” |
| Form of Government | Federal parliamentary republic |
| President | Alexander Van der Bellen |
| Chancellor | Sebastian Kurz |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $ 55,509.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $ 51,512.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
| HDI | 0.908 (2017), Rank: 20 |
| Literacy Rate (%) | NA |
| Space Agency | Austrian Space Agency |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 51 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 319 (as of 2018) |
| Driving Side | right |
| Calling Code | +43 |
| Time Zone | UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Internet TLD | .at |
Where is Austria?
Austria is a Central European country that is located to the north of both Slovenia and Italy.
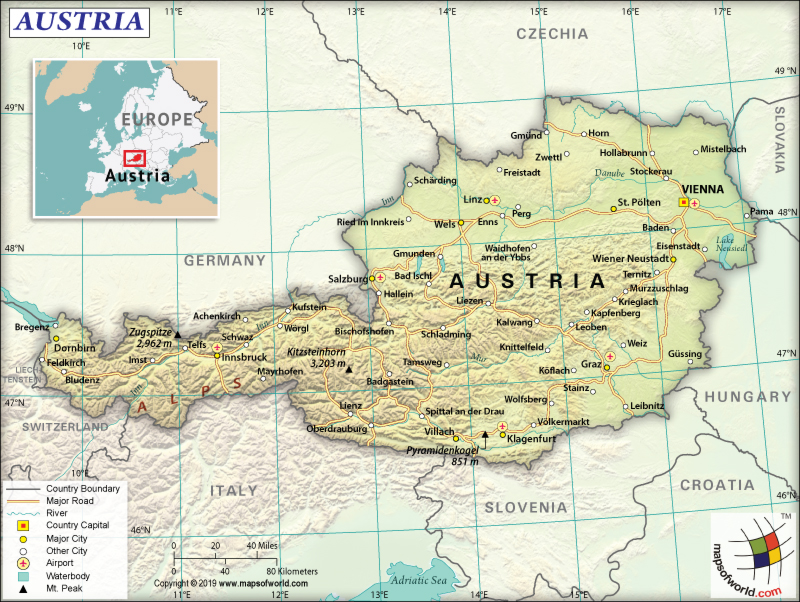
What is the Geography of Austria?
The total area of Austria is 83,879 sq. km (32,386 sq. mi), out of which 82,445 sq. km (31,832 sq. mi) is land area and 1,426 sq. km (551 sq. mi) is water area. It is a landlocked country and has no coastline or maritime claims.
The country has a 2,524 km (1,568 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with 8 neighboring countries: Germany (801 km or 498 mi), Italy (404 km or 251 mi), Czech Republic (402 km or 250 mi), Hungary (321 km or 199 mi), Slovenia (299 km or 186 mi), Switzerland (158 km or 98 mi), Slovakia (105 km or 65 mi), and Liechtenstein (34 km or 21 mi).
Austria has mainly two types of terrains: mountains and flat or gently sloping areas. While the mountains (mainly Alps) are located in the western and southern regions of Austria, the flat and gently sloping areas are located mainly in the eastern and northern margins of the country.
While the Grossglockner at 3,798 m (12,461 ft) is the highest elevation point of the country, Neusiedler See at 115 m (377 ft) is the lowest elevation point. The mean elevation of Austria is 910 m (2,986 ft). Major mountains in Austria are Grossglockner, Wildspitze, Kleinglockner, Weißkugel, Großvenediger, etc. Major rivers in the country are Danube, Rhine, Drava, Inn, Raba, Morava, etc.
Around 62% of the total area of Austria is covered by the Alps. Around 28% of the landform is either flat or moderately hilly. The flatter areas consist of the Northern Alpine Foreland including the Danube Valley, the Danube Basin, the lowlands, and the hilly regions. The remaining 10% of the landform is covered by a low mountain range, the Bohemian Granite Massif, situated to the north of the Danube Valley.
While the western and northwestern regions of Austria are influenced by the temperate Atlantic climate, the eastern regions are influenced by the continental climate. Temperature varies in accordance with the altitude. With every 300 m (984 ft) higher altitude, the average temperature drops by around 5 °C (41 °F). During summertime, the daytime temperature can reach 30 °C (86 °F) or even more. However, the evenings/nights generally remain cool even in the summer.
The extent of rainfall is almost evenly distributed around the year. While April and November months are the wettest periods of the year, May, September, and October’s first half remain the driest. The high-level areas in the Alps get more rainfall, which is above 2,000 mm (79 in) per year. However, the flatter areas get around 600 mm (24 in) of rainfall every year.
Rain is accompanied by thunderstorms and heavy hail during June-August. The mountainous regions of the Alps also get snowfall even during summertime.
The northern and eastern regions of Austria get hotter summers and colder winters as the weather is influenced by a more continental climate. As the Mediterranean climate influences the southern regions of Austria, the summers are warmer and longer. The weather can change quickly at higher altitudes.
Snowfall is a permanent phenomenon at altitudes above 2,500 m (8,202 ft). At around 1,800 m (5,906 ft), the snow cover lasts from November to May. In the valleys, the winter snow cover lasts from December to March.
What is the Economy of Austria?
Austria has a developed market economy, whose Doing Business ranking was 22nd in 2018. It also has a high HDI, whose rank was 20th out of 189 countries in 2017. The Austrian economy boasts of having a skilled labor force along with a high standard of living. Its largest trade partners are Germany and the US.
The economy had a negative trade balance in 2017. While it exported around U$148 billion value of goods, it imported US$162 billion of goods. The major export items were vehicle parts, packaged medicaments, human/animal blood, cars, flavored water, etc. The major items imported by Austria are refined petroleum, cars, packaged medicaments, and vehicle parts.
The unemployment rate in 2018 was 4.79%. During 1998-2018, the highest rate of unemployment was reached was 6.01% in 2016. OECD data shows that the poverty rate in Austria was just 0.10%.
What is the Transportation System of Austria?
Austria has a developed transport system. It has 137,039 km (85,152 mi) long roadways, including 2,232 km (1,387 mi) of expressways. The country has 5,800 km (3,604 mi) long standard-gauge railway network, including 3,826 km (2,377 mi) of the electrified railway network. 358 km (222 mi) of the waterway is also available. The major river ports are Vienna, Linz, Krems, and Enns. There are 52 airports, out of which 24 paved and 28 unpaved runways.
What International Organizations is Austria part of?
UN, WTO, Australia Group, BIS, CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, G-9, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNFICYP, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), BSEC (observer), ICC (national committees), IGAD (partners), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OIF (observer), SELEC (observer), Schengen Convention, WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links: