
How deep is the pacific ocean? The Pacific Ocean the largest and deepest ocean in the world

The Pacific Ocean is the biggest and deepest ocean on Earth. It has a major impact on the world’s weather and is home to a wide variety of plants and animals. In this article, we will learn how deep is the pacific ocean, it’s maximum depth and more.
The depth of the Pacific Ocean affects both life in the ocean and the environment around the world. It influences global weather patterns, ocean currents, and even the natural recycling of carbon. The extreme depths also create high-pressure environments that are home to unique creatures adapted to survive under such harsh conditions. Here’s a breakdown of its depths:
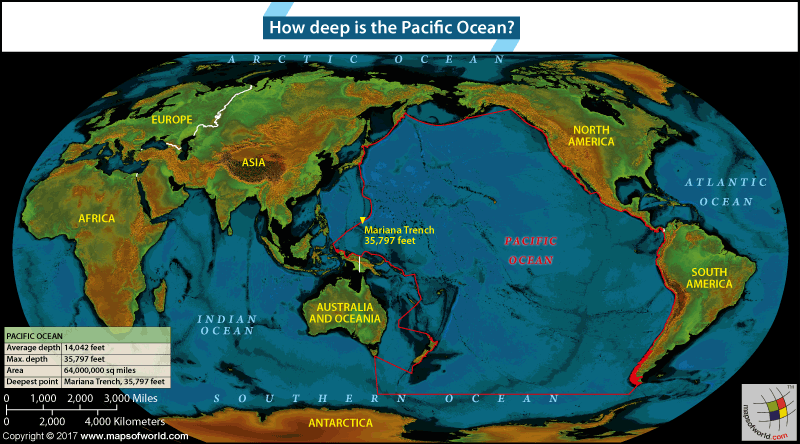
The Pacific Ocean’s average depth is about 13,215 feet (4,028 meters). This average depth includes the deep sea trenches as well as the shallower areas near coastlines, giving a middle value for its overall depth.
The maximum depth of the pacific ocean is found at a location called the Challenger Deep. This point reaches a depth of about 36,070 feet (10,994 meters), making it the deepest spot in all the world’s oceans.
The shallowest parts of the Pacific Ocean are usually close to the coast or in seas that are connected to the ocean, like the Sea of Okhotsk, the South China Sea, and the Bering Sea. These areas can be just a few hundred feet or meters deep.
The deepest part of the Pacific Ocean is called the Mariana Trench. Its deepest spot, known as the Challenger Deep, goes down several miles beneath the ocean’s surface. The rest of the trench also has a very uneven and steep landscape.
The Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is the deepest spot in the Pacific Ocean and the entire world. It’s located east of the Mariana Islands and goes down about 36,070 feet (10,994 meters). This part of the ocean is very cold and dark, with a lot of pressure, yet some unique sea creatures still manage to live there. Scientists continue to study this area and often discover new things about life in deep-sea environments.
The Pacific Ocean is the biggest ocean in the world, stretching over more than 63 million square miles (163 million square kilometers). It reaches from the Arctic Ocean in the north down to the Southern Ocean in the south, and from Asia and Australia on one side to the Americas on the other. It covers about one-third of the Earth’s total surface, which is more than all the land combined. The Pacific Ocean greatly affects the world’s weather and is home to a wide variety of sea life and ecosystems, making it very important to our planet’s environmental and biological health.
The Pacific Ocean is positioned between Asia and Australia on one side and the Americas on the other. It reaches from the Arctic Ocean at the top all the way down to the Southern Ocean near Antarctica. This huge ocean stretches across a vast area, dividing the countries on the eastern side of Asia from those on the western sides of North America and South America. It also stretches from the cold Arctic waters down to the chilly regions near Antarctica.
Related Links
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…