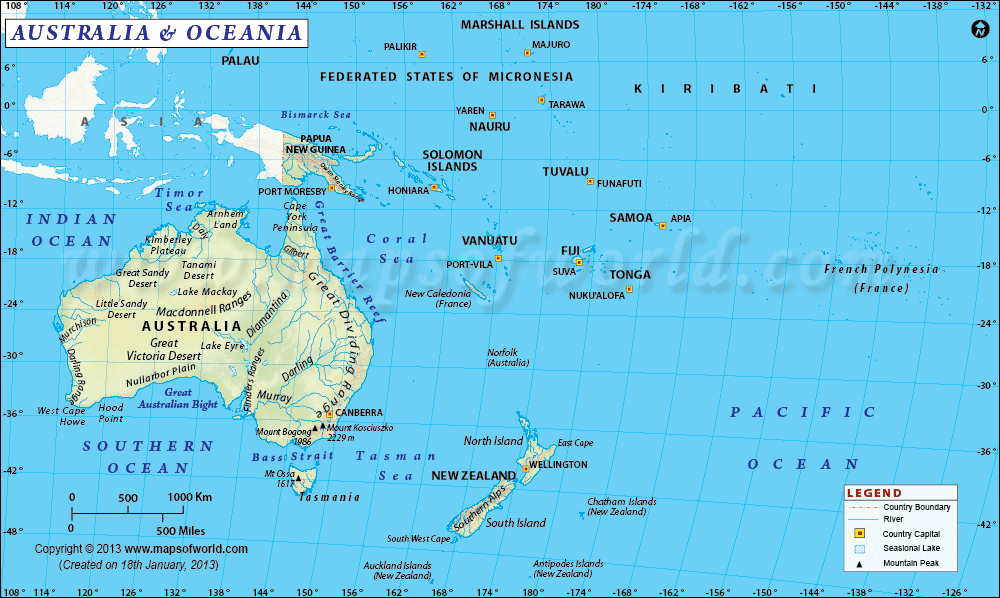
Explore this Map of Oceania to know everything you want to know about the continent. Learn about the location of Oceania in the world. Check out its geography, time zones, history, flag, and many more.
Covering an area of 3,291,903 square miles in the southeast of the Asia Pacific region, Oceania is often mistakenly considered a continent. It is however, only a collection of islands (including country islands), and sustains 14 UN recognized countries, 2 non-UN member countries and 23 territories. The most populated and largest country in Oceania is Australia, with Sydney being the largest city.
The 2 non-UN member countries in Oceania are Cook Islands and Niue. The 23 UN recognized dependent territories of Oceania are American Samoa, Ashmore and Cartier Islands, Baker Island, Coral Sea Islands, Easter Island, French Polynesia, Guam, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, New Caledonia, Norfolk Island, Northern Mariana Islands, Ogasawara Village, Palmyra Atoll, Papua Pitcairn Islands, Tokelau, Wake Island, Wallis and Futuna, and West Papua.
Despite the large number of countries and territories, Oceania is the smallest continental grouping in land area. It is the second least populated grouping, after the continent of Antarctica. 40 million people are inhabited in the region. To explore more about the continents, check out our World Continents Map.
Oceania Facts |
|
|---|---|
| Lat Long | 30.0000° S, 140.0000° E |
| Demonym | Oceanic, Oceanian |
| Countries | 14 |
| Dependencies | 25 |
| Total Area | 3,296,044 sq. mi (8,536,716 sq. km) |
| Population | 38.82 million |
| Largest Country | Australia |
| Smallest Country | Nauru |
| Largest City | Sydney |
| Major Language | English |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| Time Zone | UTC+8 to UTC-6 |
History of Oceania
It was between 50,000 and 30,000 years ago, that the earliest inhabitants arrived in Oceania. The first settlements were witnessed in Australia, New Guinea, and the large islands on the eastern side of Oceania. Europeans began their explorations in the 16th century. Between 1512 and 1526, Portuguese explorers arrived at the Tanimbar Islands, few of the Caroline Islands and west Papua New Guinea. In 18th century, James Cook, reached the Tahiti and east coast of Australia, on his first voyage. However, the major attention was brought to the Pacific region during the Second World War, owing to the rivalry between Allied Powers (United States and Australia), and Axis powers (Japan). Since, the social and political norms were altered because of the explorations, plenty discussions are being carried out recently by Oceanians, to have their individualistic identity and their own flag.
Oceania Cruises
Oceania Cruises are the world’s largest elegant cruise ship. It is a traveler’s delight, and the services one gets onboard are truly unparalleled. Sailing across the world since 2002, taking a cruise on Oceania Cruises is really worth a lot. There are three ships of the Oceania Cruises Oceania Cruises Regatta, Oceania Cruises Insignia and Oceania Cruises Nautica
Geography of Oceania
The Physical map of Oceania has all the valuable details about the topographic features of Oceania. The islands situated on the geographic extremes of Oceania are:
-
- Bonin Islands – a politically integral part of Japan
- Clipperton Island – possessed by France
- Juan Fernández Islands – a part of Insular Chile
- Campbell Islands- administrated by New Zealand.
The islands sustain four basic types: continental islands, high islands, coral reefs and uplifted coral platform. Owing to the volcanic origin of High Islands, numerous active volcanoes are located here. Bougainville, and Solomon Islands are some of the examples of these High Islands. The Great Barrier Reef in Australia is one of the coral reefs, sustaining chains of reef patches because they are stacked on dramatic lava flowing under the surface of the ocean.
Melanesia
It stretches from New Guinea island in the southwestern Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea. Moving on the east side is extends to Fiji.
Micronesia
The region lies on the north of equator and West of the International Date Line, comprising thousands of small islands, located in the Pacific Ocean.
Polynesia
The region includes islands located in the central and southern Pacific Ocean.
Australasia
It comprises Australia, New Zealand (also a part of Polynesia), neighboring islands in the Pacific Ocean and the island of New Guinea (also included in region of Melanesia).
Countries and sub-regions of geopolitical Oceania which are categorized according to the geographic sub-regions used by the UN.
| Name of region with country | Area km2 | Population 2016 | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australasia | |||
| Ashmore and Cartier Islands (Australia) | 199 | ||
| Australia | 76,86,850 | 2,41,25,848 | Canberra |
| Coral Sea Islands (Australia) | 10 | 4 | |
| New Zealand | 2,68,680 | 46,60,833 | Wellington |
| Norfolk Island (Australia) | 35 | 2,302 | Kingston |
| Melanesia | |||
| Fiji | 18,270 | 8,98,760 | Suva |
| New Caledonia (France) | 19,060 | 2,72,677 | Nouméa |
| Papua (Indonesia) | 3,19,036 | 34,86,432 | Jayapura |
| West Papua (Indonesia) | 1,40,375 | 7,60,855 | Manokwari |
| Papua New Guinea | 4,62,840 | 80,84,991 | Port Moresby |
| Solomon Islands | 28,450 | 5,99,419 | Honiara |
| Vanuatu | 12,200 | 2,70,402 | Port Vila |
| Micronesia | |||
| Federated States of Micronesia | 702 | 1,04,937 | Palikir |
| Guam (United States) | 549 | 1,62,896 | Hagåtña |
| Kiribati | 811 | 1,14,395 | South Tarawa |
| Marshall Islands | 181 | 53,066 | Majuro |
| Nauru | 21 | 11,347 | Yaren (de facto) |
| Northern Mariana Islands (United States) | 477 | 55,023 | Saipan |
| Palau | 458 | 21,503 | Ngerulmud |
| Wake Island (United States) | 2 | 150 | Wake Island |
| Polynesia | |||
| American Samoa (United States) | 199 | 55,599 | Pago Pago, Fagatogo |
| Cook Islands (New Zealand) | 240 | 17,379 | Avarua |
| Easter Island (Chile) | 164 | 5,761 | Hanga Roa |
| French Polynesia (France) | 4,167 | 2,80,208 | Papeete |
| Niue (New Zealand) | 260 | 1,624 | Alofi |
| Pitcairn Islands (United Kingdom) | 47 | 47 | Adamstown |
| Samoa | 2,944 | 1,95,125 | Apia |
| Tokelau (New Zealand) | 10 | 1,282 | Nukunonu |
| Tonga | 748 | 1,07,122 | Nuku?alofa |
| Tuvalu | 26 | 11,097 | Funafuti |
| Wallis and Futuna (France) | 274 | 11,899 | Mata-Utu |
| Total | 89,19,530 | 4,57,25,020 | |
| Total (Excluding mainland Australia) | 12,32,680 | 2,15,99,172 | |
Economy of Oceania
Ranging from the highly developed Australia and New Zealand, to the islands of Palau, Fiji and Tonga which entail medium sized economies, to countries like Kiribati and Tuvalu which are less developed – diverse economies are present in the region of Oceania.
Tourism industry also benefits the economy of the countries and islands in the region. People from Japan, the USA and the United Kingdom visit Oceania the most. Fiji Islands draw around 500,000 tourists. Vanuatu is known for its scuba-diving attractions as adventurers love to explore the rich coral reefs in the South Pacific region. Australia and New Zealand have also witnessed tourism being the significant component of its thriving economy. Australia observed around 7.4 million tourists in 2015 and in New Zealand, around 7.3 million people visited in 2013.