What countries have the longest road networks?
 The economic resources available to the economy and its efficient utilization, determine the development of a nation. The socio-economic growth of a region is based on the infrastructure facilities and connectivity through transportation networks. The penetration of road networks in the most remote of the areas of a country defines integrated and inclusive development.
The economic resources available to the economy and its efficient utilization, determine the development of a nation. The socio-economic growth of a region is based on the infrastructure facilities and connectivity through transportation networks. The penetration of road networks in the most remote of the areas of a country defines integrated and inclusive development.
In the backdrop of expanding economies, the road transport industry plays a vital role in developing dynamic societies. The dependence on road transport can be traced back to 18th century, with Adam Smith highlighting the importance of the road transport network. In his book ‘Wealth of Nations,‘ the economist laid the principles of ‘division of labor‘ and the needs of access to markets, which is possible by ensured transport networks of both water and land.
The road infrastructure of a region includes all types of roads in a given area, including various structures and serves to transport passengers and goods. It is inclusive of all road categories, facilities, structures, signage and markings and electrical systems. They are believed to enhance mobility and flexibility of both goods and people and are means to economic development.
At the global level, with economies transitioning towards open market economies, road connectedness plays a crucial factor in determining the success of globalization. It not only increases the number of partners and areas involved, but is good management of the international flow of goods and services. It is hence instrumental in interconnecting business and major world markets. The problems faced by industries which are geographically remote, can be bridged with a good developed road network.
In the case of industries with perishable products, requiring early or rapid access to distant markets saves the cost incurred by the producers. At the consumer end, it avails them to the products which are not locally available or produced. It leads to an increase in the employment levels by mobilizing capital and labor. Out migration is possible with better transport networks and inter-connectedness in a region. The connectivity of the remote locations with the urban areas leads to a decline in poverty and improves the quality of development by creating employment. The implementation of government programs, rural development, employment generation and industrialization are largely determined by connectivity provided by roads.
The most striking feature of road networks is the possibility of a ‘door-to-door‘ collection and delivery which is not possible with the fixed rail and waterways. The roadways also complement the railways and waterways by providing last-mile connectivity and through feeder roads.
It is believed that at each stage of development of the human society, a certain mode of transport has been adapted. Although, no single mode of transport was solely responsible for the region’s development, it was correlation of these transport networks, with the mobility of factors of production that made advances towards better equipped societies of today. The diversification of these networks led to the international flows resulting in expansion and intensification of goods and services. But it is largely, the investment in the road transport which acts as a tool for regional development, preceding or following socio-economic progress.
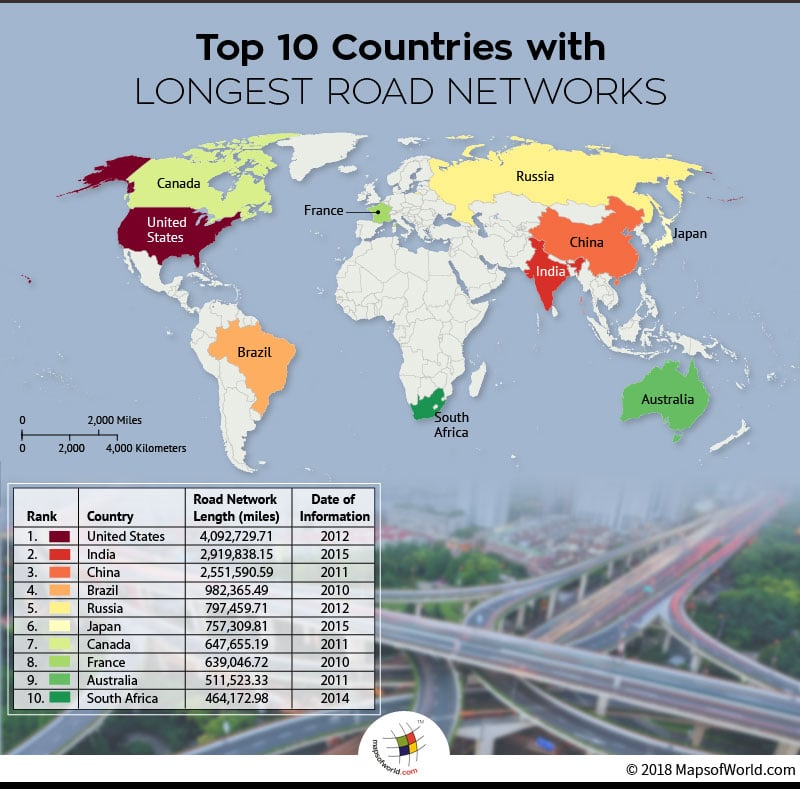
The below lying table depicts the top 10 countries with the longest road networks:
|
Rank |
Country |
Road Network Length (miles) |
Date of Information |
|
1 |
UNITED STATES |
4,092,729.71 |
2012 |
|
2 |
INDIA |
2,919,838.15 |
2015 |
|
3 |
CHINA |
2,551,590.59 |
2011 |
|
4 |
BRAZIL |
982,365.49 |
2010 |
|
5 |
RUSSIA |
797,459.71 |
2012 |
|
6 |
JAPAN |
757,309.81 |
2015 |
|
7 |
CANADA |
647,655.19 |
2011 |
|
8 |
FRANCE |
639,046.72 |
2010 |
|
9 |
AUSTRALIA |
511,523.33 |
2011 |
|
10 |
SOUTH AFRICA |
464,172.98 |
2014 |
Know more:
Related maps: