How is COVID-19 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak Affecting the Global Economy?
As China is the 2nd largest economy in the world, any fluctuation in the GDP growth rate of China is bound to impact the global growth rate. The projected fall in the growth rate of China in the first quarter of 2020 due to the coronavirus outbreak has aggravated the headache of global economy watchers/managers. As a ripple effect of this phenomenon, the fall in the GDP growth rate in the Indian economy has already become a worry for global leaders.
Stock exchanges of the US, Europe, and Japan have also witnessed similar market sentiments due to the coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemic, which is fast becoming a pandemic. Lunar New Year is the vacation time for the Chinese. In comparison to 2019, there has been a significant drop in abroad travel. While 70 lakh Chinese reportedly planned their holidays abroad, the coronavirus outbreak caused a 40% drop in the actual travel of people abroad till now.
The transport shutdown has not only affected industries adversely, but the import-export sector has also been severely affected. As China is the manufacturing hub of the world, prolonged transport shutdown will surely create a ripple effect in other parts of the globe.
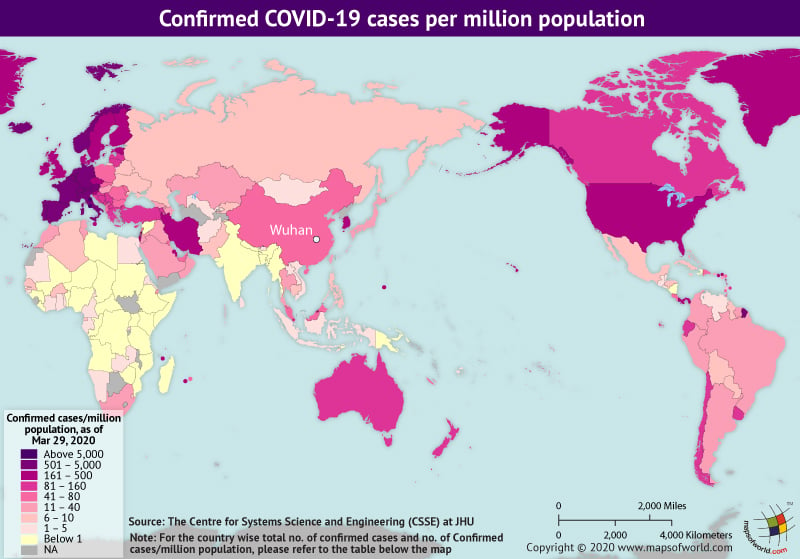
Here is a table showing the total number of confirmed cases and deaths due to coronavirus in each country:
| Country | Confirmed Cases | Cases Per Million Population | Deaths |
| Afghanistan | 110 | 2.959 | 4 |
| Akrotiri Sovereign Base Area | NA | NA | 0 |
| Albania | 197 | 68.728 | 10 |
| Algeria | 454 | 10.751 | 29 |
| American Samoa | NA | NA | 0 |
| Andorra | 308 | 3999.688 | 3 |
| Angola | 5 | 0.162 | 0 |
| Anguilla | NA | NA | 0 |
| Antarctica | NA | NA | 0 |
| Antigua | 7 | 72.700 | 0 |
| Argentina | 745 | 16.744 | 19 |
| Armenia | 407 | 137.883 | 3 |
| Aruba | NA | NA | 0 |
| Ashmore and Cartier Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Australia | 3,935 | 157.448 | 16 |
| Austria | 8,271 | 934.889 | 68 |
| Azerbaijan | 182 | 18.306 | 4 |
| Azores | NA | NA | 0 |
| Bahamas | 10 | 25.931 | 0 |
| Bahrain | 476 | 303.293 | 4 |
| Bangladesh | 48 | 0.297 | 5 |
| Barbados | 26 | 90.706 | 0 |
| Barbuda | 7 | 72.700 | 0 |
| Belarus | 94 | 9.910 | 0 |
| Belgium | 9,134 | 799.680 | 353 |
| Belize | 2 | 5.221 | 0 |
| Benin | 6 | 0.522 | 0 |
| Bermuda | NA | NA | 0 |
| Bhutan | 3 | 3.977 | 0 |
| Bolivia | 81 | 7.135 | 0 |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | 278 | 83.636 | 6 |
| Botswana | NA | NA | 0 |
| Bouvet Island | NA | NA | 0 |
| Brazil | 3,904 | 18.638 | 114 |
| British Indian Ocean Territory | NA | NA | 0 |
| British Virgin Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Brunei | 120 | 279.745 | 1 |
| Bulgaria | 331 | 47.123 | 13 |
| Burkina Faso | 207 | 10.480 | 11 |
| Burundi | NA | NA | 0 |
| Cambodia | 103 | 6.339 | 0 |
| Cameroon | 91 | 3.609 | 2 |
| Canada | 5,655 | 152.595 | 60 |
| Cape Verde | 6 | 11.034 | 1 |
| Cayman Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Central African Republic | 3 | 0.643 | 0 |
| Chad | 3 | 0.194 | 0 |
| Chile | 1,909 | 101.927 | 6 |
| Clipperton I. | NA | NA | 0 |
| Colombia | 608 | 12.246 | 6 |
| Comoros | NA | NA | 0 |
| Cook Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Coral Sea Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Costa Rica | 295 | 59.007 | 2 |
| Cote D’Ivoire | 101 | 4.029 | 0 |
| Croatia | 657 | 160.659 | 5 |
| Cuba | 119 | 10.496 | 3 |
| Curaþao | NA | NA | 0 |
| Cyprus | 179 | 150.513 | 5 |
| Czech Republic (Czechia) | 2,631 | 247.607 | 13 |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | 65 | 0.773 | 6 |
| Denmark | 2201 | 379.650 | 65 |
| Dhekelia Soverign Base Area | NA | NA | 0 |
| Djibouti | 14 | 14.600 | 0 |
| Dominica | 11 | 153.578 | 0 |
| Dominican Republic | 719 | 67.657 | 28 |
| Ecuador | 1,823 | 106.706 | 48 |
| Egypt | 576 | 5.852 | 36 |
| El Salvador | 19 | 2.959 | 0 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 12 | 9.167 | 0 |
| Eritrea | 6 | 1.867 | 0 |
| Estonia | 645 | 488.309 | 1 |
| Ethiopia | 16 | 0.146 | 0 |
| Falkland Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Faroe Islands | 155 | 3196.074 | 0 |
| Federated States of Micronesia | NA | NA | 0 |
| Fiji | 5 | 5.659 | 0 |
| Finland | 1,167 | 211.488 | 9 |
| France | 37,575 | 578.986 | 2,314 |
| French Guiana | 28 | 96.322 | 0 |
| French Polynesia | 30 | 108.038 | 0 |
| French Southern and Antarctic Lands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Gabon | 7 | 3.303 | 1 |
| Georgia | 90 | 24.122 | 0 |
| Germany | 57,695 | 695.725 | 455 |
| Ghana | 141 | 4.737 | 5 |
| Gibraltar | NA | NA | 0 |
| Greece | 1,061 | 98.903 | 32 |
| Greenland | 10 | 178.492 | 0 |
| Grenada | 7 | 62.806 | 0 |
| Guadeloupe | 102 | 270.644 | 2 |
| Guam | 55 | 331.789 | 0 |
| Guatemala | 34 | 1.971 | 1 |
| Guernsey | NA | NA | 0 |
| Guinea | 8 | 0.644 | 0 |
| Guinea-Bissau | 2 | 1.067 | 0 |
| Guyana | 8 | 10.270 | 1 |
| Haiti | 8 | 0.719 | 0 |
| Heard Island and McDonald Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Honduras | 95 | 9.909 | 1 |
| Hong Kong SAR, China | 582 | 78.110 | 4 |
| Hungary | 343 | 35.112 | 8 |
| Iceland | 963 | 2723.617 | 2 |
| India | 987 | 0.730 | 25 |
| Indian Ocean Territories | NA | NA | 0 |
| Indonesia | 1155 | 4.315 | 102 |
| Iran | 35,408 | 432.859 | 2,517 |
| Iraq | 506 | 13.166 | 42 |
| Ireland | 2,415 | 497.578 | 36 |
| Isle of Man | NA | NA | 0 |
| Israel | 3,619 | 407.371 | 12 |
| Italy | 92,472 | 1530.201 | 10,023 |
| Jamaica | 32 | 10.903 | 1 |
| Japan | 1,693 | 13.380 | 62 |
| Jersey | NA | NA | 0 |
| Jordan | 246 | 24.709 | 1 |
| Kazakhstan | 228 | 12.475 | 1 |
| Kenya | 38 | 0.739 | 1 |
| Kiribati | NA | NA | 0 |
| Korea, North | NA | NA | 0 |
| Kosovo | 91 | 49.314 | 0 |
| Kuwait | 235 | 56.800 | 0 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 58 | 9.183 | 0 |
| Laos | 8 | 1.133 | 0 |
| Latvia | 305 | 158.315 | 0 |
| Lebanon | 412 | 60.155 | 8 |
| Lesotho | NA | NA | 0 |
| Liberia | 3 | 0.623 | 0 |
| Libya | 3 | 0.449 | 0 |
| Liechtenstein | 56 | 1477.183 | 0 |
| Lithuania | 394 | 141.242 | 7 |
| Luxembourg | 1,831 | 3012.861 | 18 |
| Macao SAR, China | 37 | 58.578 | 0 |
| Madagascar | 26 | 0.990 | 0 |
| Madeira | NA | NA | 0 |
| Mainland China | 81,438 | 58.474 | 3,300 |
| Malawi | NA | NA | 0 |
| Malaysia | 2,320 | 73.584 | 27 |
| Maldives | 16 | 31.026 | 0 |
| Mali | 18 | 0.944 | 1 |
| Malta | 149 | 308.150 | 0 |
| Marshall Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Martinique | 93 | 259.234 | 1 |
| Mauritania | 5 | 1.136 | 0 |
| Mauritius | 102 | 80.613 | 2 |
| Mayotte | 63 | 225.426 | 0 |
| Mexico | 848 | 6.720 | 16 |
| Moldova | 231 | 65.146 | 2 |
| Monaco | 42 | 1085.776 | 1 |
| Mongolia | 12 | 3.785 | 0 |
| Montenegro | 84 | 134.973 | 1 |
| Montserrat | NA | NA | 0 |
| Morocco | 402 | 11.158 | 26 |
| Mozambique | 8 | 0.271 | 0 |
| Myanmar | 8 | 0.149 | 0 |
| Namibia | 8 | 3.268 | 0 |
| Nauru | NA | NA | 0 |
| Nepal | 5 | 0.178 | 0 |
| Netherlands | 9,819 | 569.844 | 639 |
| New Caledonia | 15 | 52.806 | 0 |
| New Zealand | 514 | 105.209 | 1 |
| Nicaragua | 4 | 0.619 | 0 |
| Niger | 10 | 0.446 | 1 |
| Nigeria | 97 | 0.495 | 1 |
| Norfolk Island | NA | NA | 0 |
| North Macedonia | 241 | 115.701 | 4 |
| Northern Mariana Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Norway | 4,032 | 758.702 | 23 |
| Oman | 152 | 31.473 | 0 |
| Pakistan | 1,495 | 7.045 | 13 |
| Palau | NA | NA | 0 |
| Palestine | 104 | 22.762 | 1 |
| Panama | 901 | 215.712 | 17 |
| Papua New Guinea | 1 | 0.116 | 0 |
| Paraguay | 56 | 8.051 | 3 |
| Peru | 671 | 20.976 | 16 |
| Philippines | 1,075 | 10.080 | 68 |
| Pitcairn Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Poland | 1,638 | 43.130 | 19 |
| Portugal | 5,170 | 502.832 | 100 |
| Puerto Rico | 100 | 31.297 | 0 |
| Qatar | 590 | 212.102 | 1 |
| Republic of the Congo | 4 | 0.763 | 0 |
| Reunion | 183 | 212.801 | 0 |
| Romania | 1,452 | 74.561 | 37 |
| Russia | 1,264 | 8.749 | 8 |
| Rwanda | 60 | 4.877 | 0 |
| Saint Helena | NA | NA | 0 |
| Saint Kitts and Nevis | 2 | 38.138 | 0 |
| Saint Lucia | 3 | 16.494 | 0 |
| Saint Martin | 11 | 295.191 | 0 |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | NA | NA | 0 |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 1 | 9.074 | 0 |
| Samoa | NA | NA | 0 |
| San Marino | 224 | 6630.161 | 22 |
| Sao Tome and Principe | NA | NA | 0 |
| Saudi Arabia | 1,203 | 35.697 | 4 |
| Senegal | 130 | 8.200 | 0 |
| Serbia | 659 | 94.384 | 10 |
| Seychelles | 8 | 82.677 | 0 |
| Sierra Leone | NA | NA | 0 |
| Singapore | 802 | 142.232 | 3 |
| Sint Maarten | NA | NA | 0 |
| Slovakia | 292 | 53.607 | 0 |
| Slovenia | 684 | 330.855 | 9 |
| Solomon Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Somalia | 3 | 0.200 | 0 |
| South Africa | 1187 | 20.544 | 1 |
| South Georgia and the Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| South Korea | 9,583 | 185.590 | 152 |
| South Sudan | NA | NA | 0 |
| Spain | 73,235 | 1567.404 | 5,982 |
| Special Municipalities (Neth.) | NA | NA | 0 |
| Sri Lanka | 113 | 5.215 | 1 |
| St. Barthelemy | 5 | 510.569 | 0 |
| Sudan | 5 | 0.120 | 1 |
| Suriname | 8 | 13.889 | 0 |
| Swaziland | 9 | 7.921 | 0 |
| Sweden | 3,447 | 338.500 | 105 |
| Switzerland | 14,076 | 1652.783 | 264 |
| Syria | 5 | 0.296 | 0 |
| Taiwan | 283 | 11.901 | 2 |
| Tajikistan | NA | NA | 0 |
| Tanzania | 14 | 0.249 | 0 |
| Thailand | 1,245 | 17.932 | 7 |
| The Gambia | 3 | 1.316 | 1 |
| Timor-Leste | 1 | 0.789 | 0 |
| Togo | 25 | 3.169 | 1 |
| Tokelau | NA | NA | 0 |
| Tonga | NA | NA | 0 |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 76 | 54.682 | 3 |
| Tunisia | 278 | 24.038 | 8 |
| Turkey | 7,402 | 89.918 | 108 |
| Turkmenistan | NA | NA | 0 |
| Turks and Caicos Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| Tuvalu | NA | NA | 0 |
| Uganda | 30 | 0.702 | 0 |
| Ukraine | 356 | 7.978 | 9 |
| United Arab Emirates | 468 | 48.593 | 2 |
| United Kingdom | 17,312 | 260.374 | 1,019 |
| United States of America | 124,287 | 379.888 | 2,229 |
| United States Virgin Islands | 22 | 205.652 | 0 |
| Uruguay | 304 | 88.134 | 1 |
| US Minor Outlying Islands | NA | NA | 0 |
| US Naval Base Guantanamo Bay | NA | NA | 0 |
| Uzbekistan | 104 | 3.156 | 2 |
| Vanuatu | NA | NA | 0 |
| Vatican (Holy Sea) | 6 | 6000.000 | 0 |
| Venezuela | 119 | 4.122 | 2 |
| Vietnam | 179 | 1.874 | 0 |
| Wallis and Futuna | NA | NA | 0 |
| Western Sahara | NA | NA | 0 |
| Yemen | NA | NA | 0 |
| Zambia | 28 | 1.614 | 0 |
| Zimbabwe | 7 | 0.485 | 1 |
Effects of COVID-19 (Novel Coronavirus) on the Global Stock Markets
At the time of writing this article, the global stock market is witnessing a bloodbath, one of the worst in a decade (especially since 2007-2008 US market meltdown). Investors across the globe are worried about the broader economic effects of the coronavirus on the world economy.
Major stock markets in the United States are feeling the heat of the COVID-19 (coronavirus) fear and oil slump, leading to panic sell-off across the board. The stocks that were worst affected were the energy and bank stocks.
The stock market trading was briefly suspended at the Wall Street on March 9 after the S&P 500 index plunged by more than 7% due to panic sell-off after coronavirus fears. The automatic circuit-breakers were triggered as the indices continued plunging into the red. March 9 was the worst day since the 2008 US financial crisis.
Performance of Leading Indices of the USA (as on March 9, 2020):
-
Dow Jones Industrial Average fell by -7.79% (-2,013.76 points)
-
NASDAQ Composite dropped by -7.29% (-624.94 points)
-
S&P 500 is down by -7.60% (-225.81 points)
With rising cases of coronavirus infections in Italy, France, Germany, the United Kingdom, and other European countries, the stock markets of Europe are the worst affected due to the coronavirus fear.
Performance of Leading Indices in Europe (as on March 9, 2020):
-
FTSE 100 index in London Stock Exchange (Britain) is down by -7.69% (-496.78 points).
-
DAX PERFORMANCE-INDEX in Frankfurt Stock Exchange (Germany) fell by -7.94% (-916.85 points)
-
Euronext Paris in France is down by -8.39% (-431.20 points)
-
FTSE MIB index in Italy is the worst affected as it fell by -11.17% (-2,323.98 points)
-
IBEX 35 in Spain has fallen by -7.96% (-666.90 points).
