
Five of the US territories are classified as inhabited, while the remaining eleven are classified as uninhabited
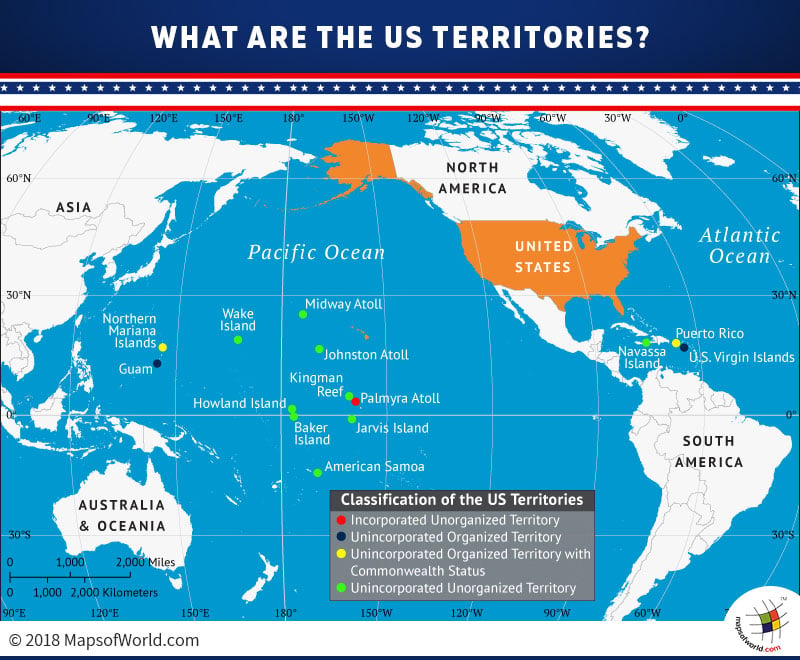
There are 16 overseas territories of the United States. Of these, five territories are classified as inhabited, while the remaining eleven are classified as uninhabited or without a permanent population.
Territories are defined as land acquired by the United States but not claimed by any of the 50 states. The overall territorial security, economic development, and social support lie with the federal government, with local administration governing under laws passed by the respective legislature in the territories.
U.S. territories have lesser political powers as compared to U.S. Commonwealths. Puerto Rico and the Northern Mariana Islands are two of the U.S. insular areas that are also part of the U.S. Commonwealth.
The five overseas U.S. territories are:
United States Virgin Islands
Northern Mariana Islands
American Samoa
Of the above territories, only residents of American Samoa are classified as non-citizens U.S. nationals.
The eleven territories that are uninhabited or without a permanent population comprise small islands, atolls, and reefs.
Midway Atoll
Palmyra Atoll
Baker Island
Kingman Reef
Johnston Atoll
Howland Island
Navassa Island
Jarvis Island
Wake Island
Bajo Nuevo Bank
Serranilla Bank
Of the eleven territories above, Serranilla Bank and Bajo Nuevo Bank are administered by Colombia. Palmyra Atoll is the only incorporated unorganized territory of the U.S. Since it remains uninhabited its status is of little significance. The Atoll was acquired by the U.S. as part of the acquisition process of the chain of Hawaiian islands. At the time, Palmyra Atoll was not made part of the Hawaiian statehood, so, it was made an incorporated territory.
Political and Administrative Status
People living in U.S. territories do not have the right to vote for members of Congress. Each of the five inhabited U.S. territories is headed by a Governor and with a locally elected legislature passing laws. The court comes under U.S. law, and all appeals are heard in the Supreme Court.
Each territory sends one delegate to the House of Representatives to represent local interests. The Representative is a non-voting delegate who can participate in all House debates, raise any issue, and participate in various Sub-Committees, but cannot vote to elect the U.S. President nor vote during the passage of Bills in the House. The rights enjoyed by the delegate from overseas territories are similar to the delegate from Washington D.C., the capital of the United States and a territory.
Visit the following to learn more about the USA:
Related Maps:
The Republic of Madagascar is an island country located in the Indian Ocean, off the…
The Euro is the official currency of the European Union. It is, however, not incumbent…
There are many countries or regions that are partially recognized by the UN, have disputes…
The Alaska Statehood Act was signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in 1958,…
The name Persia may, however, only be used to refer to Iran in some contexts.…
Hawaii is an Island State in the US. It is one of the 50 states…