Nevada Physical Map
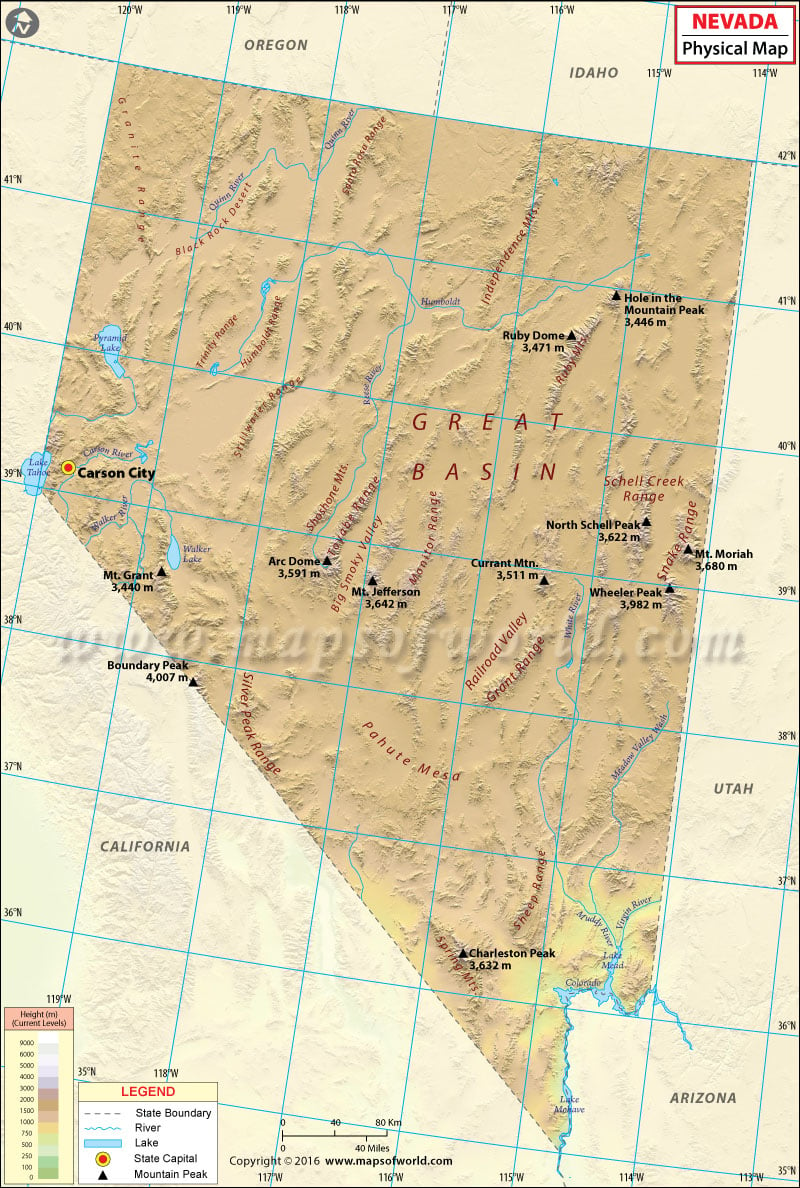
Physical features in the state of Nevada range between lush alpine forests in the west and sandy deserts in the east. Located almost entirely within the Basin and Range Province, it is the driest state in the US. The state’s desert landscape is studded with its share of incredible mountain ranges. With over 150 individual mountain ranges, it is the most mountainous state in the contiguous US.
More than 30 mountains in Nevada are 11,000 feet in elevation. The highest point in Nevada, Boundary Peak, stands at 4,007 meters (13,140 feet) along the state line with California. Major mountain ranges include the Battle, Santa Rosa, Ruby, Sierra Nevada, Snake, and Toiyabe. The Sierra Nevada range runs for 400 miles north-to-south, and is roughly 70 miles wide.
The Great Basin Desert covers mostly northern and central Nevada, while southern portion of the state falls under the Mojave Desert. The Great Basin is a series of depressions, dry lakes, and salt pans and sinks that are scattered between ribbons of mountains. The Mojave Desert spills into southern Nevada from the state of California. The desert is usually dry, hot, and windy, even more so in summer. The desert floor is highlighted by Red Rock Canyon’s bluffs, rugged cliffs and sandstone boulders. The Las Vegas Valley of the Mojave Desert lies in a relatively high-altitude region. Notable for unique paleogeologic features, the semi-arid Black Rock Desert stretches in northern Nevada section of the Great Basin.
The 40-mile-long Pahranagat Valley runs north-south and is dotted with three large natural springs: Hiko Springs, Crystal Springs, and Ash Springs. A jewel in the Sierra Nevada, Lake Tahoe is the second deepest lake in the US and the largest alpine lake in North America. Major water bodies in Nevada include Pyramid Lake, Lake Mead, Angel Lake, and Overland Lake. The Colorado, Columbia, and Humboldt are the significant rivers in Nevada.

 Wall Maps
Wall Maps