
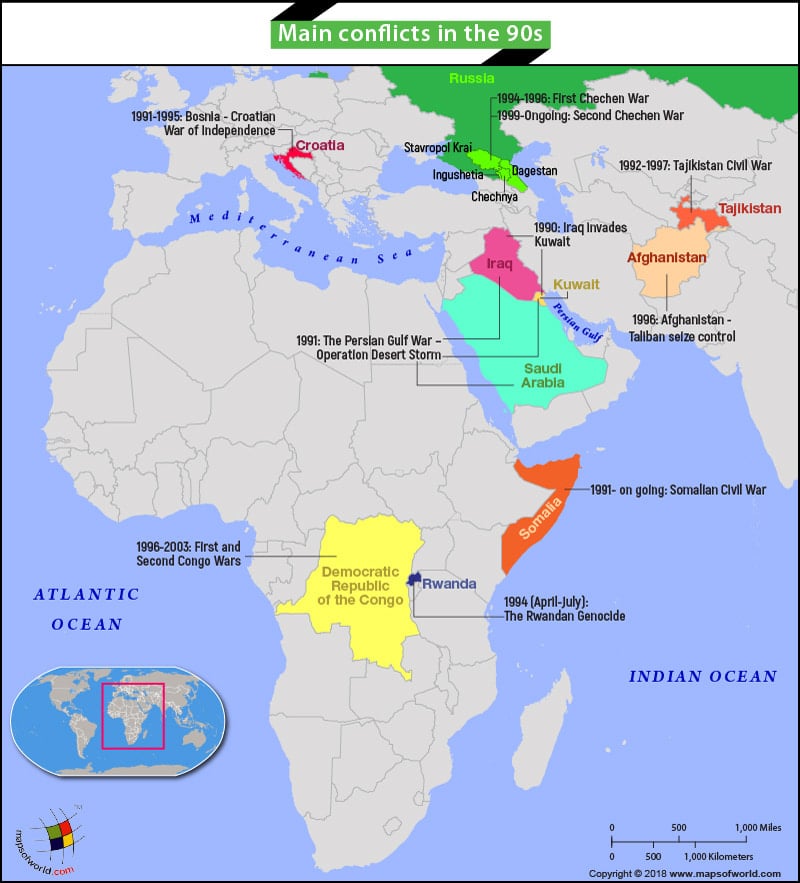
90s saw conflicts between some African, Arabian and former USSR countries
1990: Iraq invades Kuwait
On August 2nd, 1990, Iraqi Army tanks rolled into Kuwait and in two days took control of the small country. Iraq accused Kuwait of stealing oil from its reserves. The international community, led by the United States, responded and condemned the action with U.S. forces declaring war on Iraq.
1991: The Persian Gulf War – Operation Desert Storm
Immediately after the invasion of Kuwait by Iraq, the United States, supported by several Arab states, launched Operation Desert Storm to evict the Iraqi forces from Kuwait. The conflict lasted 42 days with the Iraqi forces being forced to retreat after suffering heavy casualties.
1991- ongoing: Somalian Civil War
Years of civil war among rival factions in the 1980s left the country’s population starving. In 1992, the famine situation reached crisis levels. The United Nations launched a peacekeeping mission to get emergency food and medical aid to the starving people but found itself unable to control the warring factions. On December 9th, 1992, the United States Marines, supported by United Nations- forces, launched Operation Restore Hope. The intervention was a failure with US forces suffering major casualties. By March 1994, U.S. forces began to withdraw with the U.N. forces pulling out the last of its peacekeeping forces by 1995. The conflict remains ongoing.
1991-1995: Bosnia – Croatian War of Independence
In 1991, Slovenia, Croatia, and Macedonia declared independence from the Federal People’s Republic of Yugoslavia. Large sections of the Serb-dominated Yugoslav Army resisted and began forcefully taking control over large parts of Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia. What followed was brutal ethnic cleansing led by Bosnian Serb forces resulting in the massacre of thousands of Bosnian Muslims and Croatians. U.N. intervention failed to control the emerging tragedy, and by November 1995, a federalized Bosnia was created between the Bosniak-Croat federation and a Serb republic.
1992-1997: Tajikistan Civil War
In May 1992, ethnic groups from the Garm and Gorno-Badashan regions rebelled against President Rahmon Nabiyev, thus triggering a civil conflict that would last five years. The conflict resulted in the death of thousands and finally came to end with a treaty signed between President Emmomalii Rahmon and Sayid Abdullah Nuri, the United Tajik Opposition leader, and Gerd Merrem, the Special Representative of the U.N.
1994 (April-July): The Rwandan Genocide
On April 6th, 1994, the plane carrying President Juvenal Habyarimana of Rwanda was shot down by a missile fired over the capital Kigali. President Habyarimana was a Hutu, a majority community in Rwanda that had a history of animosity against the Tutsi minority. Hutus blamed the Tutsis for assassinating the President, and so, they began to systematically identify and kill all Tutsis living in the capital city. Soon, the massacre spread to other parts of the country, and during a three-month period, over 800,000 Tutsis were brutally killed. It ended by mid-July, the same year when the Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF), an exiled Tutsi militant group, entered Rwanda and took control of the country.
1994-1996: First Chechen War
On September 6th, 1991, Dzhokhar Dudayev, a former Soviet Air Force General and Chechen-led militant members forcefully took control of the Chechen region with the aim of securing independence from the USSR. The USSR was in the process of breaking up and facing rebellion from several former states. The central government in Moscow, under Boris Yeltsin, responded by sending in Russian troops to take control. What followed was an unsuccessful military campaign that led to the death of thousands of Russian soldiers and even greater numbers of civilians; dead, injured, and/or displaced. Temporary peace prevailed with the signing of the Khasav-Yurt Accord on August 31st, 1996. Within two years, the Chechen forces invaded neighboring Dagestan, and this led to the Second Chechen War, with the Russian Federation sending its forces into Chechnya on August 26th, 1999.
1996: Afghanistan – Taliban seize control
The vacuum left after the Soviet forces withdrew from Afghanistan in February 1989, resulting in a civil war between heavily armed rival militant factions. By 1996, The Mujahideen had regrouped, and the hardline factions among them evolved as the Taliban. They were opposed by Ahmed Shah Massoud, General Rashid Dostum, and Karim Khalili, who were part of the United Islamic Front also known as the Northern Alliance. During this period, the conflict took a major toll on the people caught in the middle of this brutal battle for control over the country. Al Qaeda, promoted by Osama Bin Laden joined in support of the Taliban, led by Mullah Omar. The attacks on the twin towers in New York on September 11th, 2001, drew the U.S. into the conflict and remains embroiled in an ongoing battle with the Taliban.
1996-2003: First and Second Congo Wars
The war in Congo was an outcome of the Rwandan massacre in 1994 which resulted in over 1.5 million Tutsis along with factions of Hutus migrating to east Zaire. In 1996, the Rwandan forces led the invasion of Zaire. The campaign resulted in rebel leader Laurent-Disiri Kabila replacing President Mobutu Sisi Seko. Kabila renamed Zaire, the Democratic Republic of the Congo. His regime was corrupt and inefficient and was unable to control the militant factions. Faced with severe international condemnation, he expelled all Rwandan and Ugandan forces operating in the country. It led to escalating tensions with both neighboring countries, which in turn triggered the Second War in the Congo.
1999-Ongoing: Second Chechen War
With Chechen forces entering neighboring Dagestan, Russia sent its forces into Chechnya and Dagestan which was the culmination of the Second War in Chechnya. The conflict has resulted in a protracted guerrilla war by local Chechens that remains ongoing to date.
Visit the following to learn more about Warfare around the World:
Related Maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…