-
STOXX Europe 600 index (reflecting the overall health of the European companies) is down by -7.44% (-27.30 points).
Australian stock market has also closed after falling -7.33% (on March 9, 2020), the worst performance since the Global Financial Crisis (GFC) in 2008. Horror in the benchmark ASX200 index continues as it keeps falling (-3.7%) on March 10 too.
Leading Asian stock markets are in deep red and keep on tumbling down.
Performance of Leading Indices in Asia (as on March 9, 2020):
-
Nikkei 225 of Japan is down by -5.07% (-1050.99 points)
-
Hang Seng index in Hong Kong is down by -4.23% (-1,106.21 points)
-
Shanghai Composite Index in China is down by -3.01% (-91.22 points)
-
FTSE Straits Times Index in Singapore is down by -6.03% (-178.61 points)
-
Sensex in India dropped by -5.17% (-1,941.67 points)
One of the peculiar aspects of the trading sentiment in the US is that the stock market bloodbath took place despite the US employers adding 273,000 jobs in February 2020 (as per the US Labor Department’s monthly report). The number of jobs added not only exceeded expectation but the jobless rate also came down to 3.5%, which is at a 50-year low level. Despite such encouraging figures, the market tumbled down. This is mainly because the figures were collected before the COVID-19 (coronavirus) outbreak intensified in the United States.
In fact, the global travel industry has plunged significantly recently as the coronavirus outbreak has spread to over 90 countries. In many countries, normal life and economic factors (including work, shopping, and school) have been adversely affected. These factors had a significantly ill effect on the stock market globally.
What do the experts say?
-
Wells Fargo’s senior economist Sarah House said: “Today’s jobs report is old news.”
-
Bankrate.com’s senior economic analyst, Mark Hamrick said referring to the US job statistics is like saying “the car was in fine condition before being involved in a collision”. He concluded by saying: “The new reality, amid tremendous uncertainty, is the world has experienced a seismic shift.”
The credit and funding markets are in front of some big questions, especially due to the economic fallout from the COVID-19 coronavirus crisis. The market analysts believe that the main concerns about the market and economic prospects revolve around the “airline, travel and leisure, and retail sectors” because these are the prime sectors that are being restricted due to coronavirus outbreak and its spread across the world.
The market analysts believe that the funding and credit channels may start faltering and may lead to amplification of the economic fallout in the coming weeks and months if the spread of coronavirus continues.
Effects of Slowing Chinese Economy on the World Economy
The Chinese economy, the second-largest economy in the world, is currently more deeply intertwined with the global economy than during the SARS outbreak in 2003. The Chinese economy has a share of 17% of the total GDP of the world.
Effects on the World Economy
A Frost & Sullivan report named “The Coronavirus Outbreak and Its Impact on The Global Economy” says that there could be two extreme scenarios: the Gradual Abatement scenario and the Severe Pandemic scenario.
-
The best-case scenario is the Gradual Abatement case. According to this scenario, the COVID-19 infection cases remain concentrated in China during the first quarter of 2020. However, from March 2020, the infection cases start to get eliminated. If the Gradual abatement case does take place then the GDP growth of China will come down from 5.9% to 5.4%, leading the global economy to grow at the rate of 3.1% in 2020.
-
If the COVID-19 coronavirus crisis becomes a Severe Pandemic and spreads worldwide then it would come under control by June-July 2020. In that case, the global GDP growth will come down to below 2%.
The retail imports in the United States will drop significantly in Q1 2020 in comparison to Q4 2019. With the ongoing coronavirus crisis persisting for a longer period of time than expected, there are high chances that China will default on several of the targets.
One of the most likely scenarios is China’s inability to import $200 billion of US agricultural products by December 2021 as agreed upon in January 2020 under Phase-1 of the US-China trade deal. However, the coronavirus crisis is likely to ease up the trade hostilities between the United States and China.
China is one of the largest parts of the global supply chain. Faltering the manufacturing sector due to the COVID-19 crisis is upsetting the global production and supply chains of multiple industries including automotive, high-tech manufacturing, healthcare, travel and tourism, and retail industries.
The sector that has been hardest hit by the coronavirus crisis and Chinese lockdown is the automotive industry. This is mainly because Hubei province (the epicenter of the COVID coronavirus) is one of the five major automotive manufacturing centers in China.
Hubei province accounts for 10% of vehicle production in China. It has also come up as a major auto parts production hub for both foreign and domestic automakers. With Hubei still in a state of lockdown, there are high chances of a global auto parts shortage. If it happens then the global production volumes in 2020 are going to be adversely affected.
China is a major hub for producing smartphones and other electronic gadgets. With the continued shutdown of factories and stores (full or partial), a major upheaval in supply chains is likely. This may lead to a delay in the launches of new products, thereby dampening the high-tech manufacturing sector’s production prospects globally.
On the one hand, China is a huge draw for foreign travelers and on the other Chinese form a bulk of travelers to international destinations. With COVID-19 crisis, travel and tourism is the worst affected sector. With restrictions prevailing in China, hoteliers, restaurateurs, airlines, transport service providers, and tour operators are adversely affected.
Some of the countries that are highly dependent upon tourism such as Malaysia and Thailand are economically struggling as tourists from China and other parts of the world are abandoning their plan of venturing out.
Though the aviation industry has suffered a body blow globally due to the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic, the private business jet aviation industry is experiencing unprecedented growth. The rich, wealthy, and top business executives are abandoning the general aviation and resorting to private business jets for business trips.
Effects on Oil Prices and Interest Rates
The coronavirus pandemic is having one of the worst effects on many macroeconomic factors such as interest rates and petroleum prices.
-
Drastic fall in Oil Prices due to falling Demand from China: With manufacturing in China working well below capacity, there has been a reduced demand for petroleum from China, the largest oil importer in the world. In fact, the demand for oil has also been affected due to the drastic fall in air travel due to travel restrictions and fear of COVID-19 coronavirus infection.
-
Fall in Interest Rate to Shore up Economy: The world economy and Chinese economy, in particular, is in shambles due to the COVID-19 outbreak. To shore up the tottering economies, the countries are expected to make deeper cuts in interest rates.
Effects on Economies having Closer ties with China
The economies that have closer and deeper ties with China will be the hardest hit by China’s economic slowdown due to the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic. There are FIVE Asian countries – Vietnam, the Philippines, Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia – that have extremely close ties with China through trade and tourism. In these countries, China accounts for around 60-90% of the total exports and 50% of the revenues from tourism. That’s why economic lockdown and slowdown in China will have a significant adverse effect on these Asian economies.
Effects on the Japanese Economy
Another Asian economy that is susceptible to economic recession due to China’s economic slowdown is Japan, the 3rd largest economy in the world.
With China still in a state of partial lockdown, factories running far below capacity, and unavailability of workers (mostly migrant workers) due to travel and other restrictions, Japan will get a reduced supply of critical manufacturing parts from China.
Some economists also believe that Japan could slide into recession. Japan has now postponed the 2020 Tokyo Olympics to the summer of 2021 as the outbreak has widened and continues to persist.
Effects on the German Economy
The 4th largest economy in the world, Germany, is also particularly vulnerable to the coronavirus pandemic and falling economic prospects all over the world. The fall in economic prospects is especially bad for the German economy as it is highly dependent upon its German automotive industry. Falling vehicle sales will hit the German economy hard and may end up seeing near-zero growth in 2020.
Effects on Indian Economy
India is not only the 5th largest economy in the world but also a major importer of electronics goods from China. With the COVID-19 (novel coronavirus pandemic), there is a shortfall in the supply of Chinese electronic components and consequently a rise in the prices of these products. There are high chances of intensification of food inflationary pressures in the second quarter of 2020 in India because of the reduced imports from China.
Effects on African Economy
In recent years, the African region has built up deeper ties with China. However, the coronavirus pandemic hasn’t really affected the African nations to a large extent. Africa has a poor healthcare infrastructure and with the Chinese economy struggling the African healthcare sector may get overwhelmed. In fact, the commodity prices, as well as the export revenues in the African countries, may fall as the Chinese ports remain closed. This will, in turn, diminish the overall growth prospects of the African continent as a whole.
Final Words
Businesses throughout the world must gear up to reduce the disruption caused by the COVID-19 (coronavirus) crisis in China and other parts of the world by using a combination of preventative and recovery controls. To safeguard their prospects, the businesses must implement smart and pre-emptive strategies and also diversify supply chains by including non-China based suppliers. The ill-effects of coronavirus outbreak can only be contained if the businesses remain warned, prepared, and hopeful.
Related Links:

