What are the Key Facts of Angola?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Angola |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Luanda |
|
Largest City |
Luanda |
|
Coordinates |
-12.500000, 18.500000 |
|
Area |
481,400 sq. mi ( 1,246,700 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
3,336 mi ( 5,369 km) |
|
Coastline |
994 mi ( 1,600 km) |
|
Currency |
Kwanza (AOA) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Zambia, Namibia |
|
Population |
25,789,024 (2014 Census) |
|
Official Languages |
Portuguese |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
11 November (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Angola Avante” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary dominant-party presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
João Manuel Gonçalves Lourenço |
|
Vice President |
Bornito de Sousa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 6,441.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 3,432.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.581 (2017), Rank: 147 |
|
Literacy Rate |
66.03 % (2014, UNESCO) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
56 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+244 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (WAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.ao |
Where is Angola?
Angola is a southern African country that borders the South Atlantic Ocean. It is situated between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (to the north) and Namibia (to the south).
What is the Geography of Angola?
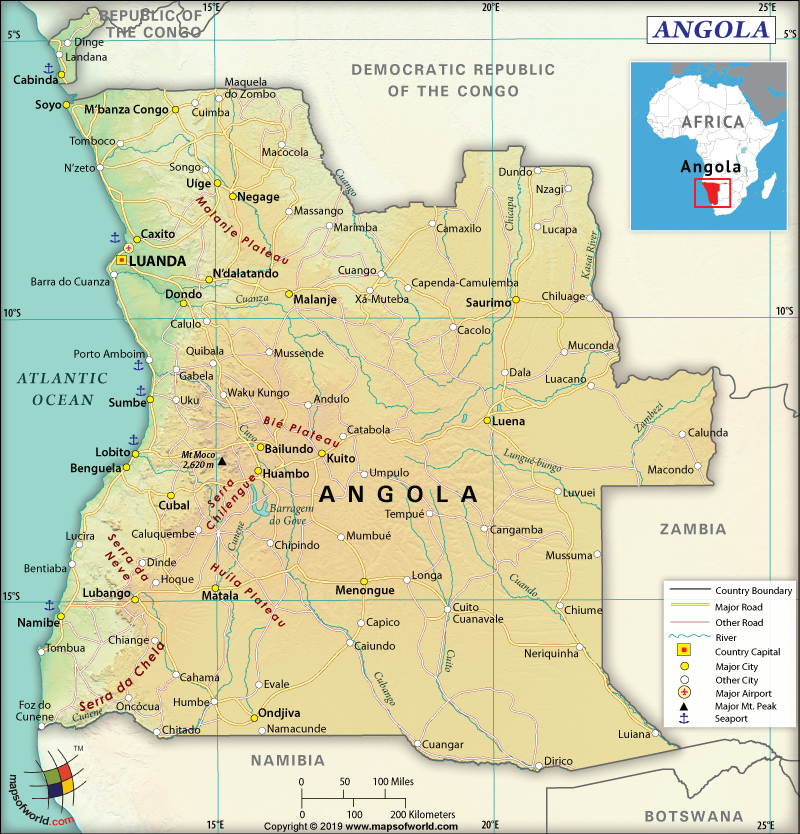
Angola is spread across a total area of 1,246,700 sq. km (481,400 sq. mi), out of which 1,246,700 sq. km (481,354 sq. mi) is land area and 0 sq. km (0 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 5,369 km (3,336 mi) long land boundary, which is shared with 4 countries: Democratic Republic of the Congo (2,646 km or 1,644 mi, which includes 225 km or 140 mi boundary of Cabinda Province), Namibia (1,427 km or 887 mi), Zambia (1,065 km or 662 mi), and Republic of the Congo (231 km or 144 mi). The country has a 1,600 km (994 mi) long coastline. Here is Angola Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
The terrain of Angola consists of a narrow coastal plain, rising abruptly to vast interior plateau. The mean elevation of the country is 1,112 m (3,648 ft). While Moca (in the Ahaggar Mountains) is the highest elevation point of Angola at 2,620 m (8,596 ft), the Atlantic Ocean is the lowest elevation point at 0 m (0 ft).
There are four regions in this country and they are coastal lowland (mainly arid), high plateau called planalto, hills and mountains rising inland, and rain forest. The stretch of the coastal belt varies within 30-100 mi (48-161 km) inland and then it merges with a rolling hill belt and a scattered mountain series.
The major mountains in Angola are Moco, Lupangue, Vavele, Mbuindo, Senha, Ungungi, etc. The high plateaus of Angola lie between 4,000 ft (1,200 m) and 6,000 ft (1,800 m). They are located to the east of the hills and mountains. There are many rivers that flow through this African country such as the Zambezi River, Congo River, Kwango River, Cuando, Cubango, etc.
One of the largest waterfalls, in terms of volume, located in Africa is Kalandula. It is 344 ft (105 m) high. A narrow strip of land belonging to the Democratic Republic of Congo separates Cabinda (a northern Angolan province) from the mainland Angola.
This large African country in the southern hemisphere overlooking the Atlantic Ocean has a sub-tropical climate. The altitude in the plateau as well as the cool sea current along the coastal belt tempers the climate.
A cool and dry season (the austral winter) called Cacimbo prevails during May-August. During mid-September-April, the austral summer (hot and rainy season) can be found in the north-eastern parts of Angola. In the central parts of the country, the austral summer prevails from mid-October to April. The southern part of the country has austral summer during November-March. While it is almost non-existent on the southern coast, in Luanda it starts in February and continues till April.
The Benguela Current, cool sea current, flowing along the coast makes the southern and central parts of the country mild and dry. More rainfall takes place in the inland areas than in the coastal areas. The northern and central parts get more rain, mainly because of greater proximity to the Equator.
Mid-May to August is the best time to visit Angola.
What is the Economy of Angola?
The Angolan economy is heavily dependent upon the oil industry. The production of oil along with the related activities accounts for half of the country’s GDP. It also contributes 70% to the government revenue. The oil sector almost entirely contributes to the export of Angola. In 2018, the nominal GDP grew at the rate of -2.133% to reach US$ 105.751 billion (far less than US$ 122.124 billion in 2017).
The economy of Angola had a positive balance of trade of US$19.9 billion in 2017. While it exported US$30.3 billion value of goods, it imported US$10.4 billion values of goods. The major exports of the country are Petroleum Gas, Crude Petroleum, Diamonds, Passenger/Cargo Ships, Refined Petroleum, etc. The major imports of Angola are Refined Petroleum, Raw Sugar, Passenger/Cargo Ships, Excavation Machinery, Poultry Meat, etc.
The rate of unemployment in Angola was 7.25% in 2018. Despite being an oil industry-based economy, 2/3rd of the economy still lives in poverty. Reports say that 94% of the rural population (which accounts for 38.5% of the total population) is considered poor (living on less than $2 per day).
What is the Transportation System of Angola?
The transport system in Angola is mainly dependent on roadways, railways, airways, and waterways. There is 26,000 km (16,156 mi) long roadway available in Angola, out of which 13,600 km (8,451 mi) are paved and 12,400 km (7,705 mi) are unpaved.
Angola has 176 airports, out of which 31 have paved runways and 145 unpaved runways. 1 heliport is also there. 2,852 km (1,772 mi) long railway track is there in the country, out of which 2,729 km (1,696 mi) is narrow gauge and the rest 123 km (76 mi) is 0.600-m gauge. 1,300 km (808 mi) long navigable waterway is also there in Angola. There are 55 merchant marine vessels in the country.
What International Organizations is Angola part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, Union Latina, ILO, ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CPLP, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPEC, SADC, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ISO (correspondent), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), WFTU (NGOs)