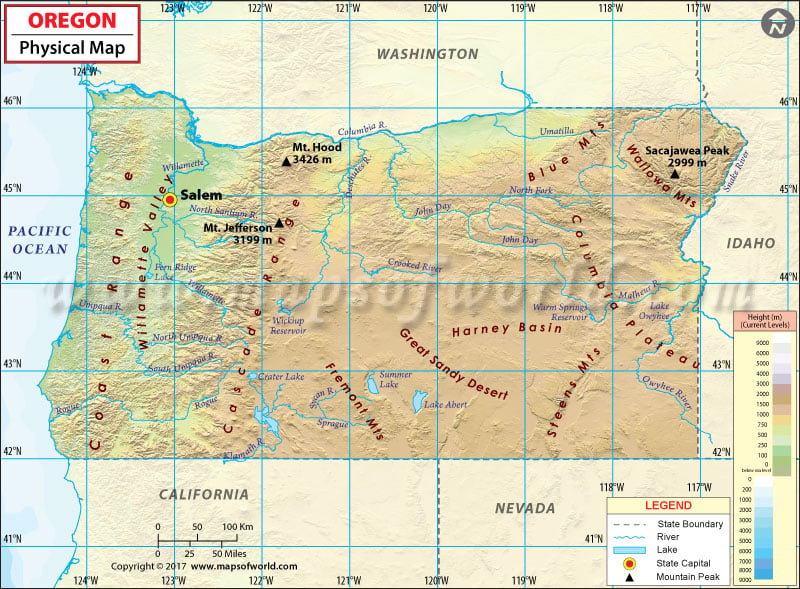
Located on the Pacific Coast, Oregon is a land of geographical diversity. The Pacific coastline harbors rocky windswept beaches; the Cascade Mountain Range features dense evergreen rainforests and Hawaiian-style volcanoes, while the giant Douglas firs and Redwoods along the rainy West Coast reflect a baffling natural wealth. The Beaver State enjoys a milder climate, which is influenced by the Pacific Ocean, especially in the western part of the state.
The highest point in Oregon is the summit of Mount Hood at 11,249 feet (3,429 meters). The Crater Lake National Park is the state’s only national park. It is home to the Crater Lake, the deepest lake in the United States at 1,943 feet (592 m). Most of the state’s area is in the Pacific Ocean Watershed and the drainage in this area is carried through the mighty Columbia River.
Western Oregon
- Oregon Coast
- Willamette Valley
- Rogue Valley
- Cascade Range
- Klamath Mountains
Central and Eastern Oregon
- Columbia Plateau
- High Desert
- Blue Mountains
The Oregon Coast is divided into three sub-regions: North Coast, Central Coast, and South Coast. The Willamette Valley is bounded by the Oregon Coast Range to the west and by the Cascade Range to the east. The Rogue Valley runs along the Siskiyou Mountains, a sub-range of the rugged Klamath Mountains, in southwestern Oregon.
The Columbia Plateau extends between the Cascade Range and the Rockies. The Oregon high desert is located east of the Cascade Range and south of the Blue Mountains. The southwest region of the desert falls under the Great Basin province.
MOW.DT.12.26.16

 Wall Maps
Wall Maps