Why so much occurrence of typhoons in Japan?
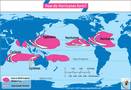
 Typhoons are areas of very intense low atmospheric pressure that occur over the north-western Pacific Ocean. These are tropical storms with sustained wind speeds of about 65 mph near the center. A typhoon is very similar to a hurricane but is formed over the Pacific region while a hurricane forms over the Atlantic. They are accompanied by high wind speeds, rise in sea levels, and torrential rainfalls. They also cause floods and landslides. Typhoons leave a trail of destruction when they make a landfall on any of the south-eastern countries such as Japan, Philippines, and Indonesia.
Typhoons are areas of very intense low atmospheric pressure that occur over the north-western Pacific Ocean. These are tropical storms with sustained wind speeds of about 65 mph near the center. A typhoon is very similar to a hurricane but is formed over the Pacific region while a hurricane forms over the Atlantic. They are accompanied by high wind speeds, rise in sea levels, and torrential rainfalls. They also cause floods and landslides. Typhoons leave a trail of destruction when they make a landfall on any of the south-eastern countries such as Japan, Philippines, and Indonesia.
The occurrence of a tropical storm is not a weather phenomenon confined to Japan alone. These occur in great number along the Atlantic shores as well. Cyclones and storms developing over the Atlantic are called Hurricanes. Similar storms that develop over the Indian Ocean are referred to as Cyclones. This having been said, it must be admitted that Japan faces more than its share of typhoons due to its location in the western Pacific Ocean – the region with the greatest number of tropical storms on Earth. This region is referred to as the Typhoon Alley. Between 2000 and 2014, meteorologists recorded the development of 41 super typhoons in this region as compared to 12 in the Atlantic Basin.
Meteorologists report that on an average about 26.7 tropical cyclones or typhoons form over the Pacific Ocean each year. Of these about 11 approach Japan and an average of 2.6 makes a landfall in the country each year. A number of “super typhoons” with wind-speeds over 150 mph have been known to hit the country. Each year some 7 or so typhoons approach the Okinawa Prefecture.
Occurrence of Typhoons in Japan
Japan is considered to be right at the heart of the Typhoon Alley making it very vulnerable to the devastation caused by these tropical storms. The main Islands of Kyushu and Shikoku receive the brunt of about 2 or 3 typhoons each year. While these are the worst affected parts, just about any part of Japan including Tokyo, Hokkaido, and Osaka may be affected by typhoons.
In Japan, the typical typhoon season lasts from early August to late September. This period is often referred to as the Akisame. With the increase in freak weather phenomenon caused due to climate change it is observed that typhoons start to form early, some originating even in June and July, which is the main rainy season in the archipelago.
Typhoons in Japan are referred to as Typhu in their language. Due to its high exposure to earthquakes and typhoons, the country has a highly developed weather prediction system. This means that the origin and course of a typical typhu can be predicted by the Japanese Meteorological Agency (JMA) with a great degree of accuracy. When the center of a typhoon is within 186 miles of the country, a typhoon warning is issued. The warning is then upgraded or downgraded as the storm approaches. Most of the destruction is borne by the coastal regions.
Japan has also developed a systematic and well-honed typhoon response system. The people in Okinawa and other vulnerable regions are well prepared for the onset of the typhoon season each year. The country has large scale evacuation measures in place. The country has put in place well-developed flood prevention measures in place. These minimize the damage done by the typhoon in case of a landfall.
The most devastating typhoon that wrought devastation in Japan (since World War II) was called the Isewan Typhoon. In September 1959, Isewan Typhoon made its landfall in the Tokai region killing over 5,000 people. In recent times the typhoons approaching Japan are numbered (rather than named) and the amount of devastation caused is greatly controlled. Some of the super typhoons that cause great destruction are, however, still named to aid the assessment of large-scale impact. About a dozen or so people, mostly fishermen still lose their lives due to typhoon related events each year in Japan.
Know more about world disasters:
Related links